Astronomy pt. 2
... can detect and collect data on radio sources. • Used anytime, no light pollution or weather ...
... can detect and collect data on radio sources. • Used anytime, no light pollution or weather ...
a description of planets and stars you may see
... third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most distant permanent objects that can be viewed with the naked eye. The Ring nebula (also known as M57) is a planetary nebula is located in the constellation of Lyra. It ...
... third-largest member of the Local Group of galaxies, which includes the Milky Way Galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy. It is one of the most distant permanent objects that can be viewed with the naked eye. The Ring nebula (also known as M57) is a planetary nebula is located in the constellation of Lyra. It ...
STARS In your textbook, read about the properties of the Sun and
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
... 6. Stars on the main sequence produce energy by fusing hydrogen into----' 7. As a contracts, its rotation forces it into a disk shape with a hot condensed object at the center, which will become a new stsr. 8. During a the entire portion of the star is blown off in a massive explosion! What are Gala ...
Bright stars and faint stars: the stellar magnitude system Magnitudes
... and you measure its apparent magnitude m, you then know its distance. This difference (m-M) is called the distance modulus ...
... and you measure its apparent magnitude m, you then know its distance. This difference (m-M) is called the distance modulus ...
Almach or Alberio
... daytime star. The dimmer blue star (known as Almach B,C, and D) is also actually a triple system of three white dwarf stars . The white dwarf stars together orbit the gold primary star at a distance of about 600 AU (600 times the Sun-Earth distance). Although the golden primary is 9.6 arc seconds on ...
... daytime star. The dimmer blue star (known as Almach B,C, and D) is also actually a triple system of three white dwarf stars . The white dwarf stars together orbit the gold primary star at a distance of about 600 AU (600 times the Sun-Earth distance). Although the golden primary is 9.6 arc seconds on ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
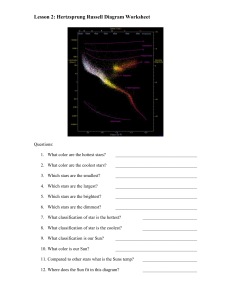
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Galaxies Reading Guide
... 15. The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. A friend tells you about a star that also has a magnitude of –26.7. How could this be true? The friend can be referring to absolute magnitude and not apparent magnitude ...
... 15. The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. A friend tells you about a star that also has a magnitude of –26.7. How could this be true? The friend can be referring to absolute magnitude and not apparent magnitude ...
The hierarchical structure of the Universe (go from little to large)
... B A reflection of sunlight in Earth’s atmosphere. C A reflection of sunlight on dust particles in the ...
... B A reflection of sunlight in Earth’s atmosphere. C A reflection of sunlight on dust particles in the ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... Stars • mass can be determined by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational effect on the bodies around it ...
... Stars • mass can be determined by the inertial properties of the body or by its gravitational effect on the bodies around it ...
The Hubble Space Telescope
... The bright orange spot in the center gathers dust and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
... The bright orange spot in the center gathers dust and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
stars - allenscience
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
... massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
Astronomy 162 Lab 4: Stars
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
... Magnitude is measured so that the smaller numbers correspond to the brightest objects. The Sun is by far the brightest object in the sky and has an Apparent Magnitude of about -30. The Apparent Magnitude of any object is determined by two things: the object's intrinsic brightness, and the object's d ...
August Newsletter
... located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects than any other constellation. There are no less than 15 Messier objects found in this constellation, including the Omega Nebula, the Trifid Nebula and a favourite of the astronomers and visitors al ...
... located in the direction of Sagittarius and because of this Sagittarius contains more deep sky objects than any other constellation. There are no less than 15 Messier objects found in this constellation, including the Omega Nebula, the Trifid Nebula and a favourite of the astronomers and visitors al ...
Stars, H-R and Life Cycle of Star
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
... Two astronomers discovered a relationship between the absolute magnitude (real brightness) of a star and its surface temperature. They plotted the data on a graph. ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
... • Their positions are related because – the direction of Polaris defines the rotation axis of the celestial sphere – The sun is somewhere on the sphere – From a “skewed” perspective everything on the sphere culminates on the meridian ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... The key is that all stars were not born at the same time. the stars which we see today are at different stages in their ...
... The key is that all stars were not born at the same time. the stars which we see today are at different stages in their ...
Chapter 21
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
April
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
... A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.