* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thermodynamics
Entropy in thermodynamics and information theory wikipedia , lookup
Calorimetry wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Equipartition theorem wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Heat capacity wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
First law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Temperature wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Extremal principles in non-equilibrium thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal radiation wikipedia , lookup
Adiabatic process wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic system wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Second law of thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Week 5- Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat and other
forms of energy. In particular, it describes how thermal energy is converted to and from other forms of
energy and how it affects matter.
Thermal energy is the energy a substance or system has due to its temperature, i.e., the energy of
moving or vibrating molecules. Thermodynamics involves measuring this energy, which can be
"exceedingly complicated," according to David McKee, a professor of physics at Missouri Southern State
University. "The systems that we study in thermodynamics … consist of very large numbers of atoms or
molecules interacting in complicated ways. But, if these systems meet the right criteria, which we call
equilibrium, they can be described with a very small number of measurements or numbers. Often this is
idealized as the mass of the system, the pressure of the system, and the volume of the system, or some other
equivalent set of numbers."
Thermodynamics, then, is concerned with several properties of matter; foremost among these is heat.
Heat is energy transferred between substances or systems due to a temperature difference between them,
according to Energy Education. As a form of energy, heat is conserved, i.e., it cannot be created or
destroyed. It can, however, be transferred from one place to another. Heat can also be converted to and from
other forms of energy. For example, a steam turbine can convert heat to kinetic energy to run a generator
that converts kinetic energy to electrical energy. A light bulb can convert this electrical energy to
electromagnetic radiation (light), which, when absorbed by a surface, is converted back into heat.
The amount of heat transferred by a substance depends on the speed and number of atoms or
molecules in motion, according to Energy Education. The faster the atoms or molecules move, the higher the
temperature, and the more atoms or molecules that are in motion, the greater the quantity of heat they
transfer.
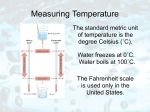
Temperature is "a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter,
expressed in terms of units or degrees designated on a standard scale". The most commonly used
temperature scale is Celsius, which is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, assigning respective
values of 0 degrees C and 100 degrees C. The Fahrenheit scale is also based on the freezing and boiling
points of water which have assigned values of 32 F and 212 F, respectively. Scientists worldwide, however,
use the Kelvin (K with no degree sign) scale, named after William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, because it
works in calculations. This scale uses the same increment as the Celsius scale, i.e., a temperature change of
1 C is equal to 1 K. However, the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, the temperature at which there is a
total absence of heat energy and all molecular motion stops. A temperature of 0 K is equal to minus 459.67
F or minus 273.15 C.
The amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a certain mass of a substance by a certain
amount is called specific heat, or specific heat capacity, according to Wolfram Research. The conventional
unit for this is calories per gram per kelvin. The calorie is defined as the amount of heat energy required to
raise the temperature of 1 gram of water at 4 C by 1 degree.
The specific heat of a metal depends almost entirely on the number of atoms in the sample, not its
mass. For instance, a kilogram of aluminum can absorb about seven times more heat than a kilogram of
lead. However, lead atoms can absorb only about 8 percent more heat than an equal number of aluminum
atoms. A given mass of water, however, can absorb nearly five times as much heat as an equal mass of
aluminum. The specific heat of a gas is more complex and depends on whether it is measured at constant
pressure or constant volume.
Thermal conductivity (k) is “the rate at which heat passes through a specified material, expressed as
the amount of heat that flows per unit time through a unit area with a temperature gradient of one degree per
unit distance,” according to the Oxford Dictionary. The unit for k is watts (W) per meter (m) per kelvin (K).
Values of k for metals such as copper and silver are relatively high at 401 and 428 W/m·K, respectively.
This property makes these materials useful for automobile radiators and cooling fins for computer chips
because they can carry away heat quickly and exchange it with the environment. The highest value of k for
any natural substance is diamond at 2,200 W/m·K.
Other materials are useful because they are extremely poor conductors of heat; this property is
referred to as thermal resistance, or R-value, which describes the rate at which heat is transmitted through
the material. These materials, such as rock wool, goose down and Styrofoam, are used for insulation in
exterior building walls, winter coats and thermal coffee mugs. R-value is given in units of square feet times
degrees Fahrenheit times hours per British thermal unit (ft2·°F·h/Btu) for a 1-inch-thick slab.
Newton's Law of Cooling
In 1701, Sir Isaac Newton first stated his Law of Cooling in a short article titled "Scala graduum
Caloris" ("A Scale of the Degrees of Heat") in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
Newton's statement of the law translates from the original Latin as, "the excess of the degrees of the heat ...
were in geometrical progression when the times are in an arithmetical progression." Worcester Polytechnic
Institute gives a more modern version of the law as "the rate of change of temperature is proportional to the
difference between the temperature of the object and that of the surrounding environment." This results in
an exponential decay in the temperature difference. For example, if a warm object is placed in a cold bath,
within a certain length of time, the difference in their temperatures will decrease by half. Then in that same
length of time, the remaining difference will again decrease by half. This repeated halving of the
temperature difference will continue at equal time intervals until it becomes too small to measure.
Heat can be transferred from one body to another or between a body and the environment by three
different means: conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction is the transfer of energy through a
solid material. Conduction between bodies occurs when they are in direct contact, and molecules transfer
their energy across the interface.
