Early Atomic History
... A nuclear reaction differs from a chemical reaction, and results in the formation of new elements as an unstable nucleus decays. ...
... A nuclear reaction differs from a chemical reaction, and results in the formation of new elements as an unstable nucleus decays. ...
Chemistry basics powerpoint Chapter 2
... Identify the four major elements 2. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: neutron and proton, atomic number and mass number, atomic weight and mass number 3. Distinguish between and discuss the biological importance of the following: nonpolar covalent ...
... Identify the four major elements 2. Distinguish between the following pairs of terms: neutron and proton, atomic number and mass number, atomic weight and mass number 3. Distinguish between and discuss the biological importance of the following: nonpolar covalent ...
12.2 Niels Bohr
... friend. Rutherford had recently published his new planetary model of the atom, which explained that an atom contains a tiny dense core surrounded by orbiting electrons. Bohr began researching the orbiting electrons, hoping to describe their behavior in greater detail. Electrons and the atom’s chemis ...
... friend. Rutherford had recently published his new planetary model of the atom, which explained that an atom contains a tiny dense core surrounded by orbiting electrons. Bohr began researching the orbiting electrons, hoping to describe their behavior in greater detail. Electrons and the atom’s chemis ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Bohr came up with an atomic model to explain the spectrum of ______________________. He said that the atom has certain _______________ levels which are allowed. These levels corresponded to ____________________ in which electrons move. If an electron absorbs a certain photon of energy, it will jump ...
... Bohr came up with an atomic model to explain the spectrum of ______________________. He said that the atom has certain _______________ levels which are allowed. These levels corresponded to ____________________ in which electrons move. If an electron absorbs a certain photon of energy, it will jump ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter2
... represents an isotope of nickel that contains 28 protons and 32 neutrons in the nucleus. • Isotopes are also represented by the notation: Name-A, where Name is the name of the element and A is the mass number of the isotope. • An example of this isotope notation is magnesium-26. This represents an i ...
... represents an isotope of nickel that contains 28 protons and 32 neutrons in the nucleus. • Isotopes are also represented by the notation: Name-A, where Name is the name of the element and A is the mass number of the isotope. • An example of this isotope notation is magnesium-26. This represents an i ...
The Cubic Atomic Model
... The idea that the atom is large structure of alternating protons and electrons is in direct conflict with the planetary Bohr/Rutherford model. It is claimed that Rutherford ‘proved’ that the positive charges in an atom must be located in a tiny compact nucleus within the atom. Bohr provided the idea ...
... The idea that the atom is large structure of alternating protons and electrons is in direct conflict with the planetary Bohr/Rutherford model. It is claimed that Rutherford ‘proved’ that the positive charges in an atom must be located in a tiny compact nucleus within the atom. Bohr provided the idea ...
Chemical Periodicity
... Table 9.4 lists the atomic radii for the first row of the transition metals. It can be seen from this table that the period trend in atomic radii is not followed as closely by the transition metals. Since we are adding electrons to the 3d orbitals, we are actually adding to the core electrons and no ...
... Table 9.4 lists the atomic radii for the first row of the transition metals. It can be seen from this table that the period trend in atomic radii is not followed as closely by the transition metals. Since we are adding electrons to the 3d orbitals, we are actually adding to the core electrons and no ...
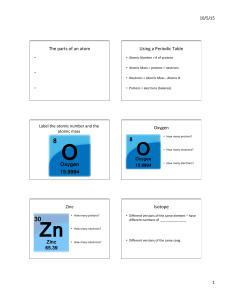
The Atom
... Most elements contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. For example, all copper is composed of copper-63 atoms and copper-65 atoms. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. A weighted average accounts for the percen ...
... Most elements contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. For example, all copper is composed of copper-63 atoms and copper-65 atoms. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element. A weighted average accounts for the percen ...
Early Atomic History
... As the early chemists explored the nature of matter, they discovered that atoms of the elements had different masses. Avogadro’s Hypothesis which states that under constant temperature and pressure equal volumes of gases contain an equal number of particles could be used to determine relative atomic ...
... As the early chemists explored the nature of matter, they discovered that atoms of the elements had different masses. Avogadro’s Hypothesis which states that under constant temperature and pressure equal volumes of gases contain an equal number of particles could be used to determine relative atomic ...
Chapter 2 - HCC Learning Web
... • Atomic symbol or chemical symbol – 1 or 2 letter designation of an element ...
