CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
... 4) How many valence electrons do atoms with the following electron configurations have? A) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4 B) 1s22s22p63s2 C) 1s22s22p63s23p64s1 D) 1s22s22p6 5) Fill in the chart below for each of the following isotopes. ...
File
... 3. The CR was made of particles 4. The CR particles had mass. ** The deflection of the cathode rays gave evidence for the negatively charged nature of electrons. ** ...
... 3. The CR was made of particles 4. The CR particles had mass. ** The deflection of the cathode rays gave evidence for the negatively charged nature of electrons. ** ...
Matter and Measurement
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
... occur in simple proportions by volume. Moreover, the ratio of the volume of each product gas to the volume of either reacting gas is a ratio of small integers. For example, if the pressure and temperature are kept constant, two volumes of H2 gas reacts with one volume of O2 gas, producing two volume ...
Unit 1: Basic Chemistry Notes (answers)
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
... alchemists. Their purpose was to find a chemical recipe to make gold from other less valuable metals. (We now know that it is only possible now if we can change the number of protons in the nucleus). In 1808, a British scientist by the name of John Dalton published his theory of atoms that would hav ...
Chapter 6 Section 3 Periodic Trends
... sodium ion, the number of electrons (10) is not equal to the number of protons (11). Because there are more positively charged protons than negatively charged electrons, the sodium ion has a net positive charge. An ion with a positive charge is called a cation. The charge for a cation is written as ...
... sodium ion, the number of electrons (10) is not equal to the number of protons (11). Because there are more positively charged protons than negatively charged electrons, the sodium ion has a net positive charge. An ion with a positive charge is called a cation. The charge for a cation is written as ...
Atoms - Mrs. Lindenlaub
... come upon a particle of copper that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. This final particle is an atom. ...
... come upon a particle of copper that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. This final particle is an atom. ...
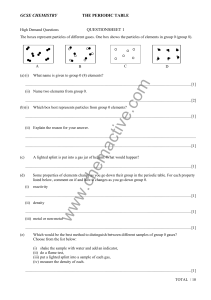
Periodic_table_questions
... Emma takes a photograph of a friend. Her friend tells her that the film is coated with silver bromide which is sensitive to light. Silver bromide can be made by reacting silver nitrate with sodium bromide. The chemical reaction can be represented as: ...
... Emma takes a photograph of a friend. Her friend tells her that the film is coated with silver bromide which is sensitive to light. Silver bromide can be made by reacting silver nitrate with sodium bromide. The chemical reaction can be represented as: ...
Chapter 1-3 Exam Review
... the isotopes as they occur in nature. Most elements occur as two or three isotopes in nature. For example, chlorine has two isotopes, both of which have 17 protons in their atomic nuclei. One isotope has 18 neutrons (Cl-35) and the other isotope has 20 neutrons (Cl-37). In order to calculate the ato ...
... the isotopes as they occur in nature. Most elements occur as two or three isotopes in nature. For example, chlorine has two isotopes, both of which have 17 protons in their atomic nuclei. One isotope has 18 neutrons (Cl-35) and the other isotope has 20 neutrons (Cl-37). In order to calculate the ato ...
THE GREATEST KNIGHT (atomic physics for kids)
... models to predict what will happen. There are things that happen in the real world that the Bohr model cannot predict. The Bohr model also predicts things that do not happen. Also, the Bohr model does not explain how energy forms into three completely different particles. Basic science classes still ...
... models to predict what will happen. There are things that happen in the real world that the Bohr model cannot predict. The Bohr model also predicts things that do not happen. Also, the Bohr model does not explain how energy forms into three completely different particles. Basic science classes still ...
1s - 固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室
... p orbitals, are being filled, electrons tend to have the same spin. The electrons occupy different orbitals so as to remain as far apart as possible. This is reasonable, since electrons have like charges and tend to repel each other. The electrons do not pair up until there is at least one electron ...
... p orbitals, are being filled, electrons tend to have the same spin. The electrons occupy different orbitals so as to remain as far apart as possible. This is reasonable, since electrons have like charges and tend to repel each other. The electrons do not pair up until there is at least one electron ...
Notebook - Science
... proton: stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with positive electric charge to that of an electron, but of opposite sign neutron: subatomic chargeless particle about the same mass as a proton, present in all atomic nuclei except ordinary hydrogen electron: stable subatomic partic ...
... proton: stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with positive electric charge to that of an electron, but of opposite sign neutron: subatomic chargeless particle about the same mass as a proton, present in all atomic nuclei except ordinary hydrogen electron: stable subatomic partic ...
SCH4U - Unit 1
... JOHN DALTON (1809) Dalton was an English schoolteacher came up with his atomic theory based on many years of experimentation by many scientists. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms can be neither subdivided nor changed into one another 3. Atoms ca ...
... JOHN DALTON (1809) Dalton was an English schoolteacher came up with his atomic theory based on many years of experimentation by many scientists. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms can be neither subdivided nor changed into one another 3. Atoms ca ...
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Law
... John Newland – noticed that if the elements were arranged according to the atomic masses, the properties of the elements were repeated. ...
... John Newland – noticed that if the elements were arranged according to the atomic masses, the properties of the elements were repeated. ...
Record: 1 THE EVOLUTION OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM Page 1 of
... have been overemphasized by historians, who have generally suggested that Mendeleev's table was accepted especially because of this feature. These scholars have failed to notice that the citation from the Royal Society of London that accompanied the Davy Medal (which Mendeleev received in 1882) make ...
... have been overemphasized by historians, who have generally suggested that Mendeleev's table was accepted especially because of this feature. These scholars have failed to notice that the citation from the Royal Society of London that accompanied the Davy Medal (which Mendeleev received in 1882) make ...
+l.
... according to their atomic masses and chemical similarities The electronic configuration of the elements explained by quantum numbers and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle explains the configuration ...
... according to their atomic masses and chemical similarities The electronic configuration of the elements explained by quantum numbers and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle explains the configuration ...
Chapter 2
... (Avogadro’s number). The significance is as follows. Consider a collection of identical objects. The following relationship will apply. If one object has a mass of X amu… …then one mole of objects has a mass of X g. This is a subtle point. Consider the unit “thousand”. We could make the following st ...
... (Avogadro’s number). The significance is as follows. Consider a collection of identical objects. The following relationship will apply. If one object has a mass of X amu… …then one mole of objects has a mass of X g. This is a subtle point. Consider the unit “thousand”. We could make the following st ...
Atomic Structure
... Know the relationship between types of electromagnetic radiation and energy; for example, gamma rays are the most damaging. Know what exhibits continuous and line spectra. Know what each of the four quantum numbers n, l, m, and ms represents. Identify the four quantum numbers for an electron in ...
... Know the relationship between types of electromagnetic radiation and energy; for example, gamma rays are the most damaging. Know what exhibits continuous and line spectra. Know what each of the four quantum numbers n, l, m, and ms represents. Identify the four quantum numbers for an electron in ...