Convection is the transfer of heat to or from a fluid medium. Molecules in a gas or liquid in contact
with a solid body transmit or absorb heat to or from that body and then move away, allowing other
molecules to move into place and repeat the process. Efficiency can be improved by increasing the surface
area to be heated or cooled, as with a radiator, and by forcing the fluid to move over the surface, as with a
fan.
Radiation is the emission of electromagnetic (EM) energy, particularly infrared photons that carry
heat energy. All matter emits and absorbs some EM radiation, the net amount of which determines whether
this causes a loss or gain in heat.
The Carnot cycle
In 1824, Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot proposed a model for a heat engine based on what has come to
be known as the Carnot cycle. The cycle exploits the relationships among pressure, volume and temperature
of gasses and how an input of energy can change form and do work outside the system.
Compressing a gas increases its temperature so it becomes hotter than its environment. Heat can then
be removed from the hot gas using a heat exchanger. Then, allowing it to expand causes it to cool. This is
the basic principle behind heat pumps used for heating, air conditioning and refrigeration.
Conversely, heating a gas increases its pressure, causing it to expand. The expansive pressure can
then be used to drive a piston, thus converting heat energy into kinetic energy. This is the basic principle
behind heat engines.
Entropy
All thermodynamic systems generate waste heat. This waste results in an increase in entropy, which
for a closed system is a quantitative measure of the amount of thermal energy not available to do work.
Entropy in any closed system always increases; it never decreases. Additionally, moving parts produce
waste heat due to friction, and radiative heat inevitably leaks from the system.
This makes so-called perpetual motion machines impossible. Siabal Mitra, a professor of physics at
Missouri State University, explains, "You cannot build an engine that is 100 percent efficient, which means
you cannot build a perpetual motion machine. However, there are a lot of folks out there who still don't
believe it, and there are people who are still trying to build perpetual motion machines."
Entropy is also defined as "a measure of the disorder or randomness in a closed system," which also
inexorably increases. You can mix hot and cold water, but because a large cup of warm water is more
disordered than two smaller cups containing hot and cold water, you can never separate it back into hot and
cold without adding energy to the system. Put another way, you can’t unscramble an egg or remove cream
from your coffee. While some processes appear to be completely reversible, in practice, none actually are.
Entropy, therefore, provides us with an arrow of time: forward is the direction of increasing entropy.
The four laws of thermodynamics
The fundamental principles of thermodynamics were originally expressed in three laws. Later, it was
determined that a more fundamental law had been neglected, apparently because it had seemed so obvious
that it did not need to be stated explicitly. To form a complete set of rules, scientists decided this most
fundamental law needed to be included. The problem, though, was that the first three laws had already been
established and were well known by their assigned numbers. When faced with the prospect of renumbering
the existing laws, which would cause considerable confusion, or placing the pre-eminent law at the end of
the list, which would make no logical sense, a British physicist, Ralph H. Fowler, came up with an
alternative that solved the dilemma: he called the new law the “Zeroth Law.” In brief, these laws are:
The Zeroth Law states that if two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with some third body, then they are
also in equilibrium with each other. This establishes temperature as a fundamental and measurable property
of matter.
The First Law states that the total increase in the energy of a system is equal to the increase in thermal
energy plus the work done on the system. This states that heat is a form of energy and is therefore subject to
the principle of conservation.
The Second Law states that heat energy cannot be transferred from a body at a lower temperature to a body
at a higher temperature without the addition of energy. This is why it costs money to run an air conditioner.
The Third Law states that the entropy of a pure crystal at absolute zero is zero. As explained above,
entropy is sometimes called "waste energy," i.e., energy that is unable to do work, and since there is no heat
energy whatsoever at absolute zero, there can be no waste energy. Entropy is also a measure of the disorder
in a system, and while a perfect crystal is by definition perfectly ordered, any positive value of temperature
means there is motion within the crystal, which causes disorder. For these reasons, there can be no physical
system with lower entropy, so entropy always has a positive value.
( source of text: http://www.livescience.com/50776-thermodynamics.html )
Comprehension Questions
What is the study object of thermodynamics?
What is thermal energy?
What is heat and how does it act as form of energy?
What is temperature defined as?
What are specific heat and heat conductivity?
What does Newton’s Law of cooling state?
How is heat transferred?
How is Carnot Cycle applied?
State if the following sentences are True or False.
1. Scientists prefer the Kelvin scale to measure temperature because it works better in calculations.
2. One calorie is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water at 6 C by 2
degrees.
3. Copper and silver are heat conductors, whereas a diamond is an insulator.
4. Not all matter emits or absorbs EM radiation.
5. Thermodynamic systems generate heat waste which results in an increase in entropy.
6. Entropy in closed systems always decreases.
Match the words and their definitions.
1. matter
a. the difference between two values of a variable; a change, positive,
b. negative, or zero, in an independent variable.
2. equilibrium
3. conserve
4. increment
5.
6.
7.
8.
gradient
exponential
inexorable
slab
9. convection
10. resistance
c. a differential operator that, operating upon a function of
several variables, results in a vector the coordinates of which are
d. the partial derivatives of the function.
e. unyielding; unalterable:
f. the transfer of heat by the circulation or movement of the heated parts of a
liquid or gas.
g. a state of rest or balance due to the equal action of opposing forces.
h. the opposition offered by one thing, force, etc., to another.
i. to hold (a property) constant during an interaction or process:
j. the substance or substances of which any physical object consists or is
composed
k. a broad, flat, somewhat thick piece of stone, wood, or other solid material.
l. rising or expanding at a steady and usually rapid rate: