Thermochemistry
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
... We can define a new state variable (one where the path to its current state does not affect its value) called enthalpy: ...
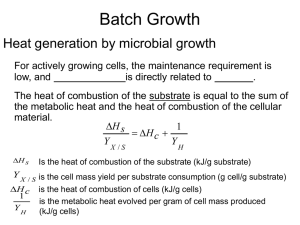
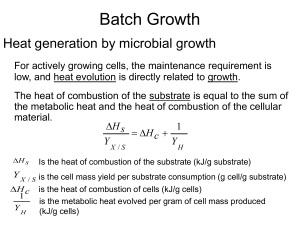
lecture notes-growth kinetics-3-heat evolution
... YX /S The higher degree of oxidation of the substrate has lower amounts of heat released: 1/YH ...
... YX /S The higher degree of oxidation of the substrate has lower amounts of heat released: 1/YH ...
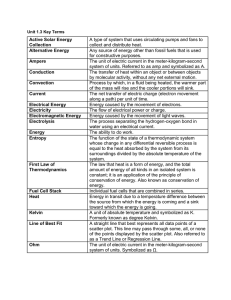
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
... which all parts of the system have attained a uniform temperature which is the same as that of the system’s surroundings. A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties such as temperature, volume, pressure, concentration, surface tension, and viscosity. The study of the e ...
Convective heat transfer
... To quantify the ease with which a particular medium conducts, engineers employ the thermal conductivity, also known as the conductivity constant or conduction coefficient, k. In thermal conductivity, k is defined as "the quantity of heat, Q, transmitted in time (t) through a thickness (L), in a dir ...
... To quantify the ease with which a particular medium conducts, engineers employ the thermal conductivity, also known as the conductivity constant or conduction coefficient, k. In thermal conductivity, k is defined as "the quantity of heat, Q, transmitted in time (t) through a thickness (L), in a dir ...
Powerpoint
... and formed a solid crust over molten interior • If solid crust floats (e.g. plagioclase on the Moon) then it will insulate the interior, which will cool slowly (~ Myrs) • If the crust sinks, then cooling is rapid (~ kyrs) • What happens once the magma ocean has solidified? ...
... and formed a solid crust over molten interior • If solid crust floats (e.g. plagioclase on the Moon) then it will insulate the interior, which will cool slowly (~ Myrs) • If the crust sinks, then cooling is rapid (~ kyrs) • What happens once the magma ocean has solidified? ...
heat evolution
... Y X / S is the cell mass yield per substrate consumption (g cell/g substrate) H c is the heat of combustion of cells (kJ/g cells) ...
... Y X / S is the cell mass yield per substrate consumption (g cell/g substrate) H c is the heat of combustion of cells (kJ/g cells) ...
Thermodynamics
... When a system gains heat, the internal energy of the system increases. Q is positive when a system gains heat and negative when a system loses heat. Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when ...
... When a system gains heat, the internal energy of the system increases. Q is positive when a system gains heat and negative when a system loses heat. Internal energy of a system can decrease if the system does work on its surroundings. Work is positive when it is done by the system and negative when ...
FIRE INVESTIGATIONS
... 9.4 billion dollars damage 5,000 fatalities 100 firefighter fatalities 25,500 injuries #1 cause of fires: cooking #1 cause of fire deaths: smoking ...
... 9.4 billion dollars damage 5,000 fatalities 100 firefighter fatalities 25,500 injuries #1 cause of fires: cooking #1 cause of fire deaths: smoking ...
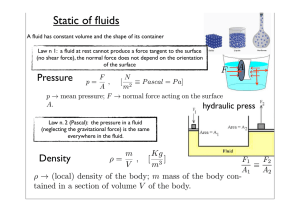
Static of fluids
... or give a quantity Q of heat where m is the mass and cL is the latent heat. ...
... or give a quantity Q of heat where m is the mass and cL is the latent heat. ...
3 - CFD - Anna University
... mechanisms between a system and its surroundings. • Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. • Both are recognised at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. • Both are path functions ...
... mechanisms between a system and its surroundings. • Systems possess energy, but not heat or work. • Both are recognised at the boundaries of a system as they cross the boundaries. • Both are path functions ...
HeatTransfer
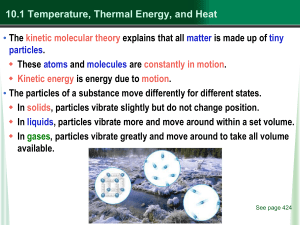
... Heat moves from higher temperature (higher kinetic energy) particles to lower temperature particles (lower kinetic energy.) e.g.: a cold spoon warms when placed in a cup of hot coffee. Thermal conductors transfer heat easily, while insulators do not. • Convection is the transfer of heat in flu ...
... Heat moves from higher temperature (higher kinetic energy) particles to lower temperature particles (lower kinetic energy.) e.g.: a cold spoon warms when placed in a cup of hot coffee. Thermal conductors transfer heat easily, while insulators do not. • Convection is the transfer of heat in flu ...
Lecture 5
... Energy is transferred through fluid motion (gases, liquids). Physical mechanism: When a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. The part of the fluid in contact with the hot object has a temperature higher than that of the surrounding cooler fluid, h ...
... Energy is transferred through fluid motion (gases, liquids). Physical mechanism: When a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. The part of the fluid in contact with the hot object has a temperature higher than that of the surrounding cooler fluid, h ...
Thermochemistry
... Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.