Chapter 2 Test Review - Mercer Island School District
... 13. An atom emits 3 colors of light, Red, Blue and Violet when excited by an E.M. wave. Draw the Bohr Model of an atom that shows these colors of light being emitted • See the “Electron: How does it behave” Notes. This packet covers EM Waves and the Bohr Model. ...
... 13. An atom emits 3 colors of light, Red, Blue and Violet when excited by an E.M. wave. Draw the Bohr Model of an atom that shows these colors of light being emitted • See the “Electron: How does it behave” Notes. This packet covers EM Waves and the Bohr Model. ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
... charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud 8.5 (B) Identify that protons determine an element’s identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... His ideas did agree with later scientific theory, but did not explain chemical behavior, and was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
... His ideas did agree with later scientific theory, but did not explain chemical behavior, and was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... seem to explain much more experimental observations and the arrangement elements in the periodic table. According to new Wave-mechanical model an electron a hydrogen atom has addition features: 1) Each shell could have sub-shells called s, p, d and f. Listed below is sub-shell description of each sh ...
... seem to explain much more experimental observations and the arrangement elements in the periodic table. According to new Wave-mechanical model an electron a hydrogen atom has addition features: 1) Each shell could have sub-shells called s, p, d and f. Listed below is sub-shell description of each sh ...
File - 7th Grade Science
... • Many buildings are made of just a few basic building materials, such as wood, nails, and glass. You can combine those materials in many different ways to make buildings of various shapes and sizes. How many things can you make from ...
... • Many buildings are made of just a few basic building materials, such as wood, nails, and glass. You can combine those materials in many different ways to make buildings of various shapes and sizes. How many things can you make from ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part A
... • Large solute particles that do not settle out • Undergo sol-gel transformations ...
... • Large solute particles that do not settle out • Undergo sol-gel transformations ...
electrons.
... The atomic number of an element gives the number of protons in the nucleus The mass number of an element gives the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus ...
... The atomic number of an element gives the number of protons in the nucleus The mass number of an element gives the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus ...
Atom
... It had been known for some time that the light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, but no one had been able to explain this. Bohr suggested that the electrons must be orbiting the nucleus in certain fixed energy levels (or shells). The nucleus is the centre of an ...
... It had been known for some time that the light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, but no one had been able to explain this. Bohr suggested that the electrons must be orbiting the nucleus in certain fixed energy levels (or shells). The nucleus is the centre of an ...
Notes - Zion Central Middle School
... Average atomic mass is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. ...
... Average atomic mass is the weighted-average mass of an element’s isotopes. ...
Created by Campesi, SMS
... Neutron-neutral particle inside the nucleus with a mass of 1 amu. Neutrons just make an atom “fat.” ...
... Neutron-neutral particle inside the nucleus with a mass of 1 amu. Neutrons just make an atom “fat.” ...
q2-w4-hw-atomic-vocab - PARADE 7/8 STEM
... 15. The _______________ is always a whole number. A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Atomic mass 16. To get the number of neutrons for an element, we take the _____ and subtract the ______. A. mass number minus the atomic number B. atomic number minus the mass number 17. In the case of Sodium, calcu ...
... 15. The _______________ is always a whole number. A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Atomic mass 16. To get the number of neutrons for an element, we take the _____ and subtract the ______. A. mass number minus the atomic number B. atomic number minus the mass number 17. In the case of Sodium, calcu ...
Name - Quia
... Explain what a nuclide is, and describe the different ways nuclides can be represented. Define and relate the terms mass defect and nuclear binding energy. Explain the relationship between nucleon number and stability of nuclei. Explain why nuclear reactions occur and know how to balance a nuclear ...
... Explain what a nuclide is, and describe the different ways nuclides can be represented. Define and relate the terms mass defect and nuclear binding energy. Explain the relationship between nucleon number and stability of nuclei. Explain why nuclear reactions occur and know how to balance a nuclear ...
