Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is the electron configuration of potassium? a. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s c. 1s 2s 3s 3p 3d b. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p d. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s ____ 53. Which of the following electromagnetic wav ...
... ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is the electron configuration of potassium? a. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s c. 1s 2s 3s 3p 3d b. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p d. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s ____ 53. Which of the following electromagnetic wav ...
The Periodic Table
... than two electrons. Fill it first. • 3) Put electrons in the second shell. It can hold up to eight. • 4) Put electrons in the third shell. It can also hold up to eight. ...
... than two electrons. Fill it first. • 3) Put electrons in the second shell. It can hold up to eight. • 4) Put electrons in the third shell. It can also hold up to eight. ...
Name Class Block ______ Directions: Read the following article
... The Greek philosopher Democritus named the tiny particles everything was made of “atoms.” Although Democritus had no way to test his theory, he was correct. Today, we know atoms are the building blocks of matter. Because scientists did not have instruments to see atoms, Democritus’ ideas were forgot ...
... The Greek philosopher Democritus named the tiny particles everything was made of “atoms.” Although Democritus had no way to test his theory, he was correct. Today, we know atoms are the building blocks of matter. Because scientists did not have instruments to see atoms, Democritus’ ideas were forgot ...
Revision topic 1-3
... superscripts must always total the number of electrons in the atom (or ion). ...
... superscripts must always total the number of electrons in the atom (or ion). ...
Atomic Structure. Chemical Bonds.
... Hydrogen and Alkali Metals: Single outer electrons, which see only +e charge and are loosely bound to the nucleus, lose the outermost electrons in chemical reactions, have similar behavior, and are chemically active ...
... Hydrogen and Alkali Metals: Single outer electrons, which see only +e charge and are loosely bound to the nucleus, lose the outermost electrons in chemical reactions, have similar behavior, and are chemically active ...
Labs - newtunings.com
... 3.4g A catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway, which has a lower activation energy than an uncatalyzed reaction. 3.4h Some chemical and physical changes can reach equilibrium. 3.4i At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. The measurable quanti ...
... 3.4g A catalyst provides an alternate reaction pathway, which has a lower activation energy than an uncatalyzed reaction. 3.4h Some chemical and physical changes can reach equilibrium. 3.4i At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. The measurable quanti ...
Chemistry FINAL: CONTENT Review Packet
... a) The least significant intermolecular forces? _______________ 10. A liquid will boil when its equilibrium vapor pressure EQUALS____________________________. 11. When a system at equilibrium is disturbed by application of a stress, it attains a new equilibrium position that minimizes the stress. Th ...
... a) The least significant intermolecular forces? _______________ 10. A liquid will boil when its equilibrium vapor pressure EQUALS____________________________. 11. When a system at equilibrium is disturbed by application of a stress, it attains a new equilibrium position that minimizes the stress. Th ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table (Chapter 2)
... Z = atomic number of an element = # protons in nucleus e.g., carbon is atomic number 6 -- all carbon atoms have 6 protons A = mass number (often omitted) = # protons + # neutrons Y = charge (on an ion) = # protons - # electrons isotopes - atoms of the same element with different mass numbers e.g., ...
... Z = atomic number of an element = # protons in nucleus e.g., carbon is atomic number 6 -- all carbon atoms have 6 protons A = mass number (often omitted) = # protons + # neutrons Y = charge (on an ion) = # protons - # electrons isotopes - atoms of the same element with different mass numbers e.g., ...
Chapt2
... Z = atomic number of an element = # protons in nucleus e.g., carbon is atomic number 6 -- all carbon atoms have 6 protons A = mass number (often omitted) = # protons + # neutrons Y = charge (on an ion) = # protons - # electrons isotopes - atoms of the same element with different mass numbers e.g., ...
... Z = atomic number of an element = # protons in nucleus e.g., carbon is atomic number 6 -- all carbon atoms have 6 protons A = mass number (often omitted) = # protons + # neutrons Y = charge (on an ion) = # protons - # electrons isotopes - atoms of the same element with different mass numbers e.g., ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
... Periods – Rows are called periods. The elements in these rows change conductivity and number of electrons as you move across the table. Groups – Columns are called groups or families. These elements have the same properties because of the number of electrons. ...
Chemistry for Biology
... Medical uses for radioactive isotopes A PET scan is one of the many medical uses for radioactive isotopes PET, short for positronemission tomography, can detect intense chemical activity in the body. Brightly colored areas indicate elevated levels of radioactively-labeled glucose and high metabolic ...
