SOL Essential Knowledge
... 1. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. 2. The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic numbers. C. Understand that: 1. Electron configuration is the arrangement of electro ...
... 1. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. 2. The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic numbers. C. Understand that: 1. Electron configuration is the arrangement of electro ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
... LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTIONS (also called the LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION): All pure samples of a given compound contain the same proportion of elements by mass ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
Lecture 2
... Only a few elements have just one naturally occurring isotope (e.g. 19F, 23Na, 31P). Most elements occur as mixtures of several isotopes. Chemists normally treat these elements as consisting of “averaged” atoms with “averaged” masses. Atomic mass (as shown on the periodic table) is the weighted aver ...
... Only a few elements have just one naturally occurring isotope (e.g. 19F, 23Na, 31P). Most elements occur as mixtures of several isotopes. Chemists normally treat these elements as consisting of “averaged” atoms with “averaged” masses. Atomic mass (as shown on the periodic table) is the weighted aver ...
The Atom: Building Blocks of The Universe
... indestructible particles called atoms. In other words the society was built with nothing more than indivisible building blocks. The word atomism derives from the ancient Greek word atomos which means "that which cannot be cut into smaller pieces". ...
... indestructible particles called atoms. In other words the society was built with nothing more than indivisible building blocks. The word atomism derives from the ancient Greek word atomos which means "that which cannot be cut into smaller pieces". ...
Name - Net Start Class
... 24. What type of chemical reaction is taking place in the above diagram? decomposition - hydrolysisi ( the DECOMPOSITION was water) 25. List and describe the penetrating power of the 3 things emitted during nuclear decay. a. Alpha radiation: very low penetrating, blocked by paper, very harmful b. Be ...
... 24. What type of chemical reaction is taking place in the above diagram? decomposition - hydrolysisi ( the DECOMPOSITION was water) 25. List and describe the penetrating power of the 3 things emitted during nuclear decay. a. Alpha radiation: very low penetrating, blocked by paper, very harmful b. Be ...
Prentice Hall Physical Science CH 4 Notes.doc
... •energy levels closest to the nucleus have the lowest amount of energy and the ones frthest away has the most energy •if the atom loses or gains energy, the electrons lose or gain energy too and must, therefore, change energy levels to match their energy •if the electron gains energy, the electron m ...
... •energy levels closest to the nucleus have the lowest amount of energy and the ones frthest away has the most energy •if the atom loses or gains energy, the electrons lose or gain energy too and must, therefore, change energy levels to match their energy •if the electron gains energy, the electron m ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide-Atomic Structure Define the following terms
... Nucleus-positive core of the atom, contains protons and neutrons Period-horizontal row on periodic table ...
... Nucleus-positive core of the atom, contains protons and neutrons Period-horizontal row on periodic table ...
Electromagnetic Radiation
... and energy of the orbital. 2. Angular Momentum QN -- l (s, p, d, & f) relates to shape of the orbital. 3. Magnetic QN -- ml (x, y, or z plane) - relates to orientation of the orbital in space relative to other orbitals. 4. Electron Spin QN -- ms (+1/2, 1/2) - relates to the spin states of the elect ...
... and energy of the orbital. 2. Angular Momentum QN -- l (s, p, d, & f) relates to shape of the orbital. 3. Magnetic QN -- ml (x, y, or z plane) - relates to orientation of the orbital in space relative to other orbitals. 4. Electron Spin QN -- ms (+1/2, 1/2) - relates to the spin states of the elect ...
Chemistry Curriculum Guide
... Standard CH.1 (scientific process) is below at the end of this document. ...
... Standard CH.1 (scientific process) is below at the end of this document. ...
Date
... The group of electrons revolving around the nucleus of an atom; a cloudlike group of electrons. Elements forming one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. A positively or negatively charged atom due to gain or loss of electrons. One of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but dif ...
... The group of electrons revolving around the nucleus of an atom; a cloudlike group of electrons. Elements forming one of the vertical columns of the periodic table. A positively or negatively charged atom due to gain or loss of electrons. One of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but dif ...
"stuff" that takes up space- is made of tiny particles called atoms
... * Atoms are tiny. About one million (1,000,000) atoms would fit across the thickness of a human hair. ...
... * Atoms are tiny. About one million (1,000,000) atoms would fit across the thickness of a human hair. ...
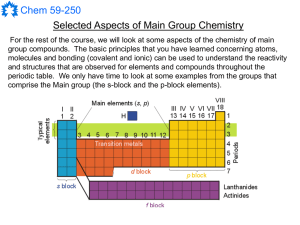
Main Group Notes 1
... compounds is that they tend to form clusters under conditions where no other sources of electrons are available. The pyrolysis of B2H6 produces a variety of clusters and evolves H2 gas. Once formed, many of these polyboranes are stable compounds and many other elements can be placed into the skeleto ...
... compounds is that they tend to form clusters under conditions where no other sources of electrons are available. The pyrolysis of B2H6 produces a variety of clusters and evolves H2 gas. Once formed, many of these polyboranes are stable compounds and many other elements can be placed into the skeleto ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... Mass number = (Number of protons) + (Number of neutrons) 84 = (Number of protons) + (Number of neutrons) 84 = 36 (number of neutrons) 48 number of neutrons ...
... Mass number = (Number of protons) + (Number of neutrons) 84 = (Number of protons) + (Number of neutrons) 84 = 36 (number of neutrons) 48 number of neutrons ...
Revision Notes chapter 1
... Henry Moseley, a member of Rutherford’s team compared the positive charges of the nuclei of different elements. He found that the charge increases by one unit from element to element in the periodic table. He showed that the sequence of elements in the table is related to the charge of the atoms ...
... Henry Moseley, a member of Rutherford’s team compared the positive charges of the nuclei of different elements. He found that the charge increases by one unit from element to element in the periodic table. He showed that the sequence of elements in the table is related to the charge of the atoms ...
Na 2 O - s3.amazonaws.com
... (overall) electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons ...
... (overall) electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons ...
Midterm Review answers - Nutley Public Schools
... 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
Mass Defect (not in book)
... the nucleus. This number is what gives an element its identity. For example, any atom with 6 protons in its nucleus is carbon. The periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Mass Number Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Such variatio ...
... the nucleus. This number is what gives an element its identity. For example, any atom with 6 protons in its nucleus is carbon. The periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. Mass Number Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Such variatio ...
Atomic Theory
... will act in a chemical reaction. • Atoms with equal numbers of valence electrons have similar properties. ...
... will act in a chemical reaction. • Atoms with equal numbers of valence electrons have similar properties. ...