Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
Thermo 2 - WordPress.com
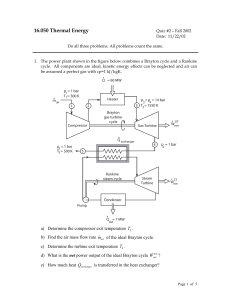
... • To do analysis of system the system needs to be at equilibrium (e.g. no system variables are changing) • Analysis can be done at Quasi-equilibrium, which is to say the system is changing in increments at which analysis can be done. If the time change at which the analysis is done is small enough, ...
... • To do analysis of system the system needs to be at equilibrium (e.g. no system variables are changing) • Analysis can be done at Quasi-equilibrium, which is to say the system is changing in increments at which analysis can be done. If the time change at which the analysis is done is small enough, ...
Heat and Thermodynamics
... loss through the wall of a house, the rate of conduction heat transfer is: ...
... loss through the wall of a house, the rate of conduction heat transfer is: ...
Thermodynamics - StrikerPhysics
... • Thermo (heat) dynamics (transfer) • Thermodynamic systems describe many many particles (molecules) which obey Newton’s laws for dynamics but which would be difficult to analyze due to their numbers. • We use macroscopic means for analysis of these systems of many particles - involving quantities s ...
... • Thermo (heat) dynamics (transfer) • Thermodynamic systems describe many many particles (molecules) which obey Newton’s laws for dynamics but which would be difficult to analyze due to their numbers. • We use macroscopic means for analysis of these systems of many particles - involving quantities s ...
Chapter 19 – The First Law of Thermodynamics
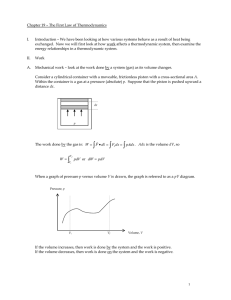
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
... Interesting Note: If a system changes from an initial state i to a final state f along different paths (e.g., Path A and Path B), the change in internal energy will be the same along those paths. And, in fact, all paths that go from i to f. That is, U = Uf - Ui . From the first law, that means that ...
Chapter 15 Notes - Valdosta State University
... type of wall. A wall that allows heat flow is called a diathermal wall. One that does not is said to be adiabatic. The state of a system is described by specifying factors that affect the internal energy of the system. In the case of a gas this would be temperature, pressure, volume, and mass. There ...
... type of wall. A wall that allows heat flow is called a diathermal wall. One that does not is said to be adiabatic. The state of a system is described by specifying factors that affect the internal energy of the system. In the case of a gas this would be temperature, pressure, volume, and mass. There ...
Topic 2 The first law of thermodynamics
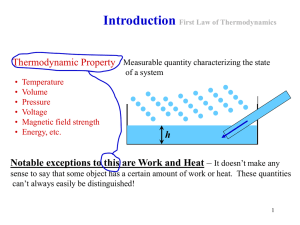
... Extensive properties: dependent on amount Intensive properties: independent on amount ...
... Extensive properties: dependent on amount Intensive properties: independent on amount ...
lecture21
... Processes proceed in a certain direction and not in the reverse direction. The first law places no restriction on direction. A process will not occur unless it satisfies both the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Second law not only identifies the direction of process, it also asserts that en ...
... Processes proceed in a certain direction and not in the reverse direction. The first law places no restriction on direction. A process will not occur unless it satisfies both the first and second laws of thermodynamics. Second law not only identifies the direction of process, it also asserts that en ...
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
... Metamorphic rocks are formed when heat and/or pressure cause rocks to change. Why? As conditions change within the earth, rocks are also forced to change. Heat and pressure may cause the chemical elements in the original rock to react and reform into minerals. These new minerals are often aligned (a ...
... Metamorphic rocks are formed when heat and/or pressure cause rocks to change. Why? As conditions change within the earth, rocks are also forced to change. Heat and pressure may cause the chemical elements in the original rock to react and reform into minerals. These new minerals are often aligned (a ...
The Heat Equation - Rose
... This is the PDE that ρ must obey and is call the “heat equation”. It’s easy (use ρ = c0 + c1 u)) to see that the temperature u obeys the same equation. We’ll usually work in terms of the temperature u, since it’s a more familiar quantity. There’s another situation in which the heat equation frequent ...
... This is the PDE that ρ must obey and is call the “heat equation”. It’s easy (use ρ = c0 + c1 u)) to see that the temperature u obeys the same equation. We’ll usually work in terms of the temperature u, since it’s a more familiar quantity. There’s another situation in which the heat equation frequent ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.