* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thermal energy - Georgetown ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
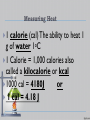
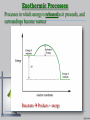
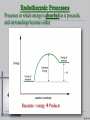
Thermal Energy All matter is made of small particles in constant motion The speed of particle motion increases with the addition of thermal energy Thermal Energy – the sum of the kinetic and potential energy of all of the atoms in an object Thermal Energy Thermal energy increases as temperature increases (q) Temperature – is the measure of the average kinetic energy of an object’s atoms or molecules Absolute Zero (-273oC) All molecular motion stops Temperature Units of temperature include Fahrenheit(F), Centigrade or Celsius (C), and Kelvin (K) F = (1.8) C0 + 32 K = C0 + 273 Heat Thermal energy that flows from something at a higher temperature to something at a lower temperature is called heat Thermal energy only flows from hot to cold. Measuring Heat 1 calorie (cal) The ability to heat 1 o g of water 1 C 1 Calorie = 1,000 calories also called a kilocalorie or kcal 1000 cal = 4180J or 1 cal = 4.18 J Specific Heat Specific heat is the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of a material by o 1 C or K Designated by Cp Units for Measuring Heat The Joule is the SI system unit for measuring heat: 2 1 kg m 1 Joule 1 newton meter 2 s The calorie is the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 Celsius degree 1calorie 4.18 Joules Energy Energy is the capacity to do work, and can take many forms Potential energy is stored energy or the energy of position Kinetic energy is the energy of motion Thermal energy (heat) is an outward manifestation of movement at the atomic level Heat (Enthalpy) Change, ΔH Definition: The amount of heat energy released or absorbed during a process. Calorimetry The amount of heat absorbed or released during a physical or chemical change can be measured, usually by the change in temperature of a known quantity of water in a calorimeter. Exothermic Processes Processes in which energy is released as it proceeds, and surroundings become warmer Reactants Products + energy Endothermic Processes Processes in which energy is absorbed as it proceeds, and surroundings become colder Reactants + energy Products SPECIFIC HEAT OF WATER 4.184 Joules per grams degree 0 Centigrade (J/g C) Q=(m)(Cp)∆T Q = Specific Heat m = mass Cp = Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure ∆T = Change in Temperature Calorimetry in enthalpy = H q = H These terms will be used interchangeably in this textbook Thus, q = H = m x C x T H is negative for an exothermic reaction H is positive for an endothermic reaction Changes Changes in Thermal Energy When heat flows into an object and it’s temp rises the change is positive When heat flows out, its temp decreases and the change is negative Chemistry Happens in MOLES An equation that includes energy is called a thermochemical equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O + 802.2 kJ 1 mole of CH4 releases 802.2 kJ of energy. When you make 802.2 kJ you also make 2 moles of water 17 Thermochemical Equations A heat of reaction is the heat change for the equation, exactly as written The physical state of reactants and products must also be given. Standard conditions for the reaction is 101.3 kPa (1 atm.) and 25 oC 18 CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O + 802.2 kJ If 10. 3 grams of CH4 are burned completely, how much heat will be produced? 10. 3 g CH4 1 mol CH4 16.05 g CH4 802.2 kJ 1 mol CH4 = 514 kJ 19 CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O + 802.2 kJ How many liters of O2 at STP would be required to produce 23 kJ of heat? How many grams of water would be produced with 506 kJ of heat? 20 Heat of Combustion The heat from the reaction that completely burns 1 mole of a substance Heat of Fusion Molar Heat of Fusion (Hfus) - the heat absorbed by one mole of a substance in melting from a solid to a liquid 21 Heat of Vaporization the heat required to change one mole of a substance from a liquid to a gas when a substance vaporizes, energy is needed. • when a substance condenses, energy is released. • 22