... Medical uses for radioactive isotopes A PET scan is one of the many medical uses for radioactive isotopes PET, short for positronemission tomography, can detect intense chemical activity in the body. Brightly colored areas indicate elevated levels of radioactively-labeled glucose and high metabolic ...
CHEMISTRY
... elements to combine and form compounds depends on the number and arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level • Atoms are most stable when their outer most energy level is full ...
... elements to combine and form compounds depends on the number and arrangement of electrons in their outermost energy level • Atoms are most stable when their outer most energy level is full ...
Atoms - McEachern High School
... • All you have to know the rules that atoms follows. • Rules – The first energy level (or ring around the nucleus) only can hold 2 electrons – Once the first ring is “full”, the next set of electrons will begin to fill in to a new energy level. – With the exception of the first energy level, All ou ...
... • All you have to know the rules that atoms follows. • Rules – The first energy level (or ring around the nucleus) only can hold 2 electrons – Once the first ring is “full”, the next set of electrons will begin to fill in to a new energy level. – With the exception of the first energy level, All ou ...
Chapters 19 & 20
... Non of these elements behaves as a metal They achive the noble gas configuration by adding 2 electrons to become 2anion G 6A elements can form covalent bonds with other nonmetals Due to the presence of empty d orbitals (except O), they form molecules in which central atom is surrounded by more than ...
... Non of these elements behaves as a metal They achive the noble gas configuration by adding 2 electrons to become 2anion G 6A elements can form covalent bonds with other nonmetals Due to the presence of empty d orbitals (except O), they form molecules in which central atom is surrounded by more than ...
Matter - Moodle
... • __________________ with other elements • _________________ __________________ into new substances Chemical properties include: ...
... • __________________ with other elements • _________________ __________________ into new substances Chemical properties include: ...
1b Atomic Structure
... losing a single electron rather than stealing seven electrons. Hence, sodium atoms lose and electron, leaving them with 10 electrons and 11 protons. Doing the math, this means the total charge on sodium ion would be (-10 + +11 = +1), and is written as Na+1. ...
... losing a single electron rather than stealing seven electrons. Hence, sodium atoms lose and electron, leaving them with 10 electrons and 11 protons. Doing the math, this means the total charge on sodium ion would be (-10 + +11 = +1), and is written as Na+1. ...
Name: Period:______ PHYSICAL SCIENCE 1st Semester Final
... Mendeleev arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that the elements with similar properties were in the same column. The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual properties of new elements showed how useful his periodic table could be. In the modern per ...
... Mendeleev arranged the elements into rows in order of increasing mass so that the elements with similar properties were in the same column. The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual properties of new elements showed how useful his periodic table could be. In the modern per ...
Intro Notes - Mrs. Gionta
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • Changes in potential energy occur in steps of fixed amounts • An ele ...
... The Energy Levels of Electrons • Energy is the capacity to cause change • Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure • The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of potential energy • Changes in potential energy occur in steps of fixed amounts • An ele ...
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation FOURTH EDITION by
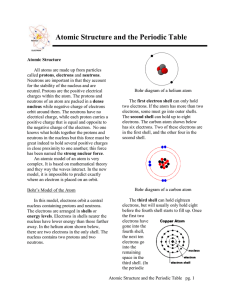
... Rutherford’s Nuclear Model The atom contains a tiny dense center called the nucleus – the volume is about 1/10 trillionth the volume of the atom The nucleus is essentially the entire mass of the atom The nucleus is positively charged – the amount of positive charge of the nucleus balances the ...
... Rutherford’s Nuclear Model The atom contains a tiny dense center called the nucleus – the volume is about 1/10 trillionth the volume of the atom The nucleus is essentially the entire mass of the atom The nucleus is positively charged – the amount of positive charge of the nucleus balances the ...
Name
... 4. Who did their research with the Cathode Ray Tube (CRT ?_________________ & __________________ 5. Who discovered the electron? _______________________ 6. Who discovered the atom is mostly empty space? _______________________ 7. Who discovered that elements of the same element have the same number ...
... 4. Who did their research with the Cathode Ray Tube (CRT ?_________________ & __________________ 5. Who discovered the electron? _______________________ 6. Who discovered the atom is mostly empty space? _______________________ 7. Who discovered that elements of the same element have the same number ...
(+) = # of electrons
... • Know how to classify atoms as metals, non-metals, and metalloids. • Know the period classifications – Alkali, Alkaline, Transition Metals, main block, halogens, noble gas ...
... • Know how to classify atoms as metals, non-metals, and metalloids. • Know the period classifications – Alkali, Alkaline, Transition Metals, main block, halogens, noble gas ...