The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... Kevin-Planck Statement: It is impossible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces no other effects than the performance of work and the exchange of heat with a single reservoir. ...
... Kevin-Planck Statement: It is impossible to construct a device that operates in a cycle and produces no other effects than the performance of work and the exchange of heat with a single reservoir. ...
Chapter 1: The first law of thermodynamics
... Whenever a quantity only depends on the present values of macroscopic variables such as the pressure and volume we say that the quantity is a function of state. Therefore, for an ideal gas in equilibrium, the system’s temperature is a function of state ( θ = F ( P,V ) ). A quantity, dG, is said to b ...
... Whenever a quantity only depends on the present values of macroscopic variables such as the pressure and volume we say that the quantity is a function of state. Therefore, for an ideal gas in equilibrium, the system’s temperature is a function of state ( θ = F ( P,V ) ). A quantity, dG, is said to b ...
Chapter 18
... Convection: Convection happens when a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. Heat is transferred through the flow of the fluid. Radiation: Heat can be exchanged via electromagnetic waves, called thermal radiation. It does not need a medium. ...
... Convection: Convection happens when a fluid comes in contact with an object whose temperature is higher than that of the fluid. Heat is transferred through the flow of the fluid. Radiation: Heat can be exchanged via electromagnetic waves, called thermal radiation. It does not need a medium. ...
Thermal Energy from Chemical Reactions
... • For Water this would become • 4.184 X mass of water X temperature rise • 1 g = 1mL for water density = 1 g mL-1 ...
... • For Water this would become • 4.184 X mass of water X temperature rise • 1 g = 1mL for water density = 1 g mL-1 ...
Thermochemistry - Valdosta State University
... H and ΔH are state functions, depending only on the initial and final states. There are many specific H’s, depending on what you want to know H ...
... H and ΔH are state functions, depending only on the initial and final states. There are many specific H’s, depending on what you want to know H ...
thermochemistry - Pace University Webspace
... • Thermal runaway begins when the heat produced by the reaction exceeds the heat removed. The surplus of heat raises the temperature of the reaction mass, which causes the rate of reaction to increase. This in turn accelerates the rate of heat production. This reaction can be hazardous and/ or cause ...
... • Thermal runaway begins when the heat produced by the reaction exceeds the heat removed. The surplus of heat raises the temperature of the reaction mass, which causes the rate of reaction to increase. This in turn accelerates the rate of heat production. This reaction can be hazardous and/ or cause ...
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
Lesson Plans - University High School
... describe phase changes as examples of dynamic equilibrium as a reversible process dependent upon energy being absorbed or released: ○ melting-freezing or vaporization-condensation describe phase transitions in terms of kinetic-molecular theory (molecular motion) and intermolecular forces (attraction ...
... describe phase changes as examples of dynamic equilibrium as a reversible process dependent upon energy being absorbed or released: ○ melting-freezing or vaporization-condensation describe phase transitions in terms of kinetic-molecular theory (molecular motion) and intermolecular forces (attraction ...
8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is
... 8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in the total entropy of the systems and its surroundings . To take another example of disordering , the melting and boiling of zinc , at its melting temperature the closed backed hexagonal crystal struct ...
... 8 second law of thermodynamics : states spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in the total entropy of the systems and its surroundings . To take another example of disordering , the melting and boiling of zinc , at its melting temperature the closed backed hexagonal crystal struct ...
Document
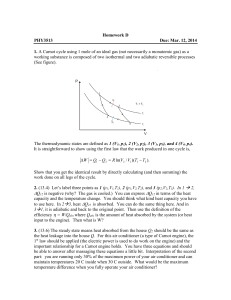
... ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat capacity and the temperature change. You should think what kind heat capacity you have to use here. In 23, heat ∆Q23 is absorbed. You can do the same thing here. And in 31, it is adiabatic and back to the original ...
... ∆Q12 is negative (why? The gas is cooled.) You can express ∆Q12 in terms of the heat capacity and the temperature change. You should think what kind heat capacity you have to use here. In 23, heat ∆Q23 is absorbed. You can do the same thing here. And in 31, it is adiabatic and back to the original ...
heat engine
... All of the heat input originates from a single temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. ...
... All of the heat input originates from a single temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... All of the heat input originates from a single temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. ...
... All of the heat input originates from a single temperature, and all the rejected heat goes into a cold reservoir at a single temperature. Since the efficiency can only depend on the reservoir temperatures, the ratio of heats can only depend on those temperatures. ...
Internal Energy
... pressure of 2 atm from 10 L to 2 L. Heat is then added to the gas at constant volume until the original temperature is reached. What is the total work done on the gas? ...
... pressure of 2 atm from 10 L to 2 L. Heat is then added to the gas at constant volume until the original temperature is reached. What is the total work done on the gas? ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
... Standard Heats of Formation Standard Heat of Formation (DHof ): The enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of a substance in its standard state from its constituent elements in their ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.