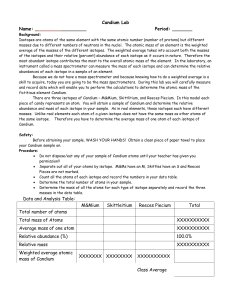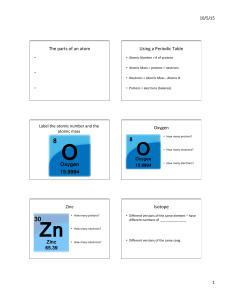
Chapter 2 – Atoms, Ions and Compounds
... Know the formulas and names of the following polyatomic ions: NH4+ = ammonium ion CO32– = carbonate ion Hg22+ = mercury (I) ion Cr2O72– = dichromate ion HCO3– = hydrogen carbonate ion SO42– = sulfate ion MnO4– = permanganate ion SO32– = sulfite ion ClO4– = perchlorate ion SCN– = thiocyanate ion O22– ...
... Know the formulas and names of the following polyatomic ions: NH4+ = ammonium ion CO32– = carbonate ion Hg22+ = mercury (I) ion Cr2O72– = dichromate ion HCO3– = hydrogen carbonate ion SO42– = sulfate ion MnO4– = permanganate ion SO32– = sulfite ion ClO4– = perchlorate ion SCN– = thiocyanate ion O22– ...
Atomic models
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness It can be verified or ...
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness It can be verified or ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number (same element) but different atomic weights: that is, isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Most elements have several naturally occurring isotopes. Different isotopes of the same element all have the same chemical ...
... Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number (same element) but different atomic weights: that is, isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Most elements have several naturally occurring isotopes. Different isotopes of the same element all have the same chemical ...
Chemistry Final Exam Practice Test
... 70. When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron _____. a) always doubles its energy b) absorbs a continuously variable amount of energy c) absorbs a quantum of energy d) moves closer to the nucleus ...
... 70. When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron _____. a) always doubles its energy b) absorbs a continuously variable amount of energy c) absorbs a quantum of energy d) moves closer to the nucleus ...
Early Theories of Matter
... experiments in the late 1890s to determine the ratio of its charge to its mass. By carefully measuring the effect of both magnetic and electric fields on a cathode ray, Thomson was able to determine the charge to mass ratio of the charged particle. He then compared that ratio to other known ratios. ...
... experiments in the late 1890s to determine the ratio of its charge to its mass. By carefully measuring the effect of both magnetic and electric fields on a cathode ray, Thomson was able to determine the charge to mass ratio of the charged particle. He then compared that ratio to other known ratios. ...
Atoms, Elements and Compounds Home
... Where in the World? Chemical elements have been discovered all over the world. In many cases the name comes from the place the element was discovered. Use a key to show on the map where each of the elements listed below was discovered. You could use either: A colour key with a different colour for ...
... Where in the World? Chemical elements have been discovered all over the world. In many cases the name comes from the place the element was discovered. Use a key to show on the map where each of the elements listed below was discovered. You could use either: A colour key with a different colour for ...
Document
... made up of particles called atoms and that atoms of different elements are different. Students will describe the structure of atoms and the electrical charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... made up of particles called atoms and that atoms of different elements are different. Students will describe the structure of atoms and the electrical charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
OCR A Level Physics B Delivery Guide Learner Resource 1: Atomic
... Work out the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for the following isotopes. ...
... Work out the number of protons, electrons and neutrons for the following isotopes. ...
"ALICE" CHAPTER 12 MODERN VIEW OF ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... neutron. These two slightly different kinds of hydrogen are often referred to as light and heavy hydrogen. ...
... neutron. These two slightly different kinds of hydrogen are often referred to as light and heavy hydrogen. ...
Document
... b- I was sitting near water and I saw salmon swimming upstream against a very strong current. They would jump out of the water which made it seem like they were flying for a few seconds and then dove back down in the water. River c- This biome has lots of grazing animals in a very open space. I was ...
... b- I was sitting near water and I saw salmon swimming upstream against a very strong current. They would jump out of the water which made it seem like they were flying for a few seconds and then dove back down in the water. River c- This biome has lots of grazing animals in a very open space. I was ...
Elements and Compounds checklist for web
... Niels Bohr to our understanding of the structure of atoms. • Identify the elements named after the above scientists. • Identify as many elements named after other scientists or places. Extension work: -‐ D ...
... Niels Bohr to our understanding of the structure of atoms. • Identify the elements named after the above scientists. • Identify as many elements named after other scientists or places. Extension work: -‐ D ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 2
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
Early Atomic History
... To indicate a specific isotope, the atomic symbol must also contain the mass number. The mass number is the number of neutrons plus protons for a particular isotope. The mass number is never found on the periodic table. Since the mass number is the number of particles (neutrons + protons) in the nuc ...
... To indicate a specific isotope, the atomic symbol must also contain the mass number. The mass number is the number of neutrons plus protons for a particular isotope. The mass number is never found on the periodic table. Since the mass number is the number of particles (neutrons + protons) in the nuc ...
Daily 40 no. – 17 Ernest Rutherford
... Ernest Rutherford, a British chemist from 1872 to 1937, was known for discovering protons by shooting alpha particles through foil. He observed that some were repulsed, so there were positive charges in the foil’s atoms. This led to atomic numbers, which were the key to completing the periodic table ...
... Ernest Rutherford, a British chemist from 1872 to 1937, was known for discovering protons by shooting alpha particles through foil. He observed that some were repulsed, so there were positive charges in the foil’s atoms. This led to atomic numbers, which were the key to completing the periodic table ...
Electron Configurations & the Periodic Table
... • Classical physics could not explain the existence of a threshold frequency, so Einstein turned to Planck’s Quantum Theory. • Einstein defined a quantum of electromagnetic radiation as a photon. • Einstein proposed that light could be thought of as a stream of photons with particle-like properties ...
... • Classical physics could not explain the existence of a threshold frequency, so Einstein turned to Planck’s Quantum Theory. • Einstein defined a quantum of electromagnetic radiation as a photon. • Einstein proposed that light could be thought of as a stream of photons with particle-like properties ...
II Atomic Theory
... – Thomson used a Crookes tube and placed it in an adjustable magnetic field. He was able to determine the mass to charge (m/e) ratio of the cathode rays. By comparing the ratio to the smallest mass to charge ratio in solution discovered that the mass of the cathode ray had to be 1/1000 the mass of h ...
... – Thomson used a Crookes tube and placed it in an adjustable magnetic field. He was able to determine the mass to charge (m/e) ratio of the cathode rays. By comparing the ratio to the smallest mass to charge ratio in solution discovered that the mass of the cathode ray had to be 1/1000 the mass of h ...
Prescriptive #54
... When nonmetal atoms bond together to form covalent compounds, they will either share the electrons equally between the atoms, or the electrons will be more attracted to one atom than another. This unequal attraction results in a polar bond and is very important in determining the properties of subst ...
... When nonmetal atoms bond together to form covalent compounds, they will either share the electrons equally between the atoms, or the electrons will be more attracted to one atom than another. This unequal attraction results in a polar bond and is very important in determining the properties of subst ...