* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 1 - cloudfront.net
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
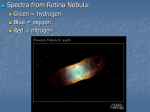
Notes 1.12-1.22 Mercator Projection of Earth: ~ a cylindrical map projection ~ the standard map projection for nautical purposes because of its ability to represent lines of constant course Mercator Projection of the sky beginning of winter has the least sun, but mid-winter are the coldest parsecs light second ~ the distance light travels in an absolute vacuum in one second about 10.5 minutes to communicate from Earth to Mars 1 parsec = 206 264.806 AU Parallax: ~ S = rθ θ must be in radians 2AU = rθ S & r are in AU’s R = (1AU)/(θ in rad) [θ is usually measured in arcsecs, not rad] 1 arcsec = 1/3600(π/180) = .000004848 rad 1 rad = 206265 arcsec ~ S = rθ r = S/θ [S is always 1 AU] suppose the paralaz is 0.25 arcsec r = (1 AU)/(0.25 arcsec)(1 rad/206265 arcsec) r = 206265(4 AU) = 4 parsecs 10 miliarcsec = 1/100 arcsec = 100 parsecs if s = 1 AU & θ in arcsec [replace s with r = 1/θ in arcsec] Andronmeda: ~ about 2.5 million light years away from earth ~ 2-3x the size of the moon luminosity ~ the amount of energy a body radiates per unit time apparent magnitude (m): ~ a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, normalized to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere ~ 5 lower magnitude: 100x brighter absolute magnitude (M): ~ the apparent magnitude of an ob ject would have if it were 10 parsecs away ~ log10^(2/5)(d/10 pscs)2 = m - M 2[log (d/10 pscs)/ log10^(2/5)] = m - M 2[log (d/10 pscs)/(2/5) = m - M 5 log (d/10 pscs) = m - M 5 (log d - 1) = m - M the sun is 6-8 parsecs away astrometry ~ the branch of astronomy that relates to precise measurements and explanations of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies brown dwarfs are the most in the universe stars in sky are mostly giant stars space is not empty so light gets blocked at times Hubble’s Law ~ the statement in physical cosmology that the redshift in light coming from distant galaxies is proportional to their distance Hubble deep field ~ an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope center of galaxies are the brightest far sounds sound lower than closer sounds (higher) wave lengths move the same as it reaches the eyes/ears things look bluer when you walk closer things look reder when you walk farther away hydrogen & helium make up most of the air billions of galaxies are moving farther away from Earth Andronmeda & our galaxy are slowly moving closer if a light gives off 1000 light years away, you see the object 1000 years ago isotropy ~ property of a system that is direction independent; uniformity in all directions red-shifts are isotropic density of earth ~ 5.52-6 g/cm3 1 supernova = bright as a galaxy (lasts for days or weeks) white dwarf: ~ a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter ~ density - 1 x 109 kg/m3 ~ it no longer undergoes fusion reactions, so the star has no source of energy ~ it is Earth-sized Type 1A supernova: ~ a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star ~ used as a standard candle in the galaxy Chandrasekhar limit: ~ limits the mass of bodies made from electron-degenerate matter, a dense form of matter which consists of nuclei immersed in a gas of electrons ~ no non-rotating white dwarf can be heavier than M = 1.4 Msun supernova explosions last a few seconds stars are usually just points Andronmeda is the closet and biggest galaxy to us 7 milimeters is usually the size range in an adult’s pupil charged couple device (CCD) are more sensitive than film Messier 13 (M13): ~ great globular cluster ~ 25, 100 light years away Messier 14 (M14): ~ distance of about 30,000 light-years Messier 42 (M42) // Orion Nebula: ~ Orion’s sword is a nebula ~ Orion is a big open cluster (almost, it’s changing) globular cluster stars usually are formed around the same time together open clusters: ~ dissipate ~ represents where stars used to be formed ~ a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud, and are still loosely gravitationally bound to each other red nebula: ~ a nebula that had drifted away from the main body of the galaxy planetary nebula: ~ an emission nebula consisting of a glowing shell of gas and plasma formed by certain types of stars when they die ~ similar to the appearance to giant planets when viewed through small optical telescopes ~ unrelated to the planets of the solar system terminator ~ defined as the line which separates day and night on the moon the moon can be seen during daylight daytime seeing of the moon is a problem when the ground is warm narrow band filter ~ type of filter which transmits light over only a very restricted range of wavelengths or over narrow spectral bands cat’s eye nebula: ~ a planetary nebula in the constellation of Draco ring nebula: ~ located in the northern constellation of Lyra ~ one of the most prominent examples of the deep-sky objects called planetary nebula nebulas grow older & dimmer (planetary nebulas) horse head nebula ~ a dark nebula in the Orion constellation nebulas are categorized by light into: ~ absorb nebula ~ reflection nebula ~ emission nebula ~ refraction nebula planets are not a problem in light pollution, but are too small to see detail EM radiation: ~ gamma rays not really possible through air ~ x-rays ~ ultraviolet marginally possible through air ~ visible ~ infrared tough through air; warm stuff gives off IR: space telescopes better ~ microwave ~ radio visible light is blocked best with something equal to a wave length almost nothing blocks radio waves barred spiral galaxy: ~ a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars ~ bars are found in approximately half of all spiral galaxies everything gives off infrared waves at all times