Atomic Model Review
... • Bohr improved on the model by determining that electrons were in specific orbits around the positively charged nucleus • These orbits have specific set of distances from the nucleus – Electrons in orbitals closer to the nucleus are harder to remove, as they are more strongly attracted to the posit ...
... • Bohr improved on the model by determining that electrons were in specific orbits around the positively charged nucleus • These orbits have specific set of distances from the nucleus – Electrons in orbitals closer to the nucleus are harder to remove, as they are more strongly attracted to the posit ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... An atom which loses an electron changes it’s name to what? What is the molecular mass of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)? What is the octet rule, where atoms want to become stable? ...
... An atom which loses an electron changes it’s name to what? What is the molecular mass of Carbon Dioxide (CO2)? What is the octet rule, where atoms want to become stable? ...
Unit 2 Review Questions Fill in the blank In a(n) change, a new
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
Chp 3 notes Click Here
... Atoms can gain from other atoms or lose electrons to other atoms. An atom that loses an electron has a net positive charge because there are more protons than electrons. Remember the atom started with equal numbers of protons and electrons. An atom that gains an electron has a net negative charge be ...
... Atoms can gain from other atoms or lose electrons to other atoms. An atom that loses an electron has a net positive charge because there are more protons than electrons. Remember the atom started with equal numbers of protons and electrons. An atom that gains an electron has a net negative charge be ...
- MrKowalik.com
... • You can’t just shove all of the electrons into the first orbit of an electron. • Electrons live in something called shells or energy levels. • Only so many electrons can be in any certain shell. • The outer most shell is called the valance shell. • The electrons in the outer most shell of any elem ...
... • You can’t just shove all of the electrons into the first orbit of an electron. • Electrons live in something called shells or energy levels. • Only so many electrons can be in any certain shell. • The outer most shell is called the valance shell. • The electrons in the outer most shell of any elem ...
Document
... Problem: How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in the following atoms: protons electrons ...
... Problem: How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in the following atoms: protons electrons ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
... 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 77. The name of the group which contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine is 78. When they react chemically, the halogens (Group VII or 17) change in what way? Naming, Bonding and W ...
Cahpter 19 – Properties of Atoms and the Periodic table
... proposed the idea that atoms make up all substances Aristotle disputed Democritus' theory and said matter was uniform throughout and not composed of smaller particles Aristotle had more clout and his theory held for more than 2000 years http://academic.shu.edu/honors/aristotle.jpg ...
... proposed the idea that atoms make up all substances Aristotle disputed Democritus' theory and said matter was uniform throughout and not composed of smaller particles Aristotle had more clout and his theory held for more than 2000 years http://academic.shu.edu/honors/aristotle.jpg ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Structure of...
... Chlorine ( Z = 17) has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 7. Since the number of electrons in the outermost shell is close to full capacity, therefore it is easier for chlorine to gain one electron rather than lose seven electrons to achieve an octet. Therefore valency is determined by subtracting s ...
... Chlorine ( Z = 17) has the electronic configuration 2, 8, 7. Since the number of electrons in the outermost shell is close to full capacity, therefore it is easier for chlorine to gain one electron rather than lose seven electrons to achieve an octet. Therefore valency is determined by subtracting s ...
Atoms and Elements
... The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. ...
... The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. ...
1. All matter is made up of
... electricity 56. Explain some of the properties of nonmetals. • They are brittle, have no luster and they are not good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... electricity 56. Explain some of the properties of nonmetals. • They are brittle, have no luster and they are not good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
... Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
... Energy levels (n=1, 2, 3, 4,…) – represented by periods on the periodic table Sublevels: (s, p, d, f) – represented by blocks on the periodic table Orbitals – region of space where up to 2 electrons may be found ...
Unit 3 Review Worksheet
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
... c. The period 6 alkaline earth metal: _____________________________________ d. The metalloid in group 16: _____________________________________ e. The only nonmetal in group 14: _____________________________________ ...
atomic number
... Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms. -cations – have more protons than electrons and are positively charged -anions – have more electrons than protons and are negatively charged ...
... Neutral atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged atoms. -cations – have more protons than electrons and are positively charged -anions – have more electrons than protons and are negatively charged ...
Section 12.1 - CPO Science
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
12.1 Structure of the Atom - appleg8
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
... 12.1 How atoms of various elements are different Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The mass number of an isotope tells you the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. How are these carbon isotopes different? ...
Measuring the Atom
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
... There are many subatomic particles, but we will limit our discussion to protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus and are therefore called nucleons. The electrons are found outside of the nucleus (more on that in a month or so) ...
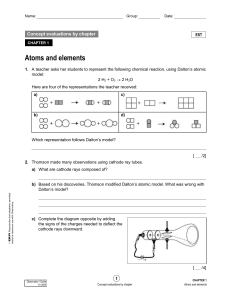
11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
... formulated certain predictions about the properties of unknown elements. For example, he predicted that the atomic mass of an element with the atomic number 32 would be 72 u and that its density would be 5.5 g/mL. Refer to the periodic table and to Appendix 1 of the student book to see whether Mende ...
... formulated certain predictions about the properties of unknown elements. For example, he predicted that the atomic mass of an element with the atomic number 32 would be 72 u and that its density would be 5.5 g/mL. Refer to the periodic table and to Appendix 1 of the student book to see whether Mende ...