Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
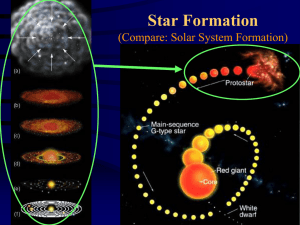
... Massive -> Super red giant -> supernova -> neutron star (large stars) ->Black hole (extra-large stars) Stellar Nursery (Nebula) ...
... Massive -> Super red giant -> supernova -> neutron star (large stars) ->Black hole (extra-large stars) Stellar Nursery (Nebula) ...
Astronomy Universe2
... What is a Main Sequence Star? • The H-R diagram represents a pattern that was discovered that allows stars to be compared by brightness and color. • The majority of stars are found in a band stretching diagonally across the diagram called the “Main Sequence”. • Stars start out in the Main Sequence ...
... What is a Main Sequence Star? • The H-R diagram represents a pattern that was discovered that allows stars to be compared by brightness and color. • The majority of stars are found in a band stretching diagonally across the diagram called the “Main Sequence”. • Stars start out in the Main Sequence ...
Notes: Astronomy and Groups of Stars
... Most are medium sized like the sun. Fusion occurs more rapidly in larger stars. Some stars are small & dense or large & less dense. ...
... Most are medium sized like the sun. Fusion occurs more rapidly in larger stars. Some stars are small & dense or large & less dense. ...
Diapositiva 1
... heart of the Orion Nebula, are four hot, massive starsknown as the Trapezium. Gathered within a region about 1.5 light-years in radius, they dominate the core of the dense Orion Nebula Star Cluster. Ultraviolet ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orion ...
... heart of the Orion Nebula, are four hot, massive starsknown as the Trapezium. Gathered within a region about 1.5 light-years in radius, they dominate the core of the dense Orion Nebula Star Cluster. Ultraviolet ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orion ...
Chapter 2: The Sky
... Celestial Sphere • When we look at the sky, we see stars but have no actual clue as to how far away they are. Therefore it is as if they were all on a sphere out a long distance from us. This conceptual device is known as the celestial sphere. • Distances between objects then are measured in angle ...
... Celestial Sphere • When we look at the sky, we see stars but have no actual clue as to how far away they are. Therefore it is as if they were all on a sphere out a long distance from us. This conceptual device is known as the celestial sphere. • Distances between objects then are measured in angle ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. C ...
... night sky from Planet Earth. Hipparchos, introduced the magnitude scale in the 1st century B.C.. ASTERISMS - An asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. C ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
... • Cloud contracts/warms, begins radiating; almost all radiated energy escapes • Cloud becomes dense opaque to radiation radiated energy trapped core heats up ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Universe is expanding Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum All galaxies outside the Local Group indicate a red shift in their spec ...
... Universe is expanding Doppler shift—light changes as it moves toward or away from an object Starlight moving toward Earth shifts to blue-violet end of spectrum Starlight moving away from Earth shifts to red end of spectrum All galaxies outside the Local Group indicate a red shift in their spec ...
Classification_of_Stars_By_Luminosity
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 31) The constellation Draco (DRAY-co) the dragon is not an easy field to play in. The area around the dragon’s tail, however, does have an interesting galaxy that rewards the star-hopper. The brightest star due east of M81-82 is the very tip of the dragons tail. Known as G ...
... (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 31) The constellation Draco (DRAY-co) the dragon is not an easy field to play in. The area around the dragon’s tail, however, does have an interesting galaxy that rewards the star-hopper. The brightest star due east of M81-82 is the very tip of the dragons tail. Known as G ...
Scientists classify stars by
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
... would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is true for stars. Two stars could be the same brightness but their distance from us makes their brightness different. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... • Stars more massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for only 10 million years • Stars less massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for 100’s of billions of years • Remember: the larger the star the shorter the life span, the smaller the star the longer the life span ...
... • Stars more massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for only 10 million years • Stars less massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for 100’s of billions of years • Remember: the larger the star the shorter the life span, the smaller the star the longer the life span ...
Coursework 7 File
... Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10−11 N kg−2 m2 Solar mass Msun = 2 × 1030 kg Solar luminosity Lsun = 3.8 × 1026 W Solar radius Rsun = 7 × 108 m Jupiter radius RJup = 7 × 107 m 1 Astronomical unit 1.5 × 1011 m 1 parsec = 3.26 light years Speed of light c = 3 × 108 m s−1 Stefan-Boltzmann constant σ ...
... Gravitational constant G = 6.67 × 10−11 N kg−2 m2 Solar mass Msun = 2 × 1030 kg Solar luminosity Lsun = 3.8 × 1026 W Solar radius Rsun = 7 × 108 m Jupiter radius RJup = 7 × 107 m 1 Astronomical unit 1.5 × 1011 m 1 parsec = 3.26 light years Speed of light c = 3 × 108 m s−1 Stefan-Boltzmann constant σ ...
Stars and Sun
... Stars revolve around the center of galaxies once every 225 million years the Sun makes a revolution ...
... Stars revolve around the center of galaxies once every 225 million years the Sun makes a revolution ...
stars - Legacy High School
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
... 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving away, the spectrum lines are displaced toward longer wavelengths of light, this is called a ______________shift. 20. When objects are toward earth, the spectrum lines are ...
WK7
... Detection of periodic radio signals in the constellation Cygnus. Mysteriously regular at 1.33701 second intervals. ...
... Detection of periodic radio signals in the constellation Cygnus. Mysteriously regular at 1.33701 second intervals. ...
May
... known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view for NGC4631, a more distant galaxy also seen edge-on. M64 is a type Sb spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Bere ...
... known as the Hockey Stick Galaxy, the key features are the angled tilt of the disk and the apparent offset of the core. If observing at low magnification look in the same field of view for NGC4631, a more distant galaxy also seen edge-on. M64 is a type Sb spiral galaxy in the constellation Coma Bere ...
Stellar Evolution
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
... layers are driven away • Core becomes hot enough to produce Carbon (C) • Star contracts to normal size when helium is used up • Carbon core left over, White dwarf remains ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... Luminosity – the brightness of a star compared to the brightness of the Sun as seen from the same distance. ...
... Luminosity – the brightness of a star compared to the brightness of the Sun as seen from the same distance. ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.