CHEMISTRY 1.2 LECTURE
... redox reaction occurs. A battery is a voltaic cell. Voltaic cells are also known as galvanic cells b. Electrolytic Cells are electrochemical cells that require electricity (flow of electrons) for a non-spontaneous redox reaction to occur. ...
... redox reaction occurs. A battery is a voltaic cell. Voltaic cells are also known as galvanic cells b. Electrolytic Cells are electrochemical cells that require electricity (flow of electrons) for a non-spontaneous redox reaction to occur. ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... Phase notations (solid, liquids, gases, aqueous) - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually ...
... Phase notations (solid, liquids, gases, aqueous) - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... M + H2O MOH (M = Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) ...
... M + H2O MOH (M = Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) ...
Module 8 - Brookville Local Schools
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
... Part of the Chemistry For Dummies Cheat Sheet In bonding, atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to have the same number of electrons as the noble gas that's nearest on the periodic table. Ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds are formed by combinations of metals and nonmetals. Metal + nonmet ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons. Reduction is defined as the gain of electrons. Oxidation and reduction always occur simultaneously. ...
... Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one species to another. Oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons. Reduction is defined as the gain of electrons. Oxidation and reduction always occur simultaneously. ...
Document
... 55) Name the three subatomic particles, their charge, and their location within the atom. Electron, -1, outside the nucleus Proton, +1, inside the nucleus Neutron, +1, inside the nucleus 56) What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element, with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutr ...
... 55) Name the three subatomic particles, their charge, and their location within the atom. Electron, -1, outside the nucleus Proton, +1, inside the nucleus Neutron, +1, inside the nucleus 56) What is an isotope? Atoms of the same element, with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutr ...
Chemistry - El Camino College
... and are called ______ or electrolytes 2. _________ Bonds are strong chemical bonds between atoms that result from the _______ of electrons in their outer orbitals. Molecules with covalent bonds are represented 2 ways: a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a ...
... and are called ______ or electrolytes 2. _________ Bonds are strong chemical bonds between atoms that result from the _______ of electrons in their outer orbitals. Molecules with covalent bonds are represented 2 ways: a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a ...
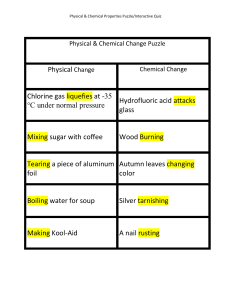
Physical Change Chlorine gas liquefies at
... Physical & Chemical Properties Puzzle/Interactive Quiz ...
... Physical & Chemical Properties Puzzle/Interactive Quiz ...
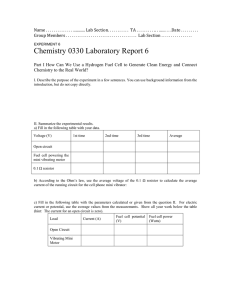
experiment 7 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... 1. Calculate Horxn and Gorxn (in kJ/mole of H2) for the following fuel cell reactions from the standard values of Hof and Gof (See Zumdahl Appendix four, or Tro Appendix II B). H2 (g)+ 1/2 O2 (g) H2O (l) ...
... 1. Calculate Horxn and Gorxn (in kJ/mole of H2) for the following fuel cell reactions from the standard values of Hof and Gof (See Zumdahl Appendix four, or Tro Appendix II B). H2 (g)+ 1/2 O2 (g) H2O (l) ...
Unit A Remediation Review
... 12. What are five clues that will allow you to conclude that a chemical change has occurred? 13. Describe what occurs in the following reaction types, the general equation and an example for each: a) Formation b) Decomposition c) Single Replacement d) Double Replacement e) Combustion 14. Write a bal ...
... 12. What are five clues that will allow you to conclude that a chemical change has occurred? 13. Describe what occurs in the following reaction types, the general equation and an example for each: a) Formation b) Decomposition c) Single Replacement d) Double Replacement e) Combustion 14. Write a bal ...
