Page 233 - ClassZone
... some of the terms shown in the word box at right. Underline each term you use in your answer. 7. Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who claimed that all matter was made of tiny particles he called atoms. Democritus said that all atoms were made of the same material. The objects of the world ...
... some of the terms shown in the word box at right. Underline each term you use in your answer. 7. Democritus was an ancient Greek philosopher who claimed that all matter was made of tiny particles he called atoms. Democritus said that all atoms were made of the same material. The objects of the world ...
VOCABULARY name, date, hour: Fill in the number of each term
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
... ___ positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom ___ stable, orbiting particle of an atom with a negative charge ___ substance that is a mixture of two or more metals ___ columns of the periodic table; also known as groups ___ number of protons carried by the nucleus of an atom ___ el ...
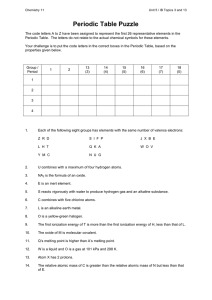
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The relative atomic mass of C is greater than the relative atomic mass of N but less than that of E. ...
... The relative atomic mass of C is greater than the relative atomic mass of N but less than that of E. ...
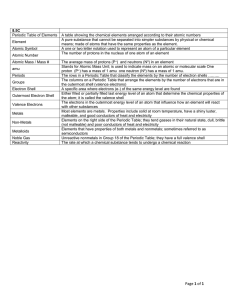
CI_Chap_1_Test_A_Study_Guide
... A metalloid is an element that has properties of both metals and non-metals. Metals are easy to shape by drawing into long thin wire and have a shiny surface. Halogens are elements often used to kill bacteria. Transition metals like Gold are toward the middle of the periodic table. The most common e ...
... A metalloid is an element that has properties of both metals and non-metals. Metals are easy to shape by drawing into long thin wire and have a shiny surface. Halogens are elements often used to kill bacteria. Transition metals like Gold are toward the middle of the periodic table. The most common e ...
History of the Atom and Periodic Table
... had a neutral charge and it is called the neutron. His discovery made us realize isotopes existed. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons. Proved Dalton’s Atomic theory was incorrect again by showing atoms of the same element can be different. ...
... had a neutral charge and it is called the neutron. His discovery made us realize isotopes existed. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons. Proved Dalton’s Atomic theory was incorrect again by showing atoms of the same element can be different. ...
Slide 1
... • 1a. You will know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. ...
... • 1a. You will know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. ...
Review: Atomic structure/Periodic Table
... Read/interpret information from the periodic table (atomic mass, name, symbol, atomic number) Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for any element Relate the organization of the Periodic Table to the arrangement of electrons within an atom Explain the relationship between ...
... Read/interpret information from the periodic table (atomic mass, name, symbol, atomic number) Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for any element Relate the organization of the Periodic Table to the arrangement of electrons within an atom Explain the relationship between ...
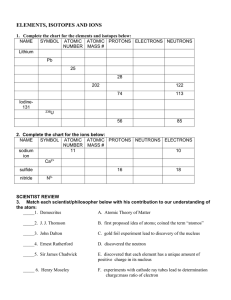
ELEMENTS, ISOTOPES AND IONS
... SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER MASS # sodium ...
... SYMBOL ATOMIC ATOMIC PROTONS NEUTRONS ELECTRONS NUMBER MASS # sodium ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... • Electron cloud – cloud that surrounds the nucleus of an atom that describes the region in which an electron is most likely to be. – Example: students in a school ...
... • Electron cloud – cloud that surrounds the nucleus of an atom that describes the region in which an electron is most likely to be. – Example: students in a school ...
The study of biology can help you better understand human
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
... Which subatomic particle determines chemical properties of an element? ...
Minerals * Chemistry Review
... the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
... the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
here
... After reading that section, click the link for Section 2d, “More Electron Basics” and read through this page. Pay attention to how ionization energy, electronegativity and atomic size (radius) are impacted as you move along the periodic table. ...
... After reading that section, click the link for Section 2d, “More Electron Basics” and read through this page. Pay attention to how ionization energy, electronegativity and atomic size (radius) are impacted as you move along the periodic table. ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
... Review“The Periodic Table” 1. How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? 2. All atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... nonmetal. Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemica ...
... nonmetal. Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemica ...
AP chemistry Test Review
... c) Most alpha particles passed through the gold foil without being deflected since the nuclei of the gold atoms represent such a small portion of the atomic mass. d) Because of the electrons small masses they did not deflect the alpha particles. e) The high charge of the gold nuclei helps to account ...
... c) Most alpha particles passed through the gold foil without being deflected since the nuclei of the gold atoms represent such a small portion of the atomic mass. d) Because of the electrons small masses they did not deflect the alpha particles. e) The high charge of the gold nuclei helps to account ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
... gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
IPC Atoms and Periodic Table
... Actinide Series • Fifteen elements that start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
... Actinide Series • Fifteen elements that start with actinium (Ac) at atomic number 89 and finishing up with lawrencium (Lr) at number 103. • They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. ...
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation (complete and noble gas). Define valence electrons and apply this knowledge to determi ...
... Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diagrams and electron configuration notation (complete and noble gas). Define valence electrons and apply this knowledge to determi ...
Ions
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
... particle called an ion. When an atom loses an electron it has more protons therefore becoming positively charged. When an atom gains an electron it has more electrons therefore becoming negatively charged. ...
– Units 5-7 Review Honors Chemistry Unit 5
... Consider the following atoms: Ne, Na, Mg. a. Which atom has the largest first ionization energy? Explain. b. Which atom is least likely to form a bond? Explain. For each of the following pairs of elements, (Li and K) and (S and Cl), pick the atom with: a. higher ionization energy b. larger size Why ...
... Consider the following atoms: Ne, Na, Mg. a. Which atom has the largest first ionization energy? Explain. b. Which atom is least likely to form a bond? Explain. For each of the following pairs of elements, (Li and K) and (S and Cl), pick the atom with: a. higher ionization energy b. larger size Why ...