Atomic Structure and Function
... • Gas (no definite shape nor definite volume) • Liquid (definite volume but no definite shape) • Solid (definite shape and definite volume) ...
... • Gas (no definite shape nor definite volume) • Liquid (definite volume but no definite shape) • Solid (definite shape and definite volume) ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... Drawing Lewis structures by this method, use the following as a guide: a) Draw skeletal Lewis structure. b) Draw the Lewis electron dot structure for each atom. (Use the method in which the electrons are spread to all four sides of an imaginary square before being paired.) For the sake of keeping th ...
... Drawing Lewis structures by this method, use the following as a guide: a) Draw skeletal Lewis structure. b) Draw the Lewis electron dot structure for each atom. (Use the method in which the electrons are spread to all four sides of an imaginary square before being paired.) For the sake of keeping th ...
Electrons - sotochem
... Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill subshells (and orbitals) so that the total energy of atom is the minimum ...
... Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill subshells (and orbitals) so that the total energy of atom is the minimum ...
Chapter 2
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
... of subatomic particles • An element’s atomic number is the number of protons in its nucleus • An element’s mass number is the sum of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus • Atomic mass, the atom’s total mass, can be approximated by the mass number Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing ...
Chemistry(Class-IX)- Atoms and Molecules
... mass of product, i.e. calcium hydroxide is also equal to 74g. This proves that the total mass of reactants is always equal to the total mass of product, which proves the Law of Conservation of Mass. Law of Constant Proportions Law of Constant Proportion states that a chemical compound always contain ...
... mass of product, i.e. calcium hydroxide is also equal to 74g. This proves that the total mass of reactants is always equal to the total mass of product, which proves the Law of Conservation of Mass. Law of Constant Proportions Law of Constant Proportion states that a chemical compound always contain ...
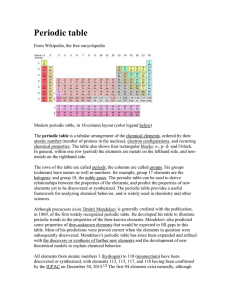
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Note that 3 is the lowest possible value that n may have for a d orbital and that 4 is the lowest possible value of n for an ƒ orbital. The total of the superscripted numbers should equal the atomic number of bismuth, 83. The electrons may be listed, as shown above in the “Total” row, in the order o ...
... Note that 3 is the lowest possible value that n may have for a d orbital and that 4 is the lowest possible value of n for an ƒ orbital. The total of the superscripted numbers should equal the atomic number of bismuth, 83. The electrons may be listed, as shown above in the “Total” row, in the order o ...
chem1a_ch02_lecture - Santa Rosa Junior College
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
chem1a_ch02_lecture - Santa Rosa Junior College
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
Study Guide for Final #1
... 1.) Know who the important contributors were who helped to derive the different models of the atom. Know what their contributions were. 2.) Be able to describe Dalton’s atomic theory. 3.) Know where the three different subatomic particles are located, their charges, and their relative sizes. 4.) Kno ...
... 1.) Know who the important contributors were who helped to derive the different models of the atom. Know what their contributions were. 2.) Be able to describe Dalton’s atomic theory. 3.) Know where the three different subatomic particles are located, their charges, and their relative sizes. 4.) Kno ...
inorganic chemistry
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
... compared to chlorine is due to very small size of the fluorine atom. As a result, there are strong inter-electronic repulsions in the relatively small 2p subshell of fluorine and thus the incoming electron does not feel much attraction. Therefore, its electron affinity is small. Thus, electron affin ...
CHAP 4 - NCERT books
... Neils Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom: (i) Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons, are allowed inside the atom. (ii) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy. ...
... Neils Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom: (i) Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons, are allowed inside the atom. (ii) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy. ...
Structure of Molecules and Compounds | Principles of Biology from
... or kJ/mol) required to form and break the bonds. Covalent bonds are strong, with free energies of 30 to 200 kcal/mol. Strong ionic bonds, such as those in a salt lattice like NaCl also have bond energies in the same range. At physiological temperatures, these types of bonds do not break easily. Stro ...
... or kJ/mol) required to form and break the bonds. Covalent bonds are strong, with free energies of 30 to 200 kcal/mol. Strong ionic bonds, such as those in a salt lattice like NaCl also have bond energies in the same range. At physiological temperatures, these types of bonds do not break easily. Stro ...
Science - Atom Structure
... From these activities, can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged? Where does this charge come from? This question can be answered by knowing that an atom is divisible and consists of charged particles. Many scientists contributed in revealing the presence ...
... From these activities, can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged? Where does this charge come from? This question can be answered by knowing that an atom is divisible and consists of charged particles. Many scientists contributed in revealing the presence ...
The Periodic Table - Whitwell High School
... also be can be separated divided smaller intoand smaller until numbers eventually until you have only a single justatom one DVD left. But aDividing remains. single DVD it any cannot be smaller would separated give into smallerthat pieces pieces are that no longer are stillatom. an DVDs. ...
... also be can be separated divided smaller intoand smaller until numbers eventually until you have only a single justatom one DVD left. But aDividing remains. single DVD it any cannot be smaller would separated give into smallerthat pieces pieces are that no longer are stillatom. an DVDs. ...
Activity 9 What Determines and Limits an Atom`s Mass?
... 5. The nucleus is a very crowded place. The protons in the nucleus are very close to one another. If these protons are repelling each other by an electrostatic force (and they are!), there must be another force, an attractive force, that keeps them there. The attractive force is the nuclear force, a ...
... 5. The nucleus is a very crowded place. The protons in the nucleus are very close to one another. If these protons are repelling each other by an electrostatic force (and they are!), there must be another force, an attractive force, that keeps them there. The attractive force is the nuclear force, a ...
10 Chemistry
... • Groups in the periodic table contain an informaEon on how many valence electrons each element has. • VIII A group – 8 electrons filled shell – most stable elements ...
... • Groups in the periodic table contain an informaEon on how many valence electrons each element has. • VIII A group – 8 electrons filled shell – most stable elements ...
The radial part of the wavefunction, R(r)
... The radial distribution function, 4 π r2 R (r)2 Let us now consider how we might represent atomic orbitals in three-dimensional space. We said earlier that a useful description of an electron in an atom is the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space. The function Ψ2 is proport ...
... The radial distribution function, 4 π r2 R (r)2 Let us now consider how we might represent atomic orbitals in three-dimensional space. We said earlier that a useful description of an electron in an atom is the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space. The function Ψ2 is proport ...
atomic number
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number r ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) 1. All matter is made of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number r ...
The Elements and the Periodic Table
... • We now know that both light and electrons exhibit wave-particle duality — that is, some properties of each are best described with a wave model, and some properties are best described by a particle model. • Quantum mechanics, which unifies the wave and particle models of light, arose from a combin ...
... • We now know that both light and electrons exhibit wave-particle duality — that is, some properties of each are best described with a wave model, and some properties are best described by a particle model. • Quantum mechanics, which unifies the wave and particle models of light, arose from a combin ...
Dalton`s atomic theory
... In 1918, Rutherford bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and observed hydrogen nuclei being emitted from the gas. Rutherford concluded that the hydrogen nuclei emerged from the nuclei of the nitrogen atoms themselves (in effect, he split the atom). He later found that the positive charge of a ...
... In 1918, Rutherford bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and observed hydrogen nuclei being emitted from the gas. Rutherford concluded that the hydrogen nuclei emerged from the nuclei of the nitrogen atoms themselves (in effect, he split the atom). He later found that the positive charge of a ...