Document
... 37. ___ The radius of an ion is always larger than the atomic radius of the original atom. 38. ___Most of the metals found above hydrogen in the activity series are found as elements in the ground. 39. __ Gold is a highly reactive metal. 40. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement rea ...
... 37. ___ The radius of an ion is always larger than the atomic radius of the original atom. 38. ___Most of the metals found above hydrogen in the activity series are found as elements in the ground. 39. __ Gold is a highly reactive metal. 40. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement rea ...
Six-Way Galvanic Cell
... 7. Place the prepared filter paper in a Petri dish or on a sheet of acetate transparency or plastic wrap. 8. Using a clean, Beral-type pipet, add 4–5 drops of potassium nitrate solution in the center of the filter paper. This will serve as the salt bridge. 9. Using a separate Beral-type pip ...
... 7. Place the prepared filter paper in a Petri dish or on a sheet of acetate transparency or plastic wrap. 8. Using a clean, Beral-type pipet, add 4–5 drops of potassium nitrate solution in the center of the filter paper. This will serve as the salt bridge. 9. Using a separate Beral-type pip ...
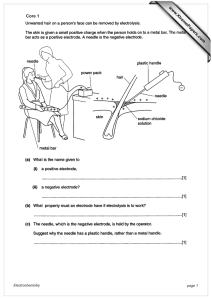
(activity) of hydrogen ions
... metal oxide, hydroxide or carbonate, often of a transition metal like iron, zinc or copper). (1)The metal, oxide, hydroxide or carbonate is stirred with the acid and maybe heated to speed up the reaction (2). When no more of the solid dissolves the solution can be partly evaporated with further heat ...
... metal oxide, hydroxide or carbonate, often of a transition metal like iron, zinc or copper). (1)The metal, oxide, hydroxide or carbonate is stirred with the acid and maybe heated to speed up the reaction (2). When no more of the solid dissolves the solution can be partly evaporated with further heat ...
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
... comparing the oxidation number of an atom before and after reaction allows us to determine whether the atom has gained or lost electrons convenient way to keep track of electrons in a redox reaction ...
... comparing the oxidation number of an atom before and after reaction allows us to determine whether the atom has gained or lost electrons convenient way to keep track of electrons in a redox reaction ...
What do you know about light?
... same! – The composition of a molecule of water. The chemical formula tells us that a water molecule s made up of 3 atoms; 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen. ...
... same! – The composition of a molecule of water. The chemical formula tells us that a water molecule s made up of 3 atoms; 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen. ...
No Slide Title
... • Cu is called the reducing agent because it caused Ag+ to be reduced; and Ag+ is called the oxidizing agent because it caused Cu to be oxidized. ...
... • Cu is called the reducing agent because it caused Ag+ to be reduced; and Ag+ is called the oxidizing agent because it caused Cu to be oxidized. ...
Rxn Pred students
... An electrolysis reaction is a reaction in which a non-spontaneous redox reaction is brought about by the passage of current under sufficient external electrical potential. The devices in which electrolysis reactions occur are called electrolytic cells. ...
... An electrolysis reaction is a reaction in which a non-spontaneous redox reaction is brought about by the passage of current under sufficient external electrical potential. The devices in which electrolysis reactions occur are called electrolytic cells. ...
SG5 Chemical Reactions and Quantities
... 1. Make sure all your formulas are correct; you may not change them 2. Remember the elements that form diatomic molecules: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 3. An element that occurs uncombined should be balanced after everything else 4. Keep polyatomic ions together whenever possible; if OH occurs, rewrite wa ...
... 1. Make sure all your formulas are correct; you may not change them 2. Remember the elements that form diatomic molecules: H2 N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 3. An element that occurs uncombined should be balanced after everything else 4. Keep polyatomic ions together whenever possible; if OH occurs, rewrite wa ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.