What is the Zodiac? The Zodiac is defined by 12 constellations
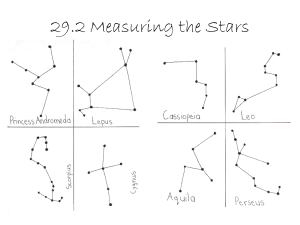
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
Sermon Notes
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... This famous cluster has been known since prehistoric times. The ancient Greeks saw this "nebula" as the manger (Phatne) associated with two asses who eat from it, Asellus Borealis, the Northern Ass (Gamma Cnc) and Asellus Australis, the Southern Ass (Delta Cnc). Erathosthenes reported that these wer ...
... This famous cluster has been known since prehistoric times. The ancient Greeks saw this "nebula" as the manger (Phatne) associated with two asses who eat from it, Asellus Borealis, the Northern Ass (Gamma Cnc) and Asellus Australis, the Southern Ass (Delta Cnc). Erathosthenes reported that these wer ...
“Do you have a good caption for the pop-eyed, thin
... Centauri, famous for being the closest visible star, 4.3 light years away. The light left that star 4.3 years ago. At 186 thousand miles per second, the light traveled over 25 trillion miles from Alpha Centauri to reach Earth. Alpha Centauri means this star is the brightest star in the constellation ...
... Centauri, famous for being the closest visible star, 4.3 light years away. The light left that star 4.3 years ago. At 186 thousand miles per second, the light traveled over 25 trillion miles from Alpha Centauri to reach Earth. Alpha Centauri means this star is the brightest star in the constellation ...
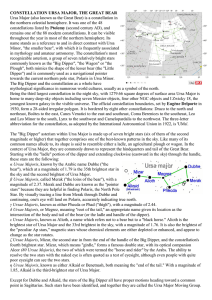
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation boundaries, set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, form a 28-sided irregular polygon. It is bordered by eight other constellat ...
... home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe. The official constellation boundaries, set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, form a 28-sided irregular polygon. It is bordered by eight other constellat ...
Quiz #4 – The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Stars
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? ________________ ...
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? ________________ ...
properties of stars 2012
... Variable Stars are those whose luminosity varies. A PULSATING variable is a star that is swelling and shrinking. As it swells, the same energy is spread over a larger area, the star cools and appears dimmer. (also, star cols because less pressure allows energy to escape) As it shrinks, it heats up ...
... Variable Stars are those whose luminosity varies. A PULSATING variable is a star that is swelling and shrinking. As it swells, the same energy is spread over a larger area, the star cools and appears dimmer. (also, star cols because less pressure allows energy to escape) As it shrinks, it heats up ...
Document
... Greek Letters- Bayer Letters (Johann Bayer) • The Alphabet of Greek letters is generally assigned to stars in a constellation in order of brightness. • The alpha star is the brightest (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon) ...
... Greek Letters- Bayer Letters (Johann Bayer) • The Alphabet of Greek letters is generally assigned to stars in a constellation in order of brightness. • The alpha star is the brightest (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon) ...
The Closest New Stars To Earth
... If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundreds of thousands (or more) times the mass of our sun, you'll get a nebula like Orion. But if your cloud is only a few thousand times the sun's mass, it's going to be much fainter. In most instances, the clumps of matter within will grow slowly, the n ...
... If you get a collapsing molecular cloud many hundreds of thousands (or more) times the mass of our sun, you'll get a nebula like Orion. But if your cloud is only a few thousand times the sun's mass, it's going to be much fainter. In most instances, the clumps of matter within will grow slowly, the n ...
Measuring Distances Beyond the Solar System The Characteristics
... The Luminosity of a star is measured by comparing it with the luminosity of the Sun, which is assigned a luminosity of 1. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky found in the constellation of Canis Major, has a luminosity of 22. This means Sirius gives off 22 times more energy each second than ...
... The Luminosity of a star is measured by comparing it with the luminosity of the Sun, which is assigned a luminosity of 1. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky found in the constellation of Canis Major, has a luminosity of 22. This means Sirius gives off 22 times more energy each second than ...
2.7 - 2.9a
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
Diapositiva 1
... the Snowflake cluster. To better understand this process, a detailed image of this region was taken in two colors of infrared light by the orbiting Spitzer Space Telescope. Bright stars from the Snowflake cluster dot the field. These stars soon heat up and destroy the gas and dust mountains in which ...
... the Snowflake cluster. To better understand this process, a detailed image of this region was taken in two colors of infrared light by the orbiting Spitzer Space Telescope. Bright stars from the Snowflake cluster dot the field. These stars soon heat up and destroy the gas and dust mountains in which ...
Chapter 5 Mid-term Study Guide
... ______ A small star becomes a white dwarf, and a large star becomes a neutron star or black hole. ______ The star collapses again and then explodes as a nova or supernova. ______ A cloud of dust and gas is drawn together by its own gravity. ______ The star continues to give off the same amount of en ...
... ______ A small star becomes a white dwarf, and a large star becomes a neutron star or black hole. ______ The star collapses again and then explodes as a nova or supernova. ______ A cloud of dust and gas is drawn together by its own gravity. ______ The star continues to give off the same amount of en ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth ...
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth ...
E3 STELLAR DISTANCES E4 COSMOLOGY
... A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measure at 4.3 x 10-9 W m-2. How far away is the star? [28 pc] ...
... A main sequence star emits most of its energy at λ = 2.4 x 10-7 m. Its apparent brightness is measure at 4.3 x 10-9 W m-2. How far away is the star? [28 pc] ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
Name
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
Groups of Stars
... • Compare the life of a star to the life of a human. Describe how the life stages are similar. You will need to choose the life cycle of either a lowmedium mass star OR a high mass star. ...
... • Compare the life of a star to the life of a human. Describe how the life stages are similar. You will need to choose the life cycle of either a lowmedium mass star OR a high mass star. ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
... D. T-Tauri stars E. white dwarfs 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR ...
labex7
... has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more lu ...
... has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitude-brightness rule to convert this into a brightness factor or luminosity. See Chp 2.1 in the online notes to do this. You will find that Polaris is 2513 times more lu ...
Corona Australis

Corona Australis /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstreɪlɨs/ or Corona Austrina /kɵˈroʊnə ɒˈstraɪnə/ is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means ""southern crown"", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.Although fainter than its namesake, the oval- or horseshoe-shaped pattern of its brighter stars renders it distinctive. Alpha and Beta Coronae Australis are the two brightest stars with an apparent magnitude of around 4.1. Epsilon Coronae Australis is the brightest example of a W Ursae Majoris variable in the southern sky. Lying alongside the Milky Way, Corona Australis contains one of the closest star-forming regions to our Solar System—a dusty dark nebula known as the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, lying about 430 light years away. Within it are stars at the earliest stages of their lifespan. The variable stars R and TY Coronae Australis light up parts of the nebula, which varies in brightness accordingly.