Document
... The cerebellum coordinates and smoothes contractions of skeletal muscles during skilled movements and helps maintain posture and balance. ...
... The cerebellum coordinates and smoothes contractions of skeletal muscles during skilled movements and helps maintain posture and balance. ...
Discrete Modeling of Multi-Transmitter Neural Networks with Neuron
... 2.1 Continuous models One of the earliest models, "integrate-and-fire", was proposed by L. Lapicque (Abbott, 1999) in 1907. It contains one differential equation describing the increase of membrane potential to a threshold value, then the emergence of a spike (or action potential), and then the regr ...
... 2.1 Continuous models One of the earliest models, "integrate-and-fire", was proposed by L. Lapicque (Abbott, 1999) in 1907. It contains one differential equation describing the increase of membrane potential to a threshold value, then the emergence of a spike (or action potential), and then the regr ...
Nervous Regulation
... the receptors toward the spinal cord and brain 3. Interneuron- relay impulses from one neuron to another 4. Motor neuron- carry impulses from brain and spinal cord toward the ...
... the receptors toward the spinal cord and brain 3. Interneuron- relay impulses from one neuron to another 4. Motor neuron- carry impulses from brain and spinal cord toward the ...
23. Parasympathetic nervous system
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
Gene Section CYP7A1 (cytochrome P450, family 7, subfamily A, polypeptide 1)
... bile acid receptor farnesyl X receptor (FXR). Also the pregnane X receptor (PXR) and the vitamin D receptor (VDR) have been identified as bile acid-activated receptors (Staudinger et al., 2001; Han and Chiang, 2009). Bile acids are also reported to suppress CYP7A1 via stimulation of inflammatory cyt ...
... bile acid receptor farnesyl X receptor (FXR). Also the pregnane X receptor (PXR) and the vitamin D receptor (VDR) have been identified as bile acid-activated receptors (Staudinger et al., 2001; Han and Chiang, 2009). Bile acids are also reported to suppress CYP7A1 via stimulation of inflammatory cyt ...
Huber et al. (2008), Sparse optical microstimulation in barrel cortex
... activity of groups of neurons and perceptual and cognitive functions1–6. However, the number and identities of neurons microstimulated, as well as the number of action potentials evoked, are difficult to ascertain7,8. To address these issues we introduced the light-gated algal channel channelrhodops ...
... activity of groups of neurons and perceptual and cognitive functions1–6. However, the number and identities of neurons microstimulated, as well as the number of action potentials evoked, are difficult to ascertain7,8. To address these issues we introduced the light-gated algal channel channelrhodops ...
08_NervousSystem
... Neural Communication Key Note A synaptic terminal releases a neurotransmitter that binds to the postsynaptic cell membrane. The result is a brief, local change in the permeability of the postsynaptic cell. Many drugs affect the nervous system by stimulating neurotransmitter receptors and thus produ ...
... Neural Communication Key Note A synaptic terminal releases a neurotransmitter that binds to the postsynaptic cell membrane. The result is a brief, local change in the permeability of the postsynaptic cell. Many drugs affect the nervous system by stimulating neurotransmitter receptors and thus produ ...
Antipsychotic drug treatment alters expression of mRNAs
... response to haloperidol treatment,16–19 while chronic haloperidol and/or clozapine administration causes changes in the expression of nuclear receptors,20 synaptic proteins21 and various neurotransmitter receptors, most reproducibly components of the glutamatergic system.22–25 Two recent studies hav ...
... response to haloperidol treatment,16–19 while chronic haloperidol and/or clozapine administration causes changes in the expression of nuclear receptors,20 synaptic proteins21 and various neurotransmitter receptors, most reproducibly components of the glutamatergic system.22–25 Two recent studies hav ...
3 Cell Communication and Multicellularity
... 7.2 A Signal Transduction Pathway This general pathway is common to many cells and situations. The ultimate effects on the cell are either short-term or long-term molecular changes, or both. ...
... 7.2 A Signal Transduction Pathway This general pathway is common to many cells and situations. The ultimate effects on the cell are either short-term or long-term molecular changes, or both. ...
BAOJ Neurology
... is surrounded by the entorhinal, parahippocampal and perirhinal cortices and is connected to cortical and sub-cortical parts of the brain. Majority of the hippocampus’s neocortical inputs come from the perirhinal and the parahippocampal cortices through the entorhinal cortex and its neocortical outp ...
... is surrounded by the entorhinal, parahippocampal and perirhinal cortices and is connected to cortical and sub-cortical parts of the brain. Majority of the hippocampus’s neocortical inputs come from the perirhinal and the parahippocampal cortices through the entorhinal cortex and its neocortical outp ...
10.4. What follows from the fact that some neurons we consider
... “share” the function of recognizing these signals, so that each subset of signals will have its “guardian angel” in the form of neuron, which will detect and recognize all signals from one sub-area, another will detect signals from another sub-area, etc. Fig. 10.17 illustrates this. ...
... “share” the function of recognizing these signals, so that each subset of signals will have its “guardian angel” in the form of neuron, which will detect and recognize all signals from one sub-area, another will detect signals from another sub-area, etc. Fig. 10.17 illustrates this. ...
Chapter 11 Outline - CM
... Neurons – excitable cell type responsible for sending and receiving signals in form of action potentials; most consist of three parts (Figures 11.4, 11.5): Cell body (soma) – most metabolically active region of neuron; manufactures all proteins needed for whole neuron; the following organelles sup ...
... Neurons – excitable cell type responsible for sending and receiving signals in form of action potentials; most consist of three parts (Figures 11.4, 11.5): Cell body (soma) – most metabolically active region of neuron; manufactures all proteins needed for whole neuron; the following organelles sup ...
