Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Chapter 3
... directly with each other. Instead, they rely on a middleman. ◦ Interneurons, which make up the majority of our neurons, relay messages from sensory neurons to other interneurons or motor neurons in complex pathways. ...
... directly with each other. Instead, they rely on a middleman. ◦ Interneurons, which make up the majority of our neurons, relay messages from sensory neurons to other interneurons or motor neurons in complex pathways. ...
Chapter 3
... Individual-Level Analysis • Begins with view that the root it is people who make policy • Involves understanding the human-decision marking process (psychology) • Groupthink, Individual decisions, etc. • Political Science and Psychology and Sociology ...
... Individual-Level Analysis • Begins with view that the root it is people who make policy • Involves understanding the human-decision marking process (psychology) • Groupthink, Individual decisions, etc. • Political Science and Psychology and Sociology ...
a psychology timeline
... • The nose smells and the brain thinks, but how do these two function together to provide the process of living. • Focus on moment to moment streams of consciousness and exploration of emotions, memories, will power and habits • Known for his outspoken views on women in the field and his writings ...
... • The nose smells and the brain thinks, but how do these two function together to provide the process of living. • Focus on moment to moment streams of consciousness and exploration of emotions, memories, will power and habits • Known for his outspoken views on women in the field and his writings ...
The Nervous System
... other neurons and send them to the cell body O 3. Axon – long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites O *Myelin sheath – insulates and protects the axon for some neurons O Multiple sclerosis – myelin sheath is destroyed ...
... other neurons and send them to the cell body O 3. Axon – long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrites O *Myelin sheath – insulates and protects the axon for some neurons O Multiple sclerosis – myelin sheath is destroyed ...
Three Controversial Hypotheses Concerning Computation in the
... Koechlin et al (2000) claim the same basic organizational principles apply to both motor and executive control. The latter term they reserve to mean the temporal and hierarchical organization of action or thought in relation to internal goals. Koechlin and Jubault (2006) suggest the posterior portio ...
... Koechlin et al (2000) claim the same basic organizational principles apply to both motor and executive control. The latter term they reserve to mean the temporal and hierarchical organization of action or thought in relation to internal goals. Koechlin and Jubault (2006) suggest the posterior portio ...
Forebrain
... relatively small resulting in a poorer sense of smell. • Even so, olfaction can have significant impact on behavior in humans. • Primary olfactory cortex is unique among sensory systems in that it receives direct input from secondary sensory neurons without an intervening thalamic relay. ...
... relatively small resulting in a poorer sense of smell. • Even so, olfaction can have significant impact on behavior in humans. • Primary olfactory cortex is unique among sensory systems in that it receives direct input from secondary sensory neurons without an intervening thalamic relay. ...
File
... that reinforcement was necessary for animals to learn such tasks. Other experiments showed that latent learning can happen in shorter durations of time (3–7 days). ...
... that reinforcement was necessary for animals to learn such tasks. Other experiments showed that latent learning can happen in shorter durations of time (3–7 days). ...
Animal Behavior
... 1. The Stickleback fish is an example of … 2. What are the 2 types of associative learning? ...
... 1. The Stickleback fish is an example of … 2. What are the 2 types of associative learning? ...
The Nervous System
... • Neurons must pick up stimuli, transform them into nerve impulses and then transmit these impulses on to the next neuron • A nerve impulse is therefore any electric signal transmitted by a neuron • As signals move from one neuron to another, they must cross the synapse. This is the transition zone ...
... • Neurons must pick up stimuli, transform them into nerve impulses and then transmit these impulses on to the next neuron • A nerve impulse is therefore any electric signal transmitted by a neuron • As signals move from one neuron to another, they must cross the synapse. This is the transition zone ...
Brain Structure and Function
... Primary motor cortex Pre-motor cortex Broca’s Area- Motor Production of speech ...
... Primary motor cortex Pre-motor cortex Broca’s Area- Motor Production of speech ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... When a baby is born he has billions of brain cells, and that many of these brain cells are not connected. "They only get connected through experience, says Carson, "so when you talk to your baby, cuddle it, and handle it, these experiences will start to make connections. If they have a variety of ...