Physical Properties
... (atomic mass – atomic number) under it. 3. Place the number of electrons (same as protons) in orbits around the nucleus by drawing circles around the nucleus. Remember: 1st shell – 2 electrons 2nd shell – 8 electrons 3rd shell – 8 electrons 4th shell – 18 electrons. ...
... (atomic mass – atomic number) under it. 3. Place the number of electrons (same as protons) in orbits around the nucleus by drawing circles around the nucleus. Remember: 1st shell – 2 electrons 2nd shell – 8 electrons 3rd shell – 8 electrons 4th shell – 18 electrons. ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 2
... • Arranged elements by chemical properties • Left space for elements unknown at the time • Predicted detailed properties for elements as yet unknown • Sc, Ga, Ge • By 1886, all these elements had been discovered, and with properties similar to those he predicted ...
... • Arranged elements by chemical properties • Left space for elements unknown at the time • Predicted detailed properties for elements as yet unknown • Sc, Ga, Ge • By 1886, all these elements had been discovered, and with properties similar to those he predicted ...
Fall 2015 Review-2
... ____ 37. The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____. a. gain electrons when they form ions c. all have ions with a 1 charge b. all form ions with a negative charge d. lose electrons when they form ions ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neu ...
... ____ 37. The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____. a. gain electrons when they form ions c. all have ions with a 1 charge b. all form ions with a negative charge d. lose electrons when they form ions ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neu ...
download
... Ionic bonding occurs between charged particles. These may be atoms or groups of atoms, but this discuss will be conducted in terms of single atoms. Ionic bonding occurs between metal atoms and nonmetal atoms. Metals usually have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in their outermost shell. Nonmetals have 5, 6, or ...
... Ionic bonding occurs between charged particles. These may be atoms or groups of atoms, but this discuss will be conducted in terms of single atoms. Ionic bonding occurs between metal atoms and nonmetal atoms. Metals usually have 1, 2, or 3 electrons in their outermost shell. Nonmetals have 5, 6, or ...
Electronic Structure
... the first core electron) rises dramatically, 27,100 kJ/mol. The 1st, 2nd, and 3rd ionization potentials for Aluminum { [Ne]3s23p1 }are respectively, 578 kJ/mol, 1820 kJ/mol & 2750 kJ/mol. But the 4th ionization potential also rises dramatically, 11,600 kJ/mol. Ionization potentials tend to increase ...
... the first core electron) rises dramatically, 27,100 kJ/mol. The 1st, 2nd, and 3rd ionization potentials for Aluminum { [Ne]3s23p1 }are respectively, 578 kJ/mol, 1820 kJ/mol & 2750 kJ/mol. But the 4th ionization potential also rises dramatically, 11,600 kJ/mol. Ionization potentials tend to increase ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry comes alive
... the nucleus of an atom Bonds are formed using the electrons in the outermost energy level Valence shell – outermost energy level containing chemically active electrons Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in thei ...
... the nucleus of an atom Bonds are formed using the electrons in the outermost energy level Valence shell – outermost energy level containing chemically active electrons Octet rule – except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have eight electrons in thei ...
What is the Matter?
... • The top number is the atomic number. The atomic number tells how many protons are in one atom of that element. • The bigger number is the atomic mass. The atomic mass is the sum of the protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
... • The top number is the atomic number. The atomic number tells how many protons are in one atom of that element. • The bigger number is the atomic mass. The atomic mass is the sum of the protons, neutrons, and electrons. ...
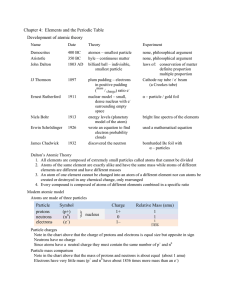
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
... Conductivity – most metals are good conductors of heat and electricity Luster – most metals are very shiny or have high metallic luster Magnetic – many metals (but not all) are attracted to magnets Chemical properties of metals Reactivity – metals react by losing electrons to form positive ions Some ...
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table - (Home) Collinsville Public
... Group 8A are noble gases Group 7A called halogens ...
... Group 8A are noble gases Group 7A called halogens ...