Activity 1 - Web Adventures
... hands. The whole world went into slow motion. Despite what some might say, this is what REALLY happened (put ball in hands of player). The dendrites in the sensory neurons of his/her hands were triggered by the touch of the ball in his/her hand. An electrical signal passed from the dendrites to the ...
... hands. The whole world went into slow motion. Despite what some might say, this is what REALLY happened (put ball in hands of player). The dendrites in the sensory neurons of his/her hands were triggered by the touch of the ball in his/her hand. An electrical signal passed from the dendrites to the ...
Document
... with plasma membrane 3. Neurotransmitter is released into synaptic cleft 4. Neurotransmitter binds to receptor on receiving neuron – Following events vary with different types of chemical synapses ...
... with plasma membrane 3. Neurotransmitter is released into synaptic cleft 4. Neurotransmitter binds to receptor on receiving neuron – Following events vary with different types of chemical synapses ...
The role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and GABAergic
... non-REM sleep is characterized by 12-14 Hz sleep spindles and K-complexes, which have higher amplitudes in their EEG patterns. Stages III and IV show delta waves with low frequency (0.5-2 Hz) and high amplitude, and are therefore also called slow-wave sleep. A phase of non-REM sleep is followed by R ...
... non-REM sleep is characterized by 12-14 Hz sleep spindles and K-complexes, which have higher amplitudes in their EEG patterns. Stages III and IV show delta waves with low frequency (0.5-2 Hz) and high amplitude, and are therefore also called slow-wave sleep. A phase of non-REM sleep is followed by R ...
R26 :: CAG GCaMP6f - The Jackson Laboratory
... international biomedical research community - adds hundreds of new strains annually. The JAX Mouse Repository is supported by NIH, The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and several private charitable foundations. ...
... international biomedical research community - adds hundreds of new strains annually. The JAX Mouse Repository is supported by NIH, The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and several private charitable foundations. ...
Delayed Puberty but Normal Fertility in Mice With Selective Deletion
... plays a pivotal role in the regulation of reproduction. Indeed, insulin has been shown to activate GnRH and LH secretion in vitro (8, 9). Mice that lack insulin signaling in brain neurons (NIRKO mice) exhibit hypothalamic hypogonadism (10) and a delay in puberty (11). Moreover, diabetic rats display ...
... plays a pivotal role in the regulation of reproduction. Indeed, insulin has been shown to activate GnRH and LH secretion in vitro (8, 9). Mice that lack insulin signaling in brain neurons (NIRKO mice) exhibit hypothalamic hypogonadism (10) and a delay in puberty (11). Moreover, diabetic rats display ...
Dysregulating Factors
... ischemia/reperfusion injury [17332467]. Both neuronal and glial cells possess a variety of chemokine receptors that can regulate calcium and other signaling pathways - in normal cirucumstances chemokine modulation of calcium homeostasis is believed to have positive effects on neuronal development, b ...
... ischemia/reperfusion injury [17332467]. Both neuronal and glial cells possess a variety of chemokine receptors that can regulate calcium and other signaling pathways - in normal cirucumstances chemokine modulation of calcium homeostasis is believed to have positive effects on neuronal development, b ...
Neurotransmitters
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
... cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. ...
File
... a. stimulation of a motor neuron b. depolarization in the axon of an interneuron c. depolarization in the axon of a sensory neuron d. release of neurotransmitter from an axon terminal ____ 11. Use the diagram above to answer the next question. When an action potential reaches the end of this cell, w ...
... a. stimulation of a motor neuron b. depolarization in the axon of an interneuron c. depolarization in the axon of a sensory neuron d. release of neurotransmitter from an axon terminal ____ 11. Use the diagram above to answer the next question. When an action potential reaches the end of this cell, w ...
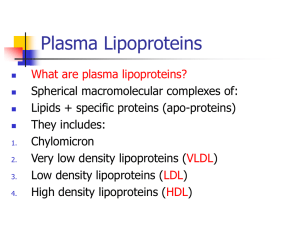
Plasma Lipoproteins
... The chylomicron remnant-, IDL-, and LDLderived cholesterol affects cellular cholesterol content in several ways. First, HMG CoA reductase is inhibited by high cholesterol, as a result of which, de novo cholesterol synthesis decreases. Second, synthesis of new LDL receptor protein is reduced by decre ...
... The chylomicron remnant-, IDL-, and LDLderived cholesterol affects cellular cholesterol content in several ways. First, HMG CoA reductase is inhibited by high cholesterol, as a result of which, de novo cholesterol synthesis decreases. Second, synthesis of new LDL receptor protein is reduced by decre ...
hypothalamic neuroanatomy and limbic inputs
... role in sexual behavior, particularly in females. The lateral hypothalamus comprises other unique cell groups, including neurons that produce orexins (also known as hypocretins), which have profound effects on sleep–wake cycles, feeding, and reward-seeking behavior, and can influence GnRH secretion. ...
... role in sexual behavior, particularly in females. The lateral hypothalamus comprises other unique cell groups, including neurons that produce orexins (also known as hypocretins), which have profound effects on sleep–wake cycles, feeding, and reward-seeking behavior, and can influence GnRH secretion. ...
posterior pituitary
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) TSH (also known as thyrotropin) – glycoportein consisting of: a b chain of 112 amino acids and an a chain of 89 amino acids. The a chain is identical to that found in two other pituitary hormones, FSH and LH as well as in the hormone chorionic ...
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) TSH (also known as thyrotropin) – glycoportein consisting of: a b chain of 112 amino acids and an a chain of 89 amino acids. The a chain is identical to that found in two other pituitary hormones, FSH and LH as well as in the hormone chorionic ...