Atomic Structure DEMOCRITUS JOHN DALTON
... • d and f are the next two orbitals. They occupy even higher energy levels and take on more complex shapes than s & p ...
... • d and f are the next two orbitals. They occupy even higher energy levels and take on more complex shapes than s & p ...
Chapter Review- Josh and Niels 1. Rutherford`s Atom • Rutherford`s
... Bohr used hydrogen to construct a model of the atom Came up with a dot in middle (nucleus) and circles around it for the atoms to go into o Wrong because different shapes per some orbitals such as p,d,f 6. The Wave Mechanical Model of the Atom Wave Mechanical Model: Bohr’s model except without ...
... Bohr used hydrogen to construct a model of the atom Came up with a dot in middle (nucleus) and circles around it for the atoms to go into o Wrong because different shapes per some orbitals such as p,d,f 6. The Wave Mechanical Model of the Atom Wave Mechanical Model: Bohr’s model except without ...
Ground state electron arrangement
... Write ground-state electron configurations for the following elements. a. Chlorine _________________________________________________ b. Silicon _________________________________________________ c. Carbon _________________________________________________ ...
... Write ground-state electron configurations for the following elements. a. Chlorine _________________________________________________ b. Silicon _________________________________________________ c. Carbon _________________________________________________ ...
rev8thgrade - PAMS
... atom of any element and you no longer have the original element in any form. Now you have a different element! ...
... atom of any element and you no longer have the original element in any form. Now you have a different element! ...
Atomic Structure
... Rutherford’s •1908 Model •Discovered that atoms have dense, positively charged nucleus •Fired charged particles at gold foil, some went through while others were deflected. ...
... Rutherford’s •1908 Model •Discovered that atoms have dense, positively charged nucleus •Fired charged particles at gold foil, some went through while others were deflected. ...
The Fundamental Ideas in Chemistry
... atom ______. Atoms with ____outer energy levels are unreactive. These are called the _____ _____. They are unreactive because their atoms have _______ arrangements of electrons . ...
... atom ______. Atoms with ____outer energy levels are unreactive. These are called the _____ _____. They are unreactive because their atoms have _______ arrangements of electrons . ...
Game Face: Quarter Test Review Answers You`re Welcome, Please
... b. Electrons are found in a large, solid, positively charged mass c. Protons and electrons are both found In the nucleus of an atom d. Electrons are found in a cloud around the positive nucleus 43. What is the nuclear (nucleus) composition of potassium – 40? a. 19 electrons + 19 protons correct numb ...
... b. Electrons are found in a large, solid, positively charged mass c. Protons and electrons are both found In the nucleus of an atom d. Electrons are found in a cloud around the positive nucleus 43. What is the nuclear (nucleus) composition of potassium – 40? a. 19 electrons + 19 protons correct numb ...
Atomic Structure - LFlemingPhysicalScience
... Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels ha ...
... Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels ha ...
Atoms - Sackville School
... This is a diagram of a CD. The diameter of its hole is one-eighth of the diameter of the ...
... This is a diagram of a CD. The diameter of its hole is one-eighth of the diameter of the ...
Atom
... • Atoms of an element don’t always have the same # of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. ...
... • Atoms of an element don’t always have the same # of neutrons. • These atoms are called isotopes. ...
Inside An Atom
... Protons are the positively charged particles found inside the nucleus of an atom Every element has a unique atomic #. This # is the amount of protons inside that elements nucleus For Example: Oxygen has an atomic # of 8. How many protons does it have? ...
... Protons are the positively charged particles found inside the nucleus of an atom Every element has a unique atomic #. This # is the amount of protons inside that elements nucleus For Example: Oxygen has an atomic # of 8. How many protons does it have? ...
Name Date Period DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 5. Atoms of one element change into atoms of another element during chemical reactions. 6. Atoms combine in one-to-one ratios to form compounds. 7. Atoms of one element are different from a ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 5. Atoms of one element change into atoms of another element during chemical reactions. 6. Atoms combine in one-to-one ratios to form compounds. 7. Atoms of one element are different from a ...
Chapter 3 Test 2000
... A neutral atom of chlorine 35 has ______________________. a. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. b. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. c. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. d. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. ...
... A neutral atom of chlorine 35 has ______________________. a. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 18 neutrons. b. 35 protons, 35 electrons, and 17 neutrons. c. 17 protons, 17 electrons, and 52 neutrons. d. 18 protons, 18 electrons, and 17 neutrons. ...
Atom? - Its All about the Science
... Atomic Theory: Like charges repel so the nucleus must have a positive charge. If electrons have a negative charge they could not be in a positively charged nucleus. Electrons must surround the nucleus at a distance. Result: The diameter of the nucleus is 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of th ...
... Atomic Theory: Like charges repel so the nucleus must have a positive charge. If electrons have a negative charge they could not be in a positively charged nucleus. Electrons must surround the nucleus at a distance. Result: The diameter of the nucleus is 100,000 times smaller than the diameter of th ...
Atomic Theories Powerpoint
... Took his own experiments and those of others to write a paper, which later became known as the Modern Atomic Theory It gave a compilation of the information at the time and allowed other scientist to test his ideas. ...
... Took his own experiments and those of others to write a paper, which later became known as the Modern Atomic Theory It gave a compilation of the information at the time and allowed other scientist to test his ideas. ...
2. Atomic structure
... wave. It is impossible to know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but it is possibly to calculate the region in which it is likely to be found. ...
... wave. It is impossible to know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but it is possibly to calculate the region in which it is likely to be found. ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Atomic Structure Fall 2012
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... they fired Helium nuclei at a piece of gold foil which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
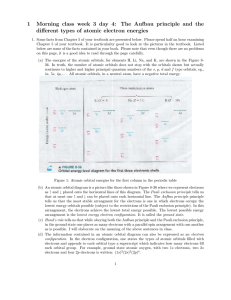
1 Morning class week 3 day 4: The Aufbau principle and the different
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...