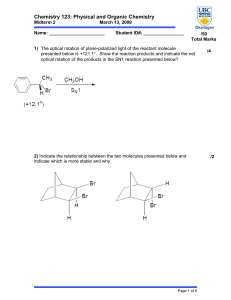
Name
... 1. Two compounds with the same formula but different structures are called what? (1) Isomers 2. Organic compounds (1) A) always contain nitrogen. B) are synthesized by only animal cells. C) always contain carbon. D) can only be synthesized in a laboratory. E) always contain oxygen. ...
... 1. Two compounds with the same formula but different structures are called what? (1) Isomers 2. Organic compounds (1) A) always contain nitrogen. B) are synthesized by only animal cells. C) always contain carbon. D) can only be synthesized in a laboratory. E) always contain oxygen. ...
The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to
... These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1. Chemical reactivi ...
... These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: 1. Chemical reactivi ...
Chapter 19 Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
... endothermic chemical reaction? (1) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. ...
... endothermic chemical reaction? (1) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. (2) The products have higher potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is positive. (3) The products have lower potential energy than the reactants, and the ΔH is negative. ...
Subject:
... Big Idea/Theme: Understanding how effective collisions encourage chemical reactions and how pressure, temperature and concentration affects the progression of equilibrium in a reversible reaction Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements) I will understand the factors that affect the rate of ...
... Big Idea/Theme: Understanding how effective collisions encourage chemical reactions and how pressure, temperature and concentration affects the progression of equilibrium in a reversible reaction Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements) I will understand the factors that affect the rate of ...
Endothermic And Exothermic Reactions
... that absorbs energy from its surroundings. More energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants than is released by the formation of bonds in the products. In these reactions, heat is shown as one This is a typical graph of an of the reactants endothermic reaction with the A + B + heat C pr ...
... that absorbs energy from its surroundings. More energy is required to break the bonds in the reactants than is released by the formation of bonds in the products. In these reactions, heat is shown as one This is a typical graph of an of the reactants endothermic reaction with the A + B + heat C pr ...
COUPLING REACTIONS IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
... The addition of dihydrogen to Vaska's complex and other transition metals is a reversible reaction. The hydrogen can be released again if the reaction moves to the left in a reductive elimination. That reversibility makes transition metal compounds useful for hydrogen storage. Hydrogen gas is volumi ...
Chapter 14, Section 1, pages 494-501
... Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactants to form products S8 + 8O2 ----------->8 SO2 Reversible Reactions are those in ...
... Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactants to form products S8 + 8O2 ----------->8 SO2 Reversible Reactions are those in ...
Erik`s Chemistry: Thermochemistry - ECHS Chemistry
... If 72.0 grams of H2O are formed from the reaction, how much heat was released? = 73.9 kJ 3. Hess' Law: The value of H for a reaction is the same whether it occurs directly or in a series of steps (state function). Htotal = H1 + H2 often used to calculate H for one step, knowing H for all steps and ...
... If 72.0 grams of H2O are formed from the reaction, how much heat was released? = 73.9 kJ 3. Hess' Law: The value of H for a reaction is the same whether it occurs directly or in a series of steps (state function). Htotal = H1 + H2 often used to calculate H for one step, knowing H for all steps and ...
Lecture 8
... Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) From the Second Law it can be shown that ΔG is always negative for a feasible reaction at constant temperature and pressure and is zero at equilibrium. ΔS and ΔG for reactions do not depend on the reaction pathway. They depend even more strongly than ΔH on concentratio ...
... Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) From the Second Law it can be shown that ΔG is always negative for a feasible reaction at constant temperature and pressure and is zero at equilibrium. ΔS and ΔG for reactions do not depend on the reaction pathway. They depend even more strongly than ΔH on concentratio ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... the gas phase, whereas most organic reactions occur in a liquid solvent where solvation energy contributes to the overall enthalpy of a reaction. • Bond dissociation energies are imperfect indicators of energy changes in a reaction; however, useful approximations of the energy changes in a reaction ...
... the gas phase, whereas most organic reactions occur in a liquid solvent where solvation energy contributes to the overall enthalpy of a reaction. • Bond dissociation energies are imperfect indicators of energy changes in a reaction; however, useful approximations of the energy changes in a reaction ...
C1_5_products_from_oils_crossword
... 9. The reaction in which the enzymes in yeast turn glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. 10. An alkene with the formula C3H6. 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something t ...
... 9. The reaction in which the enzymes in yeast turn glucose into ethanol and carbon dioxide. 10. An alkene with the formula C3H6. 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something t ...
chemistry 2 - waiukucollegescience
... In order to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propene a student said it was necessary to use bromine water rather than acidified potassium permanganate. Discuss this statement. ...
... In order to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propene a student said it was necessary to use bromine water rather than acidified potassium permanganate. Discuss this statement. ...