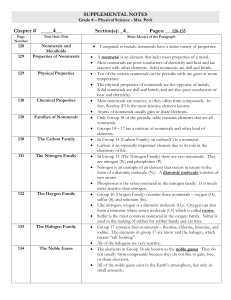
The Periodic Table
... is a shiny blue-black solid. Though different in appearance, they have very similar chemical properties. ...
... is a shiny blue-black solid. Though different in appearance, they have very similar chemical properties. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Radioactivity Outline 2.1 Atoms and Their
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
Atomic Number
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
... The elements in Group 18 are known as the noble gases. They do not usually form compounds because they do not like to gain, lose, or share electrons. All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere, but only in small amounts. ...
The Periodic Table CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR
... Photons are emitted by atoms as electrons move from higher-energy outer levels to lowerenergy inner levels. The energy of an emitted photon is equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Because an electron is restricted to discrete levels, only lights of distinct frequencies are emitt ...
... Photons are emitted by atoms as electrons move from higher-energy outer levels to lowerenergy inner levels. The energy of an emitted photon is equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Because an electron is restricted to discrete levels, only lights of distinct frequencies are emitt ...
2. Chapter 2
... You may recall that an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. The reason an element cannot be broken down further is that it is already very simple: each element is made of only one kind of atom. Elements can be found in your pencils, your coins, ...
... You may recall that an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down or separated into simpler substances. The reason an element cannot be broken down further is that it is already very simple: each element is made of only one kind of atom. Elements can be found in your pencils, your coins, ...
Final "I Can Statements" Answer Key
... A mole is a unit to measure the amount of substance. One mole of substance is equal to its gfm. It is also equal to 6.02 x 1023 particles. If the substance is a gas at STP, one mole will occupy 22.4 L of volume. 94.3 g is how many moles of NaCl? ...
... A mole is a unit to measure the amount of substance. One mole of substance is equal to its gfm. It is also equal to 6.02 x 1023 particles. If the substance is a gas at STP, one mole will occupy 22.4 L of volume. 94.3 g is how many moles of NaCl? ...
Daily 40 no. – 15 John Newlands
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
... create an early periodic table. His organization led to the modern periodic table. He realized that every eighth element had similar characteristics. His incomplete table predicted other undiscovered elements. -Eric John Newlands was born in 1837 and died in 1898. He is known for creating the first ...
The Periodic Table
... similar chemical properties. • Elements are also organized horizontally in rows, or periods. • The periodic table is divided into four blocks, the s, p, d, and f blocks. The name of each block is determined by the electron sublevel being filled in that block. ...
... similar chemical properties. • Elements are also organized horizontally in rows, or periods. • The periodic table is divided into four blocks, the s, p, d, and f blocks. The name of each block is determined by the electron sublevel being filled in that block. ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT
... Ions are atoms with a positive or negative charge. They can be divided into two types: Cations: ions that have lost electrons and gained a positive charge Anions: ions that have gained electrons and gained a negative charge To calculate the number of protons, neutrons or electrons in any atom or ion ...
... Ions are atoms with a positive or negative charge. They can be divided into two types: Cations: ions that have lost electrons and gained a positive charge Anions: ions that have gained electrons and gained a negative charge To calculate the number of protons, neutrons or electrons in any atom or ion ...
atom
... Atoms are neutral, so it’s also the number of electrons. Protons determine the identity of an element. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7, so every nitrogen has 7 protons. The mass number (A) is the total number of protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are collectively referred to ...
... Atoms are neutral, so it’s also the number of electrons. Protons determine the identity of an element. For example, nitrogen’s atomic number is 7, so every nitrogen has 7 protons. The mass number (A) is the total number of protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are collectively referred to ...
EARLY ATOMIC THEORY AND STRUCTURE
... 3. Gold nuclei are very massive (compared to an alpha particle) and have a large positive charge. As the positive alpha particles approach the atom, some are deflected by this positive charge. Alpha particles approaching a gold nucleus directly are deflected backwards by the massive positive nucleus ...
... 3. Gold nuclei are very massive (compared to an alpha particle) and have a large positive charge. As the positive alpha particles approach the atom, some are deflected by this positive charge. Alpha particles approaching a gold nucleus directly are deflected backwards by the massive positive nucleus ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
... • The aufbau diagram can be used to write correct ground-state electron configurations for all elements up to and including Vanadium, atomic number 23. • The electron configurations for certain transition metals, like chromium and copper, do not follow the aufbau diagram due to increased stability o ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint Notes
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
Atoms and Elements Atoms and Elements
... Atoms have structure and volume “Gold can be divided into smaller pieces only so far before the pieces no longer retain the properties of gold” Smallest unit of matter = atomos, atoms MAR ...
... Atoms have structure and volume “Gold can be divided into smaller pieces only so far before the pieces no longer retain the properties of gold” Smallest unit of matter = atomos, atoms MAR ...
Unit_1_The_Atom
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
Powerpoint
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
... since they have the same charge. • The nucleus is held together by a mysterious force called the strong nuclear force which only exists between nucleons (protons and neutrons) which are very close together. ...
ch02 lecture 7e
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
... All matter consists of atoms; tiny indivisible particles of an element that cannot be created or destroyed. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element. Atoms of an element are identical in mass and other properties and are different from the atoms of any other element. Co ...
Ch:3
... h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J s Electromagnetic energy (light) is quantized. Quantum: The amount of energy corresponding to one photon of light. Chapter 3/14 ...
... h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J s Electromagnetic energy (light) is quantized. Quantum: The amount of energy corresponding to one photon of light. Chapter 3/14 ...
Chapter 4 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...