PSY 301 – Summer 2004
... Introduction to Psychology Class 8: Neuroscience 1 Myers: 38-51 June 22, 2006 ...
... Introduction to Psychology Class 8: Neuroscience 1 Myers: 38-51 June 22, 2006 ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
... Brain (Neural) Plasticity • The brain’s ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Severed neurons do not usually regenerate • Instead, the brain’s neural tissue can reorganize itself • One brain area can take on functions not normally “assigned” to that area • Brain’s are most plastic w ...
homework_files\2016 Semester 1 Exam Review
... Social-Cultural, Biological, Humanistic, Psychoanalytic Perspectives Main Contributors/Contributions: James, Wundt, Tichener, Watson, Pavlov, Skinner, Maslow Chapter 2 Research Methods Types of research methods: naturalistic, case study, survey, correlational, experiment Downfalls and Benefits ...
... Social-Cultural, Biological, Humanistic, Psychoanalytic Perspectives Main Contributors/Contributions: James, Wundt, Tichener, Watson, Pavlov, Skinner, Maslow Chapter 2 Research Methods Types of research methods: naturalistic, case study, survey, correlational, experiment Downfalls and Benefits ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Personality, judgment, reasoning, problem solving, rational decision making, ▫ Logic and understanding of consequences ▫ Governs impulsivity, aggression, ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Personality, judgment, reasoning, problem solving, rational decision making, ▫ Logic and understanding of consequences ▫ Governs impulsivity, aggression, ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
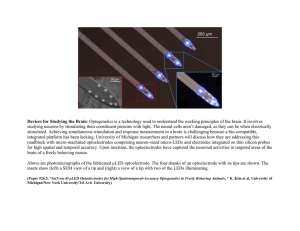
26-5 Devices for Studying the Brain
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
Psychology 101 Exam 1
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
... c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcu ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans use changes in blood flow to measure brain activity ...
... Positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans use changes in blood flow to measure brain activity ...
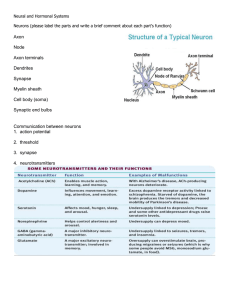
Neurons
... A neuron functions by generating an electric charge in the cell body that propagates down the axon. This is called an action potential. When a neuron generates an action potential, we say that that neuron fires. Action potentials are always the same magnitude. Neurons communicate with each other via ...
... A neuron functions by generating an electric charge in the cell body that propagates down the axon. This is called an action potential. When a neuron generates an action potential, we say that that neuron fires. Action potentials are always the same magnitude. Neurons communicate with each other via ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
Assignment 2 - Gordon State College
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
Neurochemistry of executive functions
... Neural bases of set-shifting deficits in Parkinson’s disease, O. Monchi et al., The journal of neuroscience, 2004 ...
... Neural bases of set-shifting deficits in Parkinson’s disease, O. Monchi et al., The journal of neuroscience, 2004 ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
Psychology - Kyschools.us
... Characteristics and origins of abnormal behavior Methods used in exploring abnormal behavior Major categories of abnormal behavior Impact of mental disorders ...
... Characteristics and origins of abnormal behavior Methods used in exploring abnormal behavior Major categories of abnormal behavior Impact of mental disorders ...
Course: AP Psychology
... The AP Psychology course is designed to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of human being and other animals. Students are exposed to the psychological facts, principles, and phenomena associated with each of the major subfields within psych ...
... The AP Psychology course is designed to introduce students to the systematic and scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of human being and other animals. Students are exposed to the psychological facts, principles, and phenomena associated with each of the major subfields within psych ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) childhood memories. d) genetic predispositions. 3. Cognitive neuroscience studies relationships between: a) childhood memories and psychological disorder ...
... 2. Humanistic psychologists focused attention on the importance of people's: a) potential for healthy growth. b) unconscious thought processes. c) childhood memories. d) genetic predispositions. 3. Cognitive neuroscience studies relationships between: a) childhood memories and psychological disorder ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... ____ 14. Direct stimulation of the motor cortex would be most likely to result in a. movement of the mouth and lips. b. feelings of anger. c. acceleration of heartbeat. d. intense pain. e. a sensation of being touched on the arm. ____ 15. Our lips are more sensitive than our knees to sensations of t ...
... ____ 14. Direct stimulation of the motor cortex would be most likely to result in a. movement of the mouth and lips. b. feelings of anger. c. acceleration of heartbeat. d. intense pain. e. a sensation of being touched on the arm. ____ 15. Our lips are more sensitive than our knees to sensations of t ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... interconnections between the different elements. The focus of the Brumberg’s lab research is to characterize development and the neurons of the rodent barrel cortex with a dual emphasis on the interactions between the sensory and motor systems that govern the animals whisking behavior and the role t ...
... interconnections between the different elements. The focus of the Brumberg’s lab research is to characterize development and the neurons of the rodent barrel cortex with a dual emphasis on the interactions between the sensory and motor systems that govern the animals whisking behavior and the role t ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Intensification of sensations and experiences * Dream like state * Mescaline, better known as peyote, is derived from a Chihuahan cactus found in Texas and Mexico ...
... * Intensification of sensations and experiences * Dream like state * Mescaline, better known as peyote, is derived from a Chihuahan cactus found in Texas and Mexico ...
Assignment 1 - Gordon State College
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...
... 31. The ___________________ is known as the “brain’s sensory switchboard” because information from all the senses except smell goes through here to be relayed to the appropriate part of the brain. 32. In the limbic system, the _______________________ plays a large role in the ability to form and pro ...