Energy & Power
... • During every cycle, heat QH is extracted from a reservoir at temperature TH • A portion is diverted to useful work W and the rest is discharged as heat Qc to a reservoir at temperature Tc • Because an engine operates in a cycle, U (gas) returns to its original value at the end of the cycle (ΔU = 0 ...
... • During every cycle, heat QH is extracted from a reservoir at temperature TH • A portion is diverted to useful work W and the rest is discharged as heat Qc to a reservoir at temperature Tc • Because an engine operates in a cycle, U (gas) returns to its original value at the end of the cycle (ΔU = 0 ...
PPT version
... Study of temperature, heat and related macroscopic properties of objects and matter. Specifically macroscopic properties: temperature, pressure, heat, internal energy… Thermodynamic equilibrium: two systems are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other, when they are in thermal contact and no cha ...
... Study of temperature, heat and related macroscopic properties of objects and matter. Specifically macroscopic properties: temperature, pressure, heat, internal energy… Thermodynamic equilibrium: two systems are in thermodynamic equilibrium with each other, when they are in thermal contact and no cha ...
Work and Kinetic Energy Serway (7.1 – 7.3)
... particle is equal to the increase in its kinetic energy. Proof: from Newton’s Second Law, and the definition of Work. ...
... particle is equal to the increase in its kinetic energy. Proof: from Newton’s Second Law, and the definition of Work. ...
Atomic Theory - Aurora City Schools
... – React violently with water – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QSZ-3wScePM ...
... – React violently with water – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QSZ-3wScePM ...
Topic 4: Materials - Education Umbrella
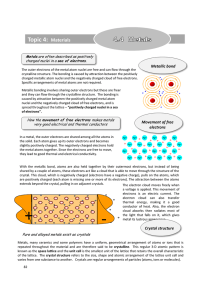
... Pure and alloyed metals exist as crystals Metals, many ceramics and some polymers have a uniform, geometrical arrangement of atoms or ions that is repeated throughout the material and are therefore said to be crystalline. This regular 3‐D atomic pattern is known as the space lattice and the unit cel ...
... Pure and alloyed metals exist as crystals Metals, many ceramics and some polymers have a uniform, geometrical arrangement of atoms or ions that is repeated throughout the material and are therefore said to be crystalline. This regular 3‐D atomic pattern is known as the space lattice and the unit cel ...
07._ConservationOfEnergy
... If it takes the same amount of work to push a trunk across a rough floor as it does to lift a weight to the same distance straight upward. How do the amounts of work compare if the trunk & weight are moved along curved paths between the same starting & end points? ...
... If it takes the same amount of work to push a trunk across a rough floor as it does to lift a weight to the same distance straight upward. How do the amounts of work compare if the trunk & weight are moved along curved paths between the same starting & end points? ...
energy - New Haven Science
... ---A flat container holds 200 g of water. Over a 10 min period, 1.5 g of water evaporates from the surface. What is the approximate temperature change of the remaining 198.5 g of water? ----If 4 kilograms of -2 degree ice are dropped from 50, 000 meters, hits the ground and changes entirely to water ...
... ---A flat container holds 200 g of water. Over a 10 min period, 1.5 g of water evaporates from the surface. What is the approximate temperature change of the remaining 198.5 g of water? ----If 4 kilograms of -2 degree ice are dropped from 50, 000 meters, hits the ground and changes entirely to water ...
Thermal Physics Tutorial
... an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass of height of 10.3 m will be needed. There is not likely to have such a tall glass. In fact, the bubble in a beer act as a nucleation site for CO2 molecules, so as the bubb ...
... an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass of height of 10.3 m will be needed. There is not likely to have such a tall glass. In fact, the bubble in a beer act as a nucleation site for CO2 molecules, so as the bubb ...
Chapter 7:The Quantum-Mechanical Model of
... Weakness: Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. It is impossible to determine both the momentum and position of an electron simultaneously; x . (mv) ≥ h/(4). Use 90% probability maps (orbitals not orbits) volume of space. 1. Electrons have quantized energy states (orbitals). 2. Electrons absorb or ...
... Weakness: Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. It is impossible to determine both the momentum and position of an electron simultaneously; x . (mv) ≥ h/(4). Use 90% probability maps (orbitals not orbits) volume of space. 1. Electrons have quantized energy states (orbitals). 2. Electrons absorb or ...
Let’s talk Chemistry!
... Each molecule of hydrochloric acid, HCl, contains one atom of hydrogen and One atom of chlorine An ionic compound is made of _____. Give an example of a common ionic compound. Ions; NaCl (table salt) ...
... Each molecule of hydrochloric acid, HCl, contains one atom of hydrogen and One atom of chlorine An ionic compound is made of _____. Give an example of a common ionic compound. Ions; NaCl (table salt) ...
10-4 Enthalpy (Section 10.6)
... the potential energy stored in the bonds of molecules. Chemists use the change in enthalpy ∆H to measure the heat content of a system (when the pressure is constant). • We define the “system” to be the chemicals and everything else is termed the “surroundings”. • Applying the First Law of Thermodyna ...
... the potential energy stored in the bonds of molecules. Chemists use the change in enthalpy ∆H to measure the heat content of a system (when the pressure is constant). • We define the “system” to be the chemicals and everything else is termed the “surroundings”. • Applying the First Law of Thermodyna ...
Chapter 11 – Work In the summary for Chapter 10
... = ‐mg. And for a spring, US = kx2/2 and Fx = ‐ dUS/dx = ‐ kx. In situations where the mechanical energy is not conserved, the difference between the initial and final values of the mechanical energy gives the amount of energy converted to other forms of energy. All of the above applies to the o ...
... = ‐mg. And for a spring, US = kx2/2 and Fx = ‐ dUS/dx = ‐ kx. In situations where the mechanical energy is not conserved, the difference between the initial and final values of the mechanical energy gives the amount of energy converted to other forms of energy. All of the above applies to the o ...
Chapter 6 ppt
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the science of
... Thermochemistry is the science of relationships between heat and energy, which is one area of thermodynamics - the study of energy and its transformations. ...
... Thermochemistry is the science of relationships between heat and energy, which is one area of thermodynamics - the study of energy and its transformations. ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.