Lecture 4. - ChemWeb (UCC)
... • Energy associated with random motion of atoms and molecules Chemical Energy • Energy stored in structural units of chemicals Units = Joules • 1 Joule (J) = 1 kg m2 /s2 • 1 Calorie (cal) = 4.184 J ...
... • Energy associated with random motion of atoms and molecules Chemical Energy • Energy stored in structural units of chemicals Units = Joules • 1 Joule (J) = 1 kg m2 /s2 • 1 Calorie (cal) = 4.184 J ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... 2. Circle the letter that best describes what happens when heat is added to a system. a. Much of it is destroyed immediately. b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost. d. It is used to overcome friction. 3. Is the following sentence true or false? The f ...
... 2. Circle the letter that best describes what happens when heat is added to a system. a. Much of it is destroyed immediately. b. It transforms to an equal amount of some other form of energy. c. Much of it is lost. d. It is used to overcome friction. 3. Is the following sentence true or false? The f ...
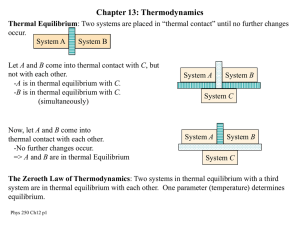
p250c13
... Efficiency is the effectiveness with which supplied heat QH is converted to work :For the ...
... Efficiency is the effectiveness with which supplied heat QH is converted to work :For the ...
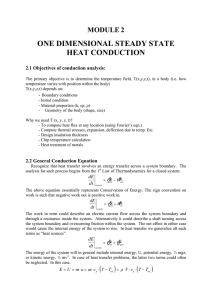
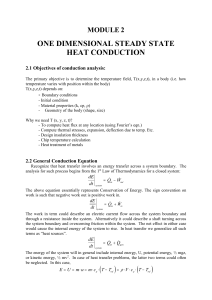
one dimensional steady state heat conduction
... The heat transfer rate may be determined from separate consideration of each element in the network. Since qx is constant throughout the network, it follows that T Ts ,1 Ts ,1 Ts , 2 Ts , 2 T , 2 ...
... The heat transfer rate may be determined from separate consideration of each element in the network. Since qx is constant throughout the network, it follows that T Ts ,1 Ts ,1 Ts , 2 Ts , 2 T , 2 ...
JIF 314 Chap 4
... integration which will result in different value for process carried out via different route (e.g. adiabatical path result in a final work done that is different from that is a non-adibatical one) ...
... integration which will result in different value for process carried out via different route (e.g. adiabatical path result in a final work done that is different from that is a non-adibatical one) ...
Lecture 3 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Fourth, heat is not a property of a system like temperature, pressure, volume or mass. It is energy in transit – energy that enters or leaves a system as a consequence of a temperature difference between the system and a body with which it is in thermal contact (including radiant heat). Neither work ...
... Fourth, heat is not a property of a system like temperature, pressure, volume or mass. It is energy in transit – energy that enters or leaves a system as a consequence of a temperature difference between the system and a body with which it is in thermal contact (including radiant heat). Neither work ...
Unit 6 Review
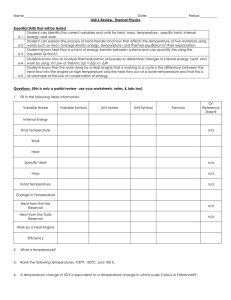
... Student can identify the correct variables and units for heat, mass, temperature, specific heat, internal 6-1 energy, and work. Student can explain the process of heat transfer and how that affects the temperature of two materials using 6-2 words such as heat, average kinetic energy, temperature, an ...
... Student can identify the correct variables and units for heat, mass, temperature, specific heat, internal 6-1 energy, and work. Student can explain the process of heat transfer and how that affects the temperature of two materials using 6-2 words such as heat, average kinetic energy, temperature, an ...
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
... usually a slow process like a balloon expanding slowly during the day. • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: ...
... usually a slow process like a balloon expanding slowly during the day. • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: ...
Internal energy is a characteristic of a given state – it is the same no
... So you can change the pressure and the temperature together, but the system does not move. That means that no work is done! Q = U Isothermal: T = 0 therefore U = 0 The temperature does not change so the system can’t gain any internal energy. Therefore any heat put into the system will be used to ...
... So you can change the pressure and the temperature together, but the system does not move. That means that no work is done! Q = U Isothermal: T = 0 therefore U = 0 The temperature does not change so the system can’t gain any internal energy. Therefore any heat put into the system will be used to ...
Relationships Between Heat and Work
... • Isothermal process – a thermodynamic process that takes place at constant temperature and in which the internal energy of a system remains unchanged – Similar to a balloon expanding as the pressure drops before a storm hits • The balloon expands to keep pressure equal with the environment ...
... • Isothermal process – a thermodynamic process that takes place at constant temperature and in which the internal energy of a system remains unchanged – Similar to a balloon expanding as the pressure drops before a storm hits • The balloon expands to keep pressure equal with the environment ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.