... • Atomic symbol or chemical symbol – 1 or 2 letter designation of an element ...
1 - Mr. J`s Chemistry 4U
... 52) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance can have different physical and chemical properties. 53) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same chemical composition. 54) T / F : A pure substance cannot be separated into other substances without changing its identity. ...
... 52) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance can have different physical and chemical properties. 53) T / F : Every sample of a given pure substance has exactly the same chemical composition. 54) T / F : A pure substance cannot be separated into other substances without changing its identity. ...
Unit Plans and Related Materials
... (M) Calculate average atomic mass (184) (M) Classify elements on the periodic table into groups and families based on similar properties (165) (M) Predict patterns in bonding and reactivity using the PT (174) (M) Predict an atom’s nuclear stability given its number of neutrons (184) (M) Describe why ...
... (M) Calculate average atomic mass (184) (M) Classify elements on the periodic table into groups and families based on similar properties (165) (M) Predict patterns in bonding and reactivity using the PT (174) (M) Predict an atom’s nuclear stability given its number of neutrons (184) (M) Describe why ...
chapter2-bur.2886332..
... Atomic Mass Units (amu) The mass of a single atom of an element, expressed in SI units, is an extremely small number. For example, the mass of a single atom of 16O is 2.6560 x 10-26 kg. For convenience, we often express values for atomic mass in terms of atomic mass units (amu). Atomic mass units a ...
... Atomic Mass Units (amu) The mass of a single atom of an element, expressed in SI units, is an extremely small number. For example, the mass of a single atom of 16O is 2.6560 x 10-26 kg. For convenience, we often express values for atomic mass in terms of atomic mass units (amu). Atomic mass units a ...
Review History of the Atom
... Dalton devised the first modern atomic model. Which one of the following characteristics is NOT part of Dalton's atomic model? a. Atoms of different elements are different. b. All atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms combine to form compounds. d. Atoms consist of positive particles and ...
... Dalton devised the first modern atomic model. Which one of the following characteristics is NOT part of Dalton's atomic model? a. Atoms of different elements are different. b. All atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms combine to form compounds. d. Atoms consist of positive particles and ...
A an electron and an alpha particle B an electron and a proton C a
... electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which negatively charged particles were embedded. The total negative charge in the atom was ...
... electric field. This suggested that cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles found in all atoms. Thomson concluded that the atom was a positively charged sphere of almost uniform density in which negatively charged particles were embedded. The total negative charge in the atom was ...
Atomic mod
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations • Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: • It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments • It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness • It can be verified or ...
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations • Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: • It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments • It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness • It can be verified or ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1 The Atom
... • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements. • Every substance is made up ...
... • In 1808, John Dalton published an atomic theory, stating that all matter is made up of atoms that cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. • This theory also stated that all atoms of a certain element are identical, but they differ from atoms of all other elements. • Every substance is made up ...
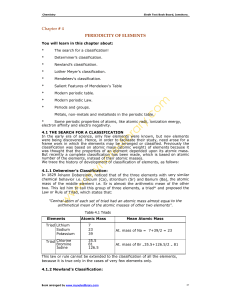
IX Chemistry Chapter 04
... left many vacant spaces in his periodic table, stating that such vacant spaces would be filled by elements not yet discovered. He did not only left vacant spaces but he also predicted the properties of the elements] which when found, would occupy these spaces^ like those, eka (below)aluminum and sil ...
... left many vacant spaces in his periodic table, stating that such vacant spaces would be filled by elements not yet discovered. He did not only left vacant spaces but he also predicted the properties of the elements] which when found, would occupy these spaces^ like those, eka (below)aluminum and sil ...
chapter 5
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations • Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: • It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments • It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness • It can be verified or ...
... predictions fail to fit the experimental data as well as other observations • Nevertheless it’s a perfectly sensible scientific theory because: • It is a mathematical model built on sound and rigorous physical arguments • It predicts some physical phenomenon with definiteness • It can be verified or ...
Ch6-Energy in Chemical Reactions-Chemical Reactions
... problem is that, when we compare amounts of one substance to another using mole, we must convert to moles from grams which are actually measured. It is also important that we understand the mole as the basis for all calculations in chemistry and have conceptual understanding of how Mole is related t ...
... problem is that, when we compare amounts of one substance to another using mole, we must convert to moles from grams which are actually measured. It is also important that we understand the mole as the basis for all calculations in chemistry and have conceptual understanding of how Mole is related t ...