... When a baby is born he has billions of brain cells, and that many of these brain cells are not connected. "They only get connected through experience, says Carson, "so when you talk to your baby, cuddle it, and handle it, these experiences will start to make connections. If they have a variety of ...
feedback-poster
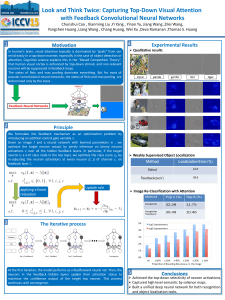
... In human’s brain, visual attention typically is dominated by “goals” from our mind easily in a top-down manner, especially in the case of object detection or attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and n ...
... In human’s brain, visual attention typically is dominated by “goals” from our mind easily in a top-down manner, especially in the case of object detection or attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and n ...
Brain Anatomy - Southwest High School
... Endocrine system (hormones) Some other organic problem. (Cancer or other disorder…) ...
... Endocrine system (hormones) Some other organic problem. (Cancer or other disorder…) ...
Central Nervous System
... equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere • Receives information from all sensory association areas…This area integrates sensory information ( especially, visual and auditory ) into a comprehensive understanding, then sends the ...
... equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere • Receives information from all sensory association areas…This area integrates sensory information ( especially, visual and auditory ) into a comprehensive understanding, then sends the ...
Chapter 2 An Introduction to ABA Concepts: Terminology, Principles
... 18. “Oh. That’s just a Pavlovian response,” your friend comments when you say you hate ...
... 18. “Oh. That’s just a Pavlovian response,” your friend comments when you say you hate ...
File
... • Focus: How healthy people strive to reach their full potential • Behavior is explained as being motivated by satisfying needs (safety, hunger, thirst, etc.), with the goal of reaching one’s full potential once basic needs are met. • Developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – behavior reflects i ...
... • Focus: How healthy people strive to reach their full potential • Behavior is explained as being motivated by satisfying needs (safety, hunger, thirst, etc.), with the goal of reaching one’s full potential once basic needs are met. • Developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – behavior reflects i ...
acetylcholine
... Parkinson’s Disease • The substantia nigra, which connects with the striatum (caudate nucleus and globus pallidus), contains black pigmented cells and, in normal individuals, produces a number of chemical transmitters, the most important of which is dopamine. Transmitters are chemicals that transmi ...
... Parkinson’s Disease • The substantia nigra, which connects with the striatum (caudate nucleus and globus pallidus), contains black pigmented cells and, in normal individuals, produces a number of chemical transmitters, the most important of which is dopamine. Transmitters are chemicals that transmi ...
Behavior - Catawba County Schools
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
Primary motor cortex
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
... when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially active when subjects hear words through ear-phones, as seen in the PET scan on the right. To create thes ...
Person Class Notes Behaviorism:
... - Parent: the shoulds, what is right and wrong; how something should be done. (the 2nd part to develop) - The Critical P: the self-critical process - The Nurturing P: it's ok... - Adult: thinking, solving problems, deciding what is the better thing to do in given circumstances; rational. - mediates ...
... - Parent: the shoulds, what is right and wrong; how something should be done. (the 2nd part to develop) - The Critical P: the self-critical process - The Nurturing P: it's ok... - Adult: thinking, solving problems, deciding what is the better thing to do in given circumstances; rational. - mediates ...
A general mechanism for perceptual decision
... We based our hypotheses on results from single-unit recording studies in monkeys, which have shown that neuronal activity in areas involved in decision-making gradually increases and then remains elevated until a response is given, with the rate of increase being slower during more difficult trials1 ...
... We based our hypotheses on results from single-unit recording studies in monkeys, which have shown that neuronal activity in areas involved in decision-making gradually increases and then remains elevated until a response is given, with the rate of increase being slower during more difficult trials1 ...
Paradigms What is a paradigm? Three to consider The Genetic
... How about thinking and feeling? • Cognitive science adds treatment options • Takes into account that we actively filter our experiences based upon past info & experience • Schemas – mental structures for organizing information about the world ...
... How about thinking and feeling? • Cognitive science adds treatment options • Takes into account that we actively filter our experiences based upon past info & experience • Schemas – mental structures for organizing information about the world ...