Optogenetic Technology and Its In Vivo Applications 4 BRIEF SCIENTIFIC REVIEWS
... The most prominent and widely used photosensitive element in nervous-system applications is the lightsensitive channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) protein isolated from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. ChR2 is a nonspecific cation channel that is activated by a covalently bound photosensitive chromophore, retinal ( ...
... The most prominent and widely used photosensitive element in nervous-system applications is the lightsensitive channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) protein isolated from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. ChR2 is a nonspecific cation channel that is activated by a covalently bound photosensitive chromophore, retinal ( ...
Central Nervous System
... of frontal lobe - Involved with intellect and complex learning (cognition) and personality - Tumors may lead to personality disorders - prefrontal lobotomy are performed in severe cases of mental illness. ...
... of frontal lobe - Involved with intellect and complex learning (cognition) and personality - Tumors may lead to personality disorders - prefrontal lobotomy are performed in severe cases of mental illness. ...
A Neuron - Gordon State College
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
PAC Newsletter - March 2015
... connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathways. These repetitions create pathways of memory. The development of your child’s brain is interdependent upon the genetic structure and life experiences, especially with you ...
... connections. These synaptic connections are enhanced by repeated use through our experiences in our environment creating pathways. These repetitions create pathways of memory. The development of your child’s brain is interdependent upon the genetic structure and life experiences, especially with you ...
Biological Basis of behavior
... Every thought, behavior, emotion, perception, etc. is rooted in our biology, particularly our brain The brain is a “psychological organ” as well as a biological one. Biology is the science of living things ---it plays an integral role in supporting psychology. ...
... Every thought, behavior, emotion, perception, etc. is rooted in our biology, particularly our brain The brain is a “psychological organ” as well as a biological one. Biology is the science of living things ---it plays an integral role in supporting psychology. ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... behind your back. Arms closest to your partner should cross each other. Work together to complete the tasks I call out. ...
... behind your back. Arms closest to your partner should cross each other. Work together to complete the tasks I call out. ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fits, it changes the chemistry of the receiving nerve’s membrane (skin). This starts off the electrical c ...
... These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fits, it changes the chemistry of the receiving nerve’s membrane (skin). This starts off the electrical c ...
Powerpoint slides are here
... mossy fibers activate parallel fibers climbing fibers Purkinje cells input synapses compare signals during movement with expected motor learning much reduced if cerebellum removed ...
... mossy fibers activate parallel fibers climbing fibers Purkinje cells input synapses compare signals during movement with expected motor learning much reduced if cerebellum removed ...
The Human brain
... Basal ganglia- lie within the white matter of the cerebrum, play an important role in movement. • The two cavities in the cerebrum are called the lateral ventricles. • The brain in folded into convolutions and in between them are shallow grooves called sulci and the deep pockets are called fissures. ...
... Basal ganglia- lie within the white matter of the cerebrum, play an important role in movement. • The two cavities in the cerebrum are called the lateral ventricles. • The brain in folded into convolutions and in between them are shallow grooves called sulci and the deep pockets are called fissures. ...
SAC 1 PRACTICE TEST 2017
... Maintaining the chemical environment surrounding nerve cells Integrating information to assist neural processing Providing scaffolds that assist neural development ...
... Maintaining the chemical environment surrounding nerve cells Integrating information to assist neural processing Providing scaffolds that assist neural development ...
The Five Senses In the Brain
... excitatory and the two blue neurons are inhibitory. • What effect would removing the two blue inhibitory neurons have on this circuit’s activity? ...
... excitatory and the two blue neurons are inhibitory. • What effect would removing the two blue inhibitory neurons have on this circuit’s activity? ...
Development of the Brain
... • The human central nervous system begins to form when the embryo is approximately 2 weeks old. ...
... • The human central nervous system begins to form when the embryo is approximately 2 weeks old. ...
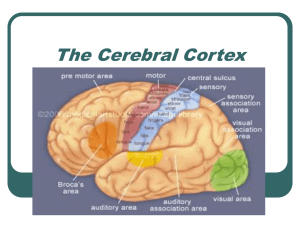
The Cerebral Cortex
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
A New Mathematics-Inspired Understanding of Breathing and the
... the two sides of the body). Synchronization is key to the network’s operation. Other mathematicians—David Terman, Jon Rubin, and colleagues—joined the modeling effort [3,6], and several remarkable network properties were deduced. The same cellular burst-generating mechanism involving persistent sodi ...
... the two sides of the body). Synchronization is key to the network’s operation. Other mathematicians—David Terman, Jon Rubin, and colleagues—joined the modeling effort [3,6], and several remarkable network properties were deduced. The same cellular burst-generating mechanism involving persistent sodi ...
Hastings1-Introducti..
... Most relevant to us Agricultural Economics - first program at University of Wisconsin in 1909 – an applied social science that deals with how producers, consumers and societies use scarce resources in the production processing and marketing of food and fiber products. Natural Resource Economic ...
... Most relevant to us Agricultural Economics - first program at University of Wisconsin in 1909 – an applied social science that deals with how producers, consumers and societies use scarce resources in the production processing and marketing of food and fiber products. Natural Resource Economic ...
The CNS - Mr. Lesiuk
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and balance. The cerebellum is involved in learning of new motor skills, such ...
... The Cerebellum – “little brain” The cerebellum receives sensory input from eyes, ears, joints and muscles and receives motor input from the cerebral cortex. It integrates this information to maintain posture, coordination and balance. The cerebellum is involved in learning of new motor skills, such ...
The Zombie Diaries
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses
... Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses ...
... Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses ...
SinirBilimin Kısa Tarihi
... Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view contends that lower level or primary sensory/motor functions are strongly localized but higher-level functions, like object recognition, memory, and language are the result of interconnections between brain areas. In a ...
... Extreme localism and holism have both been replaced by "connectionism." This view contends that lower level or primary sensory/motor functions are strongly localized but higher-level functions, like object recognition, memory, and language are the result of interconnections between brain areas. In a ...
How is information about touch relayed to the brain?
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. differentiate between the structure and function of the four somatosensory receptors. 2. define the term “dermatome.” 3. review the pathway by which somatosensory information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. differentiate between the structure and function of the four somatosensory receptors. 2. define the term “dermatome.” 3. review the pathway by which somatosensory information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. ...
Implications Of Neuroscience And Contemplative
... Abandon, release sense of self in this moment Receive the breath as a space, not as an "agent" pursuing it View experience as provisional, just the flickering brain, not “mine” ...
... Abandon, release sense of self in this moment Receive the breath as a space, not as an "agent" pursuing it View experience as provisional, just the flickering brain, not “mine” ...
notes as
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...