p250c13
... The Second Law of Thermodynamics •Heat cannot, by itself, pass from a cooler to a warmer body •It is impossible for any system to undergo a cyclic process whose sole result is the absorption of heat from a single reservoir at a single temperature and the performance of an equivalent amount of work. ...
... The Second Law of Thermodynamics •Heat cannot, by itself, pass from a cooler to a warmer body •It is impossible for any system to undergo a cyclic process whose sole result is the absorption of heat from a single reservoir at a single temperature and the performance of an equivalent amount of work. ...
Energy and Chemical Reactions Characterizing Energy:
... • At a given instant, a system has a fixed total energy: U= • We tend to focus on energy changes (Why?): – When working with energy changes, keep in mind that energy can be transferred in two ways: as heat, and as work U = – To simplify matters, we typically design experiments so that the work cont ...
... • At a given instant, a system has a fixed total energy: U= • We tend to focus on energy changes (Why?): – When working with energy changes, keep in mind that energy can be transferred in two ways: as heat, and as work U = – To simplify matters, we typically design experiments so that the work cont ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
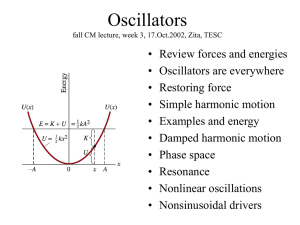
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
... First, watch simulation and predict behavior for various b. Then, model damping force proportional to velocity, Fd = - c v: S F = ma - k x - cx’ = m x” Simplify equation: multiply by m, insert w=k/m and g = c/(2m): Guess a solution: x = C e lt Sub in guessed x and solve resultant “characteristic eq ...
9. Entropy 2nd and 3rd laws/ Thermodynamic processes / Droplet
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
... 9.1 Entropy in second and third laws of thermodynamics (2pts) 1. Explain the statistical definition of entropy (4pts) 2. Consider a “thermodynamic system” of two dices and let the energy of a certain throw (state of the system) be the sum of the two values of the dices. Calculate the respective entr ...
Preparatory School to the Winter Collegue on Optics: Optical
... Chemical bond acts like a spring and can display SHM Have an effective spring constant k for the bond involved and effective mass meff Angular frequency ...
... Chemical bond acts like a spring and can display SHM Have an effective spring constant k for the bond involved and effective mass meff Angular frequency ...
Relativistic Dynamics Dennis V. Perepelitsa
... The familiar Newtonian relationships between the kinetic energy, momentum and velocity of a particle break down as its speed approaches that of light. Instead, a new set of relativistic relations must be brought to bear. By determining these relations at high speeds, we can demonstrate the correctne ...
... The familiar Newtonian relationships between the kinetic energy, momentum and velocity of a particle break down as its speed approaches that of light. Instead, a new set of relativistic relations must be brought to bear. By determining these relations at high speeds, we can demonstrate the correctne ...
BJ26404407
... band gaps . Because of these properties III-nitrides are used in the blue and UV light emitting diodes (LED’s) ,blue lasers ,UV detectors and high power , high temperature field effect transistors [2,3,4,5,6]. Aluminum nitride is a very interesting material because of it’s wide band gap (6.3 ev), hi ...
... band gaps . Because of these properties III-nitrides are used in the blue and UV light emitting diodes (LED’s) ,blue lasers ,UV detectors and high power , high temperature field effect transistors [2,3,4,5,6]. Aluminum nitride is a very interesting material because of it’s wide band gap (6.3 ev), hi ...
File
... Jose measured out 1 quart of distilled water and added to it 2 tablespoons of salt. He then brought the water to a boil and measured its maximum temperature. Jose ran two more trials using 2 tablespoons of salt. He then ran 3 trials each with 4 tablespoons of salt and 6 tablespoon of salt. For each ...
... Jose measured out 1 quart of distilled water and added to it 2 tablespoons of salt. He then brought the water to a boil and measured its maximum temperature. Jose ran two more trials using 2 tablespoons of salt. He then ran 3 trials each with 4 tablespoons of salt and 6 tablespoon of salt. For each ...
Mechanical Engineering
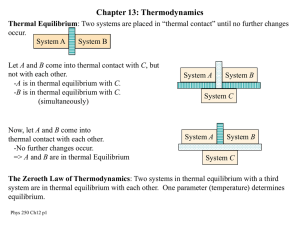
... The concept of temperature is fundamental and significant to thermodynamics. We know that a body at high temperature will transfer energy to one at lower temperature. Consider two bodies with different temperatures in contact with each other. Net energy transfer will be from the hotter body to the c ...
... The concept of temperature is fundamental and significant to thermodynamics. We know that a body at high temperature will transfer energy to one at lower temperature. Consider two bodies with different temperatures in contact with each other. Net energy transfer will be from the hotter body to the c ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.