Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... 1 hartree 27.2114 electron volts 1 rydberg 13.606 electron volts ...
... 1 hartree 27.2114 electron volts 1 rydberg 13.606 electron volts ...
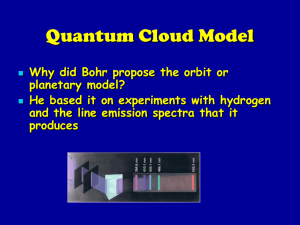
Modern Model of the Atom Student Notes and Assignment
... The ways in which electrons are arranged around the nuclei of atoms are called ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS. The rules that govern the way the electrons fill the atomic orbitals are: 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic ...
... The ways in which electrons are arranged around the nuclei of atoms are called ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS. The rules that govern the way the electrons fill the atomic orbitals are: 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic ...
PS7 - Bergen.org
... (a) Why is it that irradiating a piece of a metal with short wavelength light causes an electron to be ejected, yet irradiating the same piece of metal with longer wavelength light yields no electrons? ...
... (a) Why is it that irradiating a piece of a metal with short wavelength light causes an electron to be ejected, yet irradiating the same piece of metal with longer wavelength light yields no electrons? ...
Physical Chemistry
... • The world is deterministic » Physics was complete except for a few decimal places ! ...
... • The world is deterministic » Physics was complete except for a few decimal places ! ...
ChemicalBondingTestAnswers
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
... The charge on the nucleus – On moving from left to right, the effective nuclear charge increases. The distance of the electron from the nucleus – On moving from left to right in a period, the distance of the electron from the nucleus decreases a little . The number of electrons between the outer ele ...
1. The primitive translation vectors of the hexagonal space lattice
... electron gas in which the electrons are restricted to move freely within its boundary (3-D: L3, 2-D: L2, 1-D: L). (a) Show that the density of states, g E , for the 3-D, 2-D and 1-D systems are (i) E (ii) constant (iii) 1 ...
... electron gas in which the electrons are restricted to move freely within its boundary (3-D: L3, 2-D: L2, 1-D: L). (a) Show that the density of states, g E , for the 3-D, 2-D and 1-D systems are (i) E (ii) constant (iii) 1 ...
Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
... elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound ...
Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom
... • 1 eV = kinetic energy of an electron that has been accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V ...
... • 1 eV = kinetic energy of an electron that has been accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V ...
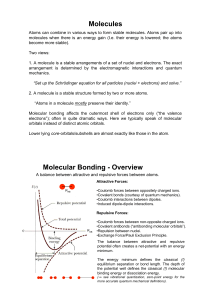
Molecules Molecular Bonding
... The balance between attractive and repulsive potential often creates a net-potential with an energy minimum. The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecular binding energy or dissociation energy. ...
... The balance between attractive and repulsive potential often creates a net-potential with an energy minimum. The energy minimum defines the classical (!) equilibrium separation or bond length. The depth of the potential well defines the classical (!) molecular binding energy or dissociation energy. ...
AP Chemistry
... What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with visible light of wavelength 550 nm? ...
... What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with visible light of wavelength 550 nm? ...
Atomic Radii Answers File
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
NAME PRACTICE: QUANTUM CONFIGURATIONS 1) Each of the
... ___31) N2 molecules absorb ultraviolet light but not visible light. I2 molecules absorb both visible and ultraviolet light. Which of the following statements explains the observations? 1) More energy is required to make N2 molecules vibrate than is required to make I2 molecules vibrate 2) More energ ...
... ___31) N2 molecules absorb ultraviolet light but not visible light. I2 molecules absorb both visible and ultraviolet light. Which of the following statements explains the observations? 1) More energy is required to make N2 molecules vibrate than is required to make I2 molecules vibrate 2) More energ ...
Superconcepts
... ix. De Broglie found that electrons behaved as waves in diffraction experiments in 1924. x. Schrödinger showed that atomic wave spectra (electrons) could be predicted by wave functions in 1926. xi. Heisinger found that atomic properties were ‘indeterminant’ or uncertain in 1927. xii. When the double ...
... ix. De Broglie found that electrons behaved as waves in diffraction experiments in 1924. x. Schrödinger showed that atomic wave spectra (electrons) could be predicted by wave functions in 1926. xi. Heisinger found that atomic properties were ‘indeterminant’ or uncertain in 1927. xii. When the double ...
Name
... III. S has a greater number of electrons than P, so the third energy level is further from the nucleus in S than in P. IV. S has a greater number of electrons than P, so the Coulombic attraction between the electron cloud and the nucleus is greater in S than in P. ...
... III. S has a greater number of electrons than P, so the third energy level is further from the nucleus in S than in P. IV. S has a greater number of electrons than P, so the Coulombic attraction between the electron cloud and the nucleus is greater in S than in P. ...
Atomic Theory (Or a quick Chemistry Review)
... Atomic Theory Q: What does science study? A: The natural world, the physical universe Q: What are the components of the P.U? A: matter, energy, forces ...
... Atomic Theory Q: What does science study? A: The natural world, the physical universe Q: What are the components of the P.U? A: matter, energy, forces ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy

X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a material with a beam of X-rays while simultaneously measuring the kinetic energy and number of electrons that escape from the top 0 to 10 nm of the material being analyzed. XPS requires high vacuum (P ~ 10−8 millibar) or ultra-high vacuum (UHV; P < 10−9 millibar) conditions, although a current area of development is ambient-pressure XPS, in which samples are analyzed at pressures of a few tens of millibar.XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its as-received state, or after some treatment, for example: fracturing, cutting or scraping in air or UHV to expose the bulk chemistry, ion beam etching to clean off some or all of the surface contamination (with mild ion etching) or to intentionally expose deeper layers of the sample (with more extensive ion etching) in depth-profiling XPS, exposure to heat to study the changes due to heating, exposure to reactive gases or solutions, exposure to ion beam implant, exposure to ultraviolet light.XPS is also known as ESCA (Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis), an abbreviation introduced by Kai Siegbahn's research group to emphasize the chemical (rather than merely elemental) information that the technique provides.In principle XPS detects all elements. In practice, using typical laboratory-scale X-ray sources, XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot easily detect hydrogen (Z = 1) or helium (Z = 2).Detection limits for most of the elements (on a modern instrument) are in the parts per thousand range. Detection limits of parts per million (ppm) are possible, but require special conditions: concentration at top surface or very long collection time (overnight).XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.XPS is less routinely used to analyze the hydrated forms of some of the above materials by freezing the samples in their hydrated state in an ultra pure environment, and allowing or causing multilayers of ice to sublime away prior to analysis. Such hydrated XPS analysis allows hydrated sample structures, which may be different from vacuum-dehydrated sample structures, to be studied in their more relevant as-used hydrated structure. Many bio-materials such as hydrogels are examples of such samples.