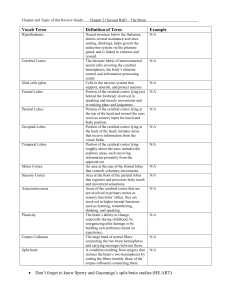
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
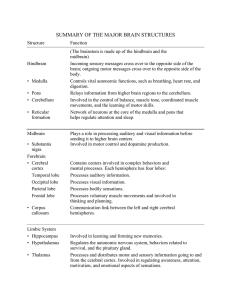
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
... Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays information from higher brain regions to the cerebellum. Involved in t ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... White matter is made of myelinated axons Brain stem: PONS, MIDBRAIN, and MEDULLA OBLONGATA. ...
... White matter is made of myelinated axons Brain stem: PONS, MIDBRAIN, and MEDULLA OBLONGATA. ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
Myers Module Six
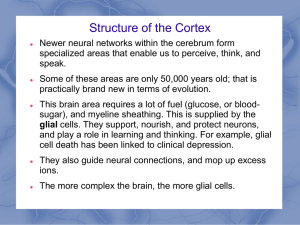
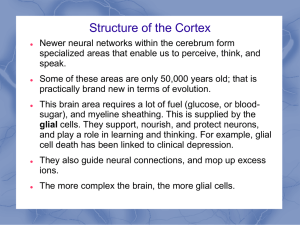
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
... Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They support, nourish, and protect neurons, and play a role in learning and ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
... 1. In the beginning of the video, Philip Zimbardo compared our brain to a _____________. 2. The human brain houses approximately _____________ number of brain cells. 3. Neurons and glia are designed to do 3 things: a. ___________________________________________________________ b. ___________________ ...
Reinforcement learning and human behavior
... 2. organism queries stored value of state X; 3. organism updates stored value of state X based on current reward information; 4. organism selects action based on stored policy 5. organism transitions to state Y and receives reward information. ...
... 2. organism queries stored value of state X; 3. organism updates stored value of state X based on current reward information; 4. organism selects action based on stored policy 5. organism transitions to state Y and receives reward information. ...
Abstract - University of Colorado Boulder
... considerations could be the beliefs, feelings, or actions of a particular individual, or more broadly, codes of conduct informed by cultural customs and social norms. The goal of my research program is to understand how we integrate this complex social information with more self-interested value sig ...
... considerations could be the beliefs, feelings, or actions of a particular individual, or more broadly, codes of conduct informed by cultural customs and social norms. The goal of my research program is to understand how we integrate this complex social information with more self-interested value sig ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - "Gateway to Memory" - involved in storing new information for future use. - e.g., A man by the name of Clive Wearing is a fascinating example of what can happen to a person when their hippocampus is damaged due to a disease. - Clive retained his old memories of his wife and music, but he could not ...
... - "Gateway to Memory" - involved in storing new information for future use. - e.g., A man by the name of Clive Wearing is a fascinating example of what can happen to a person when their hippocampus is damaged due to a disease. - Clive retained his old memories of his wife and music, but he could not ...
Learning about Learning - by Directly Driving Networks of Neurons
... Associate Professor of Bioengineering University of Pittsburgh New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To ...
... Associate Professor of Bioengineering University of Pittsburgh New behaviors require new patterns of neural activity among the population of neurons that control behavior. How can the brain find a pattern of activity appropriate for the desired behavior? Why does that learning process take time? To ...
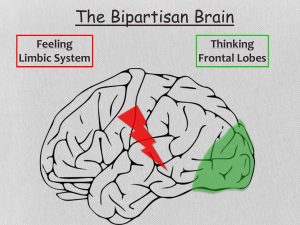
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
... used only 10% of our brains. Surgically lesioned animals and brain-damaged humans bear witness that association areas are not dormant. Figure 6.8: The Strange Case of Phineas Gage Parietal association areas enable mathematical and ...
... used only 10% of our brains. Surgically lesioned animals and brain-damaged humans bear witness that association areas are not dormant. Figure 6.8: The Strange Case of Phineas Gage Parietal association areas enable mathematical and ...
AP Psych Lesson Plan October 3-7
... Recount historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research (e. g., case studies, split-brain research, imaging techniques). Discuss psychology’s abiding interest in how heredity, environment, and evolution work together to shape behavior. Predict how traits an ...
... Recount historic and contemporary research strategies and technologies that support research (e. g., case studies, split-brain research, imaging techniques). Discuss psychology’s abiding interest in how heredity, environment, and evolution work together to shape behavior. Predict how traits an ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... - Types of descriptive research: case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, correlation - The major psychological perspectives (to explain human behavior): o Biological o Cognitive o Behavioral o Socio-cultural o Psychoanalytic/Psychody namic The Scientific Method - Understand the difference b ...
... - Types of descriptive research: case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, correlation - The major psychological perspectives (to explain human behavior): o Biological o Cognitive o Behavioral o Socio-cultural o Psychoanalytic/Psychody namic The Scientific Method - Understand the difference b ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... - Types of descriptive research: case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, correlation - The major psychological perspectives (to explain human behavior): o Biological o Cognitive o Behavioral o Socio-cultural o Psychoanalytic/Psychody namic The Scientific Method - Understand the difference b ...
... - Types of descriptive research: case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, correlation - The major psychological perspectives (to explain human behavior): o Biological o Cognitive o Behavioral o Socio-cultural o Psychoanalytic/Psychody namic The Scientific Method - Understand the difference b ...
Bayesian Curve Fitting and Neuron Firing Patterns
... Joint with the Committee on Computational Neuroscience. ...
... Joint with the Committee on Computational Neuroscience. ...
the central nervous system chapter 2 holiday
... 23. Were lobotomies ethical? Why or why not? You must refer to the guidelines mentioned in question 19. ...
... 23. Were lobotomies ethical? Why or why not? You must refer to the guidelines mentioned in question 19. ...
The Promise and Peril of Tomorrow`s Neuroscience
... Synopsis of the July 2005 Futurist Book Group meeting; summarized by Ken Harris The chapter book group discussed The Future of the Brain by Steven Rose at its July 6 meeting. Rose is a Professor of Biology and Director of the Brain and Behavior Research Group at the Open University in the UK and a V ...
... Synopsis of the July 2005 Futurist Book Group meeting; summarized by Ken Harris The chapter book group discussed The Future of the Brain by Steven Rose at its July 6 meeting. Rose is a Professor of Biology and Director of the Brain and Behavior Research Group at the Open University in the UK and a V ...
Dynamic Decision Making in Complex Task Environments
... • Aim 1: Investigate dynamics of decision making in classical tasks via – Theory and Modeling – Primate Neurophysiology – Human Cognitive Neuroscience ...
... • Aim 1: Investigate dynamics of decision making in classical tasks via – Theory and Modeling – Primate Neurophysiology – Human Cognitive Neuroscience ...