* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Matter - Moodle
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Einsteinium wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Valley of stability wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Nanochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
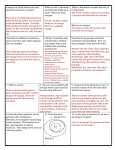
Earth Chemistry Chapter 4 Section 1 Matter Page 80 Matter • • Anything that has _______________ and takes up _______________ _______________ are matter Physical Properties • • Physical properties _____________matter Some are observed through the ___________________: • _______________ , _______________ , _____________, _____________ • Some can be ______________ – ____________point, strength, hardness, ability to – conduct electricity (__________________), magnetism or heat Density _____________________________ is a physical property • Density is how much ________________something has for its ________________ • Another way to say it is . . . how _______________ something is for its size • Density is ________ divided by __________ Example: If 10cm3 of ice has a mass of 9.17g, what is the density of ice? Mass m=9.17g Volume = 10cm3 d = m/v 9.17g 10cm3 = ______________________ Physical properties help determine uses • • Why is copper used in electric power lines?___________________ Why is Styrofoam used for coffee cups? ________________________ Chemical properties • Determine how a substance will _________________ • Generally ___________ as easy to observe as physical properties • The chemical composition ______________________ A chemical property describes how a substance ________________ into a new substance Either by: • __________________ with other elements • _________________ __________________ into new substances Chemical properties include: • • _____________________ ____________________-ability to burn Characteristic properties help to ___________________and ______________________ substances • Characteristic Properties are the _______________or _____________________ characteristics the substance is known for Example: • Helium is light and non-flammable so it is good for _____________________ element A substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by __________________ means More than _______elements occur naturally on Earth Atoms are made of • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons Fill in this chart Particle Proton Neutron Electron Charge Mass Location Elements are classified by the number of ____________ their atoms contain, which is their _________________________ ________________________ 1 H 1.00797 Hydrogen has an atomic number of ______________ • This means it has one proton (and so 1 ______________________) • The bottom number is the ____________________ ____________________. • H, hydrogen, has a mass of 1.00797. 111.007 Neutral Atoms 1.0 0797 97 In a neutral atom # of protons= # of • • • ___________ The _______________ of an atom is usually ___________________ The number of protons _________________ the number of electrons Ex. C (carbon) atomic number of 6, so 6 protons and ____electrons Mass Number • The mass number equals the number of ____________ and the number of ___________________ • ______________ = protons + neutrons • The mass number of Carbon is 12.0107 Isotope • An atom with a different number of _________________ is called an isotope • Hydrogen usually is a proton and an electron If it _____ a neutron it is considered an isotope • Fill in the blank with the names of these isotopes of Hydrogen _____________ 0 neutrons _______________ 1 neutron ____________________ 2 neutrons Half-lives • The ____________of decay of an isotope is called the half-life. A half-life is the amount of time it takes for ___________ of the amount to decay. It is __________________ Different elements have different half-lives Radium-226=1620 years Uranium-238 = ________ billion years What have we studied that is roughly 4.5 billion years old? _________________ Average Atomic Mass •Because the isotopes of an element have different masses the periodic table uses __________________ atomic mass Amu---_____________ ___________ __________ ••Found by calculating the _____________ _____________ of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopesBohr Planetary Model Electrons __________ the nucleus like ____________ orbiting the sun. The orbits are called electron _________ or_______________, those close to the nucleus hold fewer electrons than those far away. Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties •Elements in the periodic table are arranged in columns based on similarities in their _________________properties •These columns are called ________________ • Valence electrons are the electrons in the ___________energy level • Every atom has between one and ____ valence electrons _______________ dictate the many properties of a material including chemical reactivity and physical attributes, like taste, texture, appearance and color. Quick Lab How can physical properties separate a mixture? Materials Water Plastic cups Paper towels Filter paper Sample of mixture Plastic spoon Magnet 1. Design an experiment in which the given materials are used to separate the components of the sample mixture. (Hint: Consider physical properties such as solubility, density, and magnetism.) 2. Once you have separated the components of the sample mixture, describe them by their physical properties. Analysis 1. What properties did you observe in each of the components of the mixture? 2. How did these properties help you to separate the components of the sample? 3. Did any of the components share similar properties? 4. Based on your observations, what do you think the mixture was composed of? 5. How could you improve your experimental design? 6. How could you make the experiment more complicated?