Nervous System
... information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
... information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... Involves a reinforcing or pushing “signals” – context dependent Reinforcement signal is information poor but motivation rich Involves “basic” brain structures that do not “process” information o E.g. drug addiction: deficit in the control of the reinforcing value Reinforcement: the ventral tegmental ...
... Involves a reinforcing or pushing “signals” – context dependent Reinforcement signal is information poor but motivation rich Involves “basic” brain structures that do not “process” information o E.g. drug addiction: deficit in the control of the reinforcing value Reinforcement: the ventral tegmental ...
Research methods in psychology
... 2. Sample of the study: The portion of the population selected for study and from which generalizations are made about the population. Advantages: 1. Private information 2. Amount of data from large group of people Disadvantages: 1. Representative sample out of a population 2. Courtesy bias 3. Misre ...
... 2. Sample of the study: The portion of the population selected for study and from which generalizations are made about the population. Advantages: 1. Private information 2. Amount of data from large group of people Disadvantages: 1. Representative sample out of a population 2. Courtesy bias 3. Misre ...
Slide ()
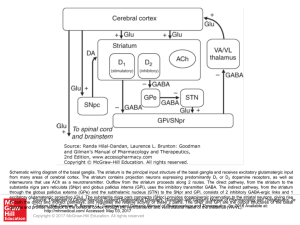
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
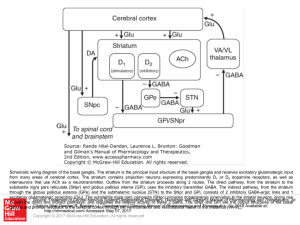
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Brain Scan Lie Detec..
... relative to the action of individual neurons. Furthermore, neurons work by activating and inhibiting other neurons, but inhibition is much more difficult to interpret from fMRI data, as "deactivation" could also be the transient flow of blood toward an area of activation. These somewhat murky result ...
... relative to the action of individual neurons. Furthermore, neurons work by activating and inhibiting other neurons, but inhibition is much more difficult to interpret from fMRI data, as "deactivation" could also be the transient flow of blood toward an area of activation. These somewhat murky result ...
File
... Psychosocial Development The approach that encompasses changes in our interactions with and understanding of one another, as well as in our knowledge and understanding of ourselves as members of society. ...
... Psychosocial Development The approach that encompasses changes in our interactions with and understanding of one another, as well as in our knowledge and understanding of ourselves as members of society. ...
The Brain.
... which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the left cerebral hemisphere are linked to the right side of the body and vice versa. The regions of the body with many sensory neurones have correspondingly large areas of the cortex linked to them. For example, the lips occ ...
... which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the left cerebral hemisphere are linked to the right side of the body and vice versa. The regions of the body with many sensory neurones have correspondingly large areas of the cortex linked to them. For example, the lips occ ...
BOX 42.1 HOW DO WE LEARN ABOUT BRAIN EVOLUTION? There
... There are three main ways to learn about how different brains have evolved. First, the fossil record can be studied. Because bones readily fossilize, whereas soft tissues seldom do, we know a lot about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much abou ...
... There are three main ways to learn about how different brains have evolved. First, the fossil record can be studied. Because bones readily fossilize, whereas soft tissues seldom do, we know a lot about the bones of our ancestors, but much less about everything else. Of course one can infer much abou ...
Massive Modularity
... many groups of animals. A phylogeny of the major animal groups shows that the craniate vertebrate (backboned) animals and invertebrates have long and separate lineages with many branches. Only in animals with several life history, ecological, and physiological attributes did play appear, become prom ...
... many groups of animals. A phylogeny of the major animal groups shows that the craniate vertebrate (backboned) animals and invertebrates have long and separate lineages with many branches. Only in animals with several life history, ecological, and physiological attributes did play appear, become prom ...
The unexamined life is not worth living.
... Study the physiological mechanisms in the brain and nervous system that organize and control behavior Focus may be at various levels individual neurons areas of the brain specific functions like eating, emotion or learning ...
... Study the physiological mechanisms in the brain and nervous system that organize and control behavior Focus may be at various levels individual neurons areas of the brain specific functions like eating, emotion or learning ...
BOX 28.5 NEURAL CONTROL OF HUMAN WALKING Human
... Spontaneous involuntary rhythmic leg movements have also been reported after a clinically complete and incomplete SCI. However, even though this evidence suggests the existence of a CPG network in humans, in all these cases sensory input likely contributed to rhythm generation. Furthermore, clinical ...
... Spontaneous involuntary rhythmic leg movements have also been reported after a clinically complete and incomplete SCI. However, even though this evidence suggests the existence of a CPG network in humans, in all these cases sensory input likely contributed to rhythm generation. Furthermore, clinical ...
Consciousness and Creativity in Brain
... commercially almost successful, but never become massively parallel and the company went bankrupt. CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the large-scale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. Evolutionary algorithms require supervi ...
... commercially almost successful, but never become massively parallel and the company went bankrupt. CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the large-scale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. Evolutionary algorithms require supervi ...
Nervous System and Behavior
... anything else. It also has folds that increase the surface area. ...
... anything else. It also has folds that increase the surface area. ...
Chapter 5 Quiz
... A) New stimuli can be conditioned to produce reflexive behaviors. B) Learning can only occur when the CS provides information about the probability of the UCS occurring. C) Rewarded behaviors are more likely to be repeated, while unrewarded behaviors are less likely to be repeated. D) By first obser ...
... A) New stimuli can be conditioned to produce reflexive behaviors. B) Learning can only occur when the CS provides information about the probability of the UCS occurring. C) Rewarded behaviors are more likely to be repeated, while unrewarded behaviors are less likely to be repeated. D) By first obser ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks
... realizability of the task on humanoid robot platform, Darwin-Op. Point neurons are used in modeling cortex which consists of channels for each action to be elected. The plastic all-to-all connections from the sensory stimuli to the basal ganglia structures are modulated with reward. In the task, the ...
... realizability of the task on humanoid robot platform, Darwin-Op. Point neurons are used in modeling cortex which consists of channels for each action to be elected. The plastic all-to-all connections from the sensory stimuli to the basal ganglia structures are modulated with reward. In the task, the ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can ...
... Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used in MRI. MRI cannot be done if the person has certain metal devices inside their body (such as a pacemaker, implanted port or pump). The magnetic force is so strong that it can ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... body and is the site of intelligence, learning, and judgment – Cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the muscles so the body can move gracefully – Brain stem regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body – Thalamus receives messages from all sensory recept ...
... body and is the site of intelligence, learning, and judgment – Cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the muscles so the body can move gracefully – Brain stem regulates the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body – Thalamus receives messages from all sensory recept ...
File
... ˃ Parasympathetic: Calms (when stress subsides) ˃ Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to keep us at a ...
... ˃ Parasympathetic: Calms (when stress subsides) ˃ Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to keep us at a ...
Jenkins “Defining Psychology” AP Psych Unit I: Thinking Critically
... scientists. Psychology is a rigorous discipline that tests assumptions, bringing scientific data to bear on the questions of central interest to human beings. Psychologists conduct research and rely on that research to provide evidence for their conclusions. They examine the available evidence abou ...
... scientists. Psychology is a rigorous discipline that tests assumptions, bringing scientific data to bear on the questions of central interest to human beings. Psychologists conduct research and rely on that research to provide evidence for their conclusions. They examine the available evidence abou ...