HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Investigate variables that affect the rate of a reaction (nature of reactants, concentration, surface area, and temperature Explain that nature of reactants can refer to their complexity and the number of bonds that must be broken and reformed in the course of reaction Explain collision theory and r ...
... Investigate variables that affect the rate of a reaction (nature of reactants, concentration, surface area, and temperature Explain that nature of reactants can refer to their complexity and the number of bonds that must be broken and reformed in the course of reaction Explain collision theory and r ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
enthalpy worksheet
... Almost all chemical and physical reactions involve energy (usually in the form of heat) being released or added. An exothermic change is a reaction that releases energy. An endothermic change is one in which the energy must be added for the reaction to occur. For exothermic reactions, energy can be ...
... Almost all chemical and physical reactions involve energy (usually in the form of heat) being released or added. An exothermic change is a reaction that releases energy. An endothermic change is one in which the energy must be added for the reaction to occur. For exothermic reactions, energy can be ...
Key to Exam 3
... 3. (20 pts) Answer the following question in reference to the reaction energy diagrams below. The labeled points on the reaction energy diagrams are either energies or chemical species, depending on the sentence. G ...
... 3. (20 pts) Answer the following question in reference to the reaction energy diagrams below. The labeled points on the reaction energy diagrams are either energies or chemical species, depending on the sentence. G ...
Exam 2 Review A
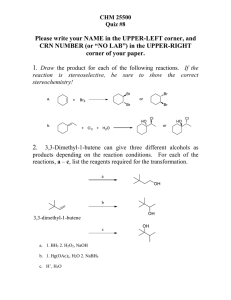
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
Exam 2 Review A
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
... You should be familiar with the detailed mechanisms of the SN1 and SN2 reactions. Rate determining steps are important to consider, as are the transition states associated with these steps. Compare and contrast the SN1 and SN2 reactions with respect to kinetics, nature of the electrophile [structure ...
$doc.title
... http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
... http://www.chem.wisc.edu/areas/clc (Resource page) Reactions of Alcohols #8: Reaction of a 1° Alcohol with Hydrogen Halides ...
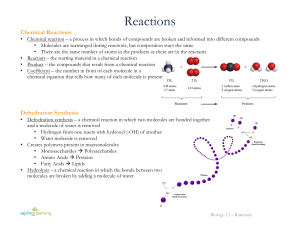
Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
... Energy must be added to break bonds that hold the reactant molecules together. This is called activation energy (Ae). This amount of energy is what “activates” or gets the reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atom ...
... Energy must be added to break bonds that hold the reactant molecules together. This is called activation energy (Ae). This amount of energy is what “activates” or gets the reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atom ...
Too Hot to Handle Lab
... (endothermic), and where heat is lost (exothermic). Background: A Chemical reaction in which energy is released is an exothermic reaction. The word exothermic comes from the root – “thermic”, which refers to heat, and the prefix – “exo” which means out of. Heat comes out of, or is released from, a r ...
... (endothermic), and where heat is lost (exothermic). Background: A Chemical reaction in which energy is released is an exothermic reaction. The word exothermic comes from the root – “thermic”, which refers to heat, and the prefix – “exo” which means out of. Heat comes out of, or is released from, a r ...
Johnson Group Research
... cleavage and functionalization of carbon-carbon bonds. While carbon-carbon single bonds are inert under a vast majority of standard reaction conditions, certain transition metal complexes promote the activation of these bonds. Research in the Johnson group will follow several avenues of study, inclu ...
... cleavage and functionalization of carbon-carbon bonds. While carbon-carbon single bonds are inert under a vast majority of standard reaction conditions, certain transition metal complexes promote the activation of these bonds. Research in the Johnson group will follow several avenues of study, inclu ...