Stars
... E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light ...
... E0102-72 is a supernova remnant in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. This galaxy is 190,000 light years from Earth. E0102 -72, which is approximately a thousand years old, is believed to have resulted from the explosion of a massive star. Stretching across forty light ...
Chapter 17 and 18 Vocabulary Quist
... 44. Our Sun is considered to be a star of this color ______________________ 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone __________________ or _______________________ 46. A star that is very small and has so much gravity that electromagnetic energy cannot escape its surface is called a ________ ...
... 44. Our Sun is considered to be a star of this color ______________________ 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone __________________ or _______________________ 46. A star that is very small and has so much gravity that electromagnetic energy cannot escape its surface is called a ________ ...
Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... Light Years: The distance that light travels in one year. Speed of light is 300,000 km/sec. Light travels about 9.5 trillion km in one year. Fun Fact: Light from the sun takes 8 min. to reach Earth!!! ...
... Light Years: The distance that light travels in one year. Speed of light is 300,000 km/sec. Light travels about 9.5 trillion km in one year. Fun Fact: Light from the sun takes 8 min. to reach Earth!!! ...
May 2016 night sky chart
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
... For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the star chart. To use this star chart, rotate the chart so that the direct ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... Given the information below about some stars, find the distances to each star using the technique of spectroscopic parallax. Use Voyager data panel to find the apparent magnitude (m) and absolute magnitude (M). Then calculate the distance in parsecs using the formula for D below Fig 2. Check your di ...
... Given the information below about some stars, find the distances to each star using the technique of spectroscopic parallax. Use Voyager data panel to find the apparent magnitude (m) and absolute magnitude (M). Then calculate the distance in parsecs using the formula for D below Fig 2. Check your di ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... Our suns will expand out into a red giant and then collapse into a white dwarf. ...
... Our suns will expand out into a red giant and then collapse into a white dwarf. ...
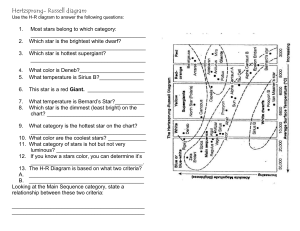
Hertzsprung - Russel Diagram
... Most stars belong to which category: _______________________________________ Which star is the brightest white dwarf? _______________________________________ Which star is hottest supergiant? _______________________________________ ...
... Most stars belong to which category: _______________________________________ Which star is the brightest white dwarf? _______________________________________ Which star is hottest supergiant? _______________________________________ ...
Starry Starry Night Vocabulary
... Nebula: Any of the numerous clouds of gas or dust located in interstellar space. Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in ...
... Nebula: Any of the numerous clouds of gas or dust located in interstellar space. Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in ...
Physics 1025: Lecture 18 Stellar Magnitudes, Absolute Magnitudes
... brighter than red. For example among the brighter stars, Rigel is blue and Betelgeuse is red—which is brighter? Thirdly, the eye cannot integrate add up light – it either sees a dim object or not; it is an instantaneous detector. Eye estimates of brightness are called visual magnitudes, mv It is bet ...
... brighter than red. For example among the brighter stars, Rigel is blue and Betelgeuse is red—which is brighter? Thirdly, the eye cannot integrate add up light – it either sees a dim object or not; it is an instantaneous detector. Eye estimates of brightness are called visual magnitudes, mv It is bet ...
Astronomy
... spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself as Apollo and made Callisto his lover. They had a child named Arcas. Of course Zeus knew that both Hera, his wife, and Artemis would be angry with Callisto so to protect her he turned her into a bear to keep her hidden from Artemis and Hera. One da ...
... spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself as Apollo and made Callisto his lover. They had a child named Arcas. Of course Zeus knew that both Hera, his wife, and Artemis would be angry with Callisto so to protect her he turned her into a bear to keep her hidden from Artemis and Hera. One da ...
Stars
... range greatly in size from large supergiants to very small dwarfs. Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
... range greatly in size from large supergiants to very small dwarfs. Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
ppt
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
... • From there we can calculate how much further away the star must be than the Sun to make it the brightness we see from Earth • Delta Cephei shows has a period of about 5 days • This is a reasonably bright star in the constellation of Cepheus • Cepheids are in other galaxies also, and used similarly ...
The Science behind the Stars ctY Astrophysics by Spencer McClung
... n day three of CTY Astrophysics, we were given a series of images of light from a star and had to determine the mass of its binary companion. For an hour we used two sticks to monitor small changes in the star’s light and then used a very long series of calculations with very big numbers. In the end ...
... n day three of CTY Astrophysics, we were given a series of images of light from a star and had to determine the mass of its binary companion. For an hour we used two sticks to monitor small changes in the star’s light and then used a very long series of calculations with very big numbers. In the end ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky. Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms ...
... nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky. Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms ...
A star is a - Trimble County Schools
... • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, some stars are not visible during particular seasons Constellations • _____________________________ ...
... • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, some stars are not visible during particular seasons Constellations • _____________________________ ...
Notes 1 - cloudfront.net
... Messier 42 (M42) // Orion Nebula: ~ Orion’s sword is a nebula ~ Orion is a big open cluster (almost, it’s changing) ...
... Messier 42 (M42) // Orion Nebula: ~ Orion’s sword is a nebula ~ Orion is a big open cluster (almost, it’s changing) ...
Only Thirty Questions To Go (150,000 points) 1.) If the distance
... 12.) The Earth is closest to the Sun when… A – it is at perihelion. B – it going the fastest. C – when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere. D – All of the above. 13.) The Hubble Space Telescope in orbit is in… B – free-fall. 14.) Most people spend little time looking at the stars because… A – ai ...
... 12.) The Earth is closest to the Sun when… A – it is at perihelion. B – it going the fastest. C – when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere. D – All of the above. 13.) The Hubble Space Telescope in orbit is in… B – free-fall. 14.) Most people spend little time looking at the stars because… A – ai ...
Introduction - Willmann-Bell
... “Great Eruption” in the 1840s. Of course, there are numerous other objects to explore in Carina, not the least of which is the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), which lies just east of the dark, hourglass-shaped Keyhole Nebula; NGC 2516, also known as the Southern Beehive; the planetary NGC 2867 with its ho ...
... “Great Eruption” in the 1840s. Of course, there are numerous other objects to explore in Carina, not the least of which is the Carina Nebula (NGC 3372), which lies just east of the dark, hourglass-shaped Keyhole Nebula; NGC 2516, also known as the Southern Beehive; the planetary NGC 2867 with its ho ...
3.6 spectral classes
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
Properties of Stars
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.