HW Set IV– page 1 of 6 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions
... PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 8-58 A factory worker accidentally releases a 180 kg crate that was being held at rest at the top of a 3.7 m-long-ramp inclined at 39° to the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ramp, and between the crate and the horizontal f ...
... PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 8-58 A factory worker accidentally releases a 180 kg crate that was being held at rest at the top of a 3.7 m-long-ramp inclined at 39° to the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ramp, and between the crate and the horizontal f ...
Widely separated binary systems of very low mass stars Phan Bao
... Example: A block of mass 1.0 kg is released from rest and slides down a rough track of radius R = 1.0 m (Figure 1). If the speed of the block at the bottom of the track is 3.0 m/s, what is the work done by the frictional force acting on the block? (Final exam, June 2014) ...
... Example: A block of mass 1.0 kg is released from rest and slides down a rough track of radius R = 1.0 m (Figure 1). If the speed of the block at the bottom of the track is 3.0 m/s, what is the work done by the frictional force acting on the block? (Final exam, June 2014) ...
Sample Papers - SA2 (Science Class 9 )
... Weight of the boy, mg = 50 kg x 10 ms-2 = 500N Height of the staircase, H = 45x15/100 m = 6.75m Time taken to climb, t = 9S Power, P = Work done /time taken ...
... Weight of the boy, mg = 50 kg x 10 ms-2 = 500N Height of the staircase, H = 45x15/100 m = 6.75m Time taken to climb, t = 9S Power, P = Work done /time taken ...
Thermodynamics and the aims of statistical mechanics
... An absolutely central concept is thermal equilibrium. Equilibrium is any state a system is in once it has stopped exchanging heat with its surroundings; or, if it has no surroundings (= is isolated), once it has settled down to a macroscopically unchanging state. (Feynman: “equilibrium is when all t ...
... An absolutely central concept is thermal equilibrium. Equilibrium is any state a system is in once it has stopped exchanging heat with its surroundings; or, if it has no surroundings (= is isolated), once it has settled down to a macroscopically unchanging state. (Feynman: “equilibrium is when all t ...
Document
... density at s.t.p. is 1.0x10-2gm/litreoC. Calculate the value of its specific heat at constant volume in joules/kg oC. (4mks) Explain why the difference between the principal specific heats of a solid is small. (1mk) Question 7. (a)(i). What is meant a black body (1mk) (ii). State the relation betwee ...
... density at s.t.p. is 1.0x10-2gm/litreoC. Calculate the value of its specific heat at constant volume in joules/kg oC. (4mks) Explain why the difference between the principal specific heats of a solid is small. (1mk) Question 7. (a)(i). What is meant a black body (1mk) (ii). State the relation betwee ...
The Chemical Bond
... where Q1 and Q2 are the ionic charges, r is their separation, and a and b are empirical constants. To a good approximation, a is the same for all molecules and is given by a = 0.30 × 10-8 cm. Assuming this function is satisfactory for KCl, a. evaluate the constant b for KCl so that the minimum in th ...
... where Q1 and Q2 are the ionic charges, r is their separation, and a and b are empirical constants. To a good approximation, a is the same for all molecules and is given by a = 0.30 × 10-8 cm. Assuming this function is satisfactory for KCl, a. evaluate the constant b for KCl so that the minimum in th ...
AS Revision Flash Cards File
... mass, distance, time, speed, density, energy, power, temperature, charge, resistance, p.d. A vector quantity has magnitude and direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, acceleration, force, weight, gravitational field strength, current. The resultant (or effective combination) of two vectors ...
... mass, distance, time, speed, density, energy, power, temperature, charge, resistance, p.d. A vector quantity has magnitude and direction. Examples: velocity, displacement, acceleration, force, weight, gravitational field strength, current. The resultant (or effective combination) of two vectors ...
Syllabus - Tor Vergata International Medical School
... Medical Physics Syllabus Nicola Toschi Faculty of Medicine, Building H Office Hours: Tue 13.00-14.00 (Oct-Feb) [email protected] Textbook: Douglas C. Giancoli “PHYSICS: Principles with Applications” Sixth edition, Pearson Education. Inc, ISBN 0-13-060620-0 Notes: NOTE1: Paragraphs in Italics ar ...
... Medical Physics Syllabus Nicola Toschi Faculty of Medicine, Building H Office Hours: Tue 13.00-14.00 (Oct-Feb) [email protected] Textbook: Douglas C. Giancoli “PHYSICS: Principles with Applications” Sixth edition, Pearson Education. Inc, ISBN 0-13-060620-0 Notes: NOTE1: Paragraphs in Italics ar ...
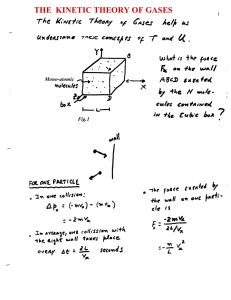
The kinetic theory of the gases
... reached when the pressure at both side is the same. According to expression (1), P = (2/3) (N/V) <½ mv2>; thus a condition of MECHANICAL EQUILIBRIUM, would imply, (2/3) (N1/V1) <½ m1v12> = (2/3) (N2/V2) <½ m2v22> It turns out, as argued in the Feynman lectures Vol-1, chapter 39), this condition is n ...
... reached when the pressure at both side is the same. According to expression (1), P = (2/3) (N/V) <½ mv2>; thus a condition of MECHANICAL EQUILIBRIUM, would imply, (2/3) (N1/V1) <½ m1v12> = (2/3) (N2/V2) <½ m2v22> It turns out, as argued in the Feynman lectures Vol-1, chapter 39), this condition is n ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... temperature while holding volume or pressure constant. • Then calculations can be made as to the work performed and/or heat generated. ...
... temperature while holding volume or pressure constant. • Then calculations can be made as to the work performed and/or heat generated. ...
topic 1 sol review homework
... 2. The mass of the calcium atom is due primarily to the mass of its a) protons only b) neutrons only c) protons and neutrons d) protons and electrons 3. Which structure represents a nonpolar molecule? a) H – Cl b) H – H c) H – :O: – H d) NaBr 4. In an aqueous solution, which substance yields hydroge ...
... 2. The mass of the calcium atom is due primarily to the mass of its a) protons only b) neutrons only c) protons and neutrons d) protons and electrons 3. Which structure represents a nonpolar molecule? a) H – Cl b) H – H c) H – :O: – H d) NaBr 4. In an aqueous solution, which substance yields hydroge ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.