The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... begins in a shell. This causes the star to expand to become a red giant (bright, cool, and large) as it evolves toward the upper right in the H-R diagram . This will happen to the Sun in some 5 billion years, when it will swallow the Earth. Then they start to burn oxygen at the core, and helium in a ...
... begins in a shell. This causes the star to expand to become a red giant (bright, cool, and large) as it evolves toward the upper right in the H-R diagram . This will happen to the Sun in some 5 billion years, when it will swallow the Earth. Then they start to burn oxygen at the core, and helium in a ...
Lecture 13
... 1 au : Earth-Sun semimajor axis 5 au : Jupiter's semimajor axis, start of outer Solar System 30 au : Neptune's semimajor axis, end of planetary system 30-1000 au : The Kuiper Belt 1000 au – 50,000 au : The Oort cloud How far away are the stars? How can one measure it??? ...
... 1 au : Earth-Sun semimajor axis 5 au : Jupiter's semimajor axis, start of outer Solar System 30 au : Neptune's semimajor axis, end of planetary system 30-1000 au : The Kuiper Belt 1000 au – 50,000 au : The Oort cloud How far away are the stars? How can one measure it??? ...
Galactic Address/Stars/Constellations
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
... What is a star? • A star is an object in space that produces its own light and heat through nuclear ...
Evan_Skillman_1
... Pleiades now has no stars with life expectancy less than around 100 million years. ...
... Pleiades now has no stars with life expectancy less than around 100 million years. ...
Mon Oct 22, 2012 MOON IN CAPRICORNUS The moon is waxing
... The moon is in its waxing gibbous phase, and has entered a part of the sky known as “the sea.” A large part of the sky has been designated as such because of all the watery constellations found there. In the zodiac there is Capricornus the Sea Goat, followed to the east by Aquarius, the water carrie ...
... The moon is in its waxing gibbous phase, and has entered a part of the sky known as “the sea.” A large part of the sky has been designated as such because of all the watery constellations found there. In the zodiac there is Capricornus the Sea Goat, followed to the east by Aquarius, the water carrie ...
Black Hole
... its outer layers as a planetary nebula. The electrons and protons have been packed as closely as possible by gravity. An example of the white dwarf is the Pup, companion star of Sirius in Canis major. ...
... its outer layers as a planetary nebula. The electrons and protons have been packed as closely as possible by gravity. An example of the white dwarf is the Pup, companion star of Sirius in Canis major. ...
Chapter 12
... stars. The preceding chapter told us how stars form, and the next chapter tells us how stars die. This chapter is the heart of the story—how stars live. As always, we accept nothing at face value. We expect theory to be supported by evidence. We expect carefully constructed models to help us underst ...
... stars. The preceding chapter told us how stars form, and the next chapter tells us how stars die. This chapter is the heart of the story—how stars live. As always, we accept nothing at face value. We expect theory to be supported by evidence. We expect carefully constructed models to help us underst ...
Review Questions for Exam #2
... In order to figure out the mass of a star we observe binary star systems and use Kepler’s 3rd Law, (M1 + M2) P2 = 4π2*a3/G Discuss how we determine, P and a. How do we solve for individual mass (like M1) rather than (M1 + M2)? ...
... In order to figure out the mass of a star we observe binary star systems and use Kepler’s 3rd Law, (M1 + M2) P2 = 4π2*a3/G Discuss how we determine, P and a. How do we solve for individual mass (like M1) rather than (M1 + M2)? ...
Question: Fossilized footprints of Coelophysis
... Picking the right table: The Inferred Properties of Earth’s Interior table (p. NY28) has a diagram of Earth’s interior, along with graphs that show how pressure and temperature change with depth. From this table, you can find the temperature at the boundary between Earth’s mantle and core (5000 °C). ...
... Picking the right table: The Inferred Properties of Earth’s Interior table (p. NY28) has a diagram of Earth’s interior, along with graphs that show how pressure and temperature change with depth. From this table, you can find the temperature at the boundary between Earth’s mantle and core (5000 °C). ...
Chapter 12
... 1. The nebular hypothesis of solar system formation is that the Sun and planets formed when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
... 1. The nebular hypothesis of solar system formation is that the Sun and planets formed when a large nebula condensed and was collected together by gravity. 2. Our solar system formed more than 4.5 billion years ago. 3. Inner or terrestrial planets and outer or Jovian planets. ...
Level 2 Earth and Space Science (91192) 2015
... Pleiades is known to us as Matariki, and is an open star cluster of over 1400 stars. Its appearance in the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginnin ...
... Pleiades is known to us as Matariki, and is an open star cluster of over 1400 stars. Its appearance in the early morning sky marks the dawn of the Māori New Year. In this cluster there is a star named HD 23514, which has been observed with dust particles around it that are thought to be the beginnin ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 26. When a massive, dying star blows itself apart, if the remaining mass is less than three times the mass of the sun, the leftover material will form a ______. 28. Cosmologists think the material in our bodies was once part of a massive star. Explain how it went from a star to our bodies. 29. Descr ...
... 26. When a massive, dying star blows itself apart, if the remaining mass is less than three times the mass of the sun, the leftover material will form a ______. 28. Cosmologists think the material in our bodies was once part of a massive star. Explain how it went from a star to our bodies. 29. Descr ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
... traditionally some stars are "shared" by overlapping mythological pictures). The first really accurate map, which had about 1022 stars grouped into 48 constellations, was drawn by the Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy (150 A.D.?), the "Almagest". It was more than 1500 years before more constellation ...
... traditionally some stars are "shared" by overlapping mythological pictures). The first really accurate map, which had about 1022 stars grouped into 48 constellations, was drawn by the Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy (150 A.D.?), the "Almagest". It was more than 1500 years before more constellation ...
Objects in the Sky Power Point
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
... On the first day of January 1801, Giuseppe Piazzi discovered an object which he first thought was a new comet. But after its orbit was better determined it was clear that it was not a comet but more like a small planet. Piazzi named it Ceres, after the Sicilian goddess of grain. Three other small b ...
Measuring Stars
... Luminosity from Spectral Class Suppose you have a G2 star. What is its luminosity? •90% of all stars are main sequence G2: L L B5: L 800 L K5: L 0.1L •For main sequence stars, the spectral type tells you the luminosity •Together with brightness, this tells you the distance ...
... Luminosity from Spectral Class Suppose you have a G2 star. What is its luminosity? •90% of all stars are main sequence G2: L L B5: L 800 L K5: L 0.1L •For main sequence stars, the spectral type tells you the luminosity •Together with brightness, this tells you the distance ...
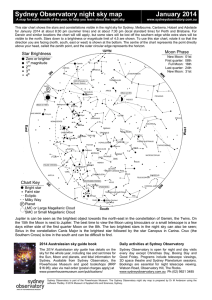
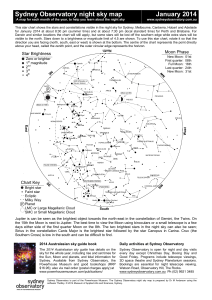
Sydney Observatory night sky map January 2014
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.