Battery Materials
... - Double layer capacitors (“Supercapacitors“) - Double layer capacitors with near-surface redox processes (“Ultracapacitors“) • Fuel cells ...
... - Double layer capacitors (“Supercapacitors“) - Double layer capacitors with near-surface redox processes (“Ultracapacitors“) • Fuel cells ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment - 2015
... 3. Metallic chlorates, when heated, decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen gas. EX. 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) 4. Some acids, when heated, decompose into nonmetallic oxides and water. EX. H2SO4 → H2O(l) + SO3(g) 5. Some oxides, when heated, decompose to the elemental metal and O2. EX. 2HgO(s ...
... 3. Metallic chlorates, when heated, decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen gas. EX. 2KClO3(s) → 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) 4. Some acids, when heated, decompose into nonmetallic oxides and water. EX. H2SO4 → H2O(l) + SO3(g) 5. Some oxides, when heated, decompose to the elemental metal and O2. EX. 2HgO(s ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF LETHBRIDGE DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY
... Hydrogen bonds are the dominant IMF in the structure of ice; these must be partially broken to allow liquid water to form. Water is though to have a structure near the m.p. of “flickering clusters” of the IceI structure. Additional IMF that contribute to the structure are DP-DP and dispersion forces ...
... Hydrogen bonds are the dominant IMF in the structure of ice; these must be partially broken to allow liquid water to form. Water is though to have a structure near the m.p. of “flickering clusters” of the IceI structure. Additional IMF that contribute to the structure are DP-DP and dispersion forces ...
Chemical Equations Balancing Chemical Equations Try One…
... reaction type. In a chemical reaction, only 2 things are conserved the number of atoms and the conserved... number of grams. an arrow is used to separate reactants (the starting substances) and the products (what is made), the arrow is the same as an “equals sign” (=) in math for the number of e ...
... reaction type. In a chemical reaction, only 2 things are conserved the number of atoms and the conserved... number of grams. an arrow is used to separate reactants (the starting substances) and the products (what is made), the arrow is the same as an “equals sign” (=) in math for the number of e ...
CHEMISTRY
... • Most chemical reactions require energy to begin • The amount of energy needed to start the reaction is called activation energy ...
... • Most chemical reactions require energy to begin • The amount of energy needed to start the reaction is called activation energy ...
Precipitation and Redox Reactions
... How do I know if REDOX occurs • If one (or more) element(s) in the reaction loses electrons (LEO) and one (or more) element(s) in the reaction gains electrons (GER) then REDOX ...
... How do I know if REDOX occurs • If one (or more) element(s) in the reaction loses electrons (LEO) and one (or more) element(s) in the reaction gains electrons (GER) then REDOX ...
AP Electrochemistry Class Packet Unit 10
... balanced chemical equations. The role of stoichiometry in real-world applications is important to note, so that it does not seem to be simply an exercise done by only chemists. 3.B.3 In oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, there is a net transfer of electrons. The species that loses electrons is ...
... balanced chemical equations. The role of stoichiometry in real-world applications is important to note, so that it does not seem to be simply an exercise done by only chemists. 3.B.3 In oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, there is a net transfer of electrons. The species that loses electrons is ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
... 1. Determine the oxidation numbers for all atoms in the reaction. 2. Determine which atom is being oxidized and which is being reduced. 3. Write a half reaction for the reduction process (addition of electrons…electrons added to the left side). 4. Write a half reaction for the oxidation process (los ...
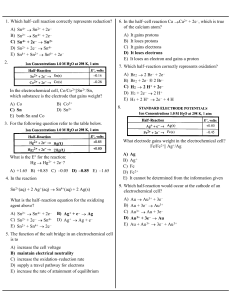
A) Sn4+ → Sn2+ + 2e
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
... B) Anode: 2 Cl – ® Cl 2 + 2e – Cathode: 2 H 2O + 2e – ® H 2 + 2 OH – C) Anode: 2 H 2O ® O 2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 2 Zn2+ + 4e – ® 2 Zn D) Anode: 2 H2O ® O2 + 4 H+ + 4e – Cathode: 4 H 2 O + 4e – ® 2 H 2 + 4 OH – E) Anode: Cl 2 + 2e – ® 2 Cl – Cathode: Zn ® Zn 2+ + 2e – 69. What are the anode and cat ...
chemistry - ALLEN Jaipur
... (vi) The boiling points of aldehyde and ketones are lower than of the corresponding acids. (vii) The aldehyde and ketones undergo a number of addition reactions but carboxylic acids does not (viii) Ortho-nitro phenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol (ix) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. ( ...
... (vi) The boiling points of aldehyde and ketones are lower than of the corresponding acids. (vii) The aldehyde and ketones undergo a number of addition reactions but carboxylic acids does not (viii) Ortho-nitro phenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol (ix) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. ( ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) unre ...
... Lead (Pb) is above H, so is Al. But these metals are not attacked by 6M HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) unre ...
The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to
... 1. Types of solutions and factors affecting solubility 2. Methods of expressing concentration (use of normalities is not tested) 3. Raoult’s law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis 4. Nonideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
... 1. Types of solutions and factors affecting solubility 2. Methods of expressing concentration (use of normalities is not tested) 3. Raoult’s law and colligative properties (nonvolatile solutes); osmosis 4. Nonideal behavior (qualitative aspects) ...
Name: Date: Block:______ GRADE 8 SCIENCE SOL QUESTIONS
... 1. Which process is a physical change? a. Rusting iron b. Burning coal c. Tarnishing silver d. Melting ice _ 2. When a base is mixed with an acidic solution, neutralization occurs because the — a. base reaches absolute zero b. acid evaporates c. base chemically reacts with the acid d. mass of the so ...
... 1. Which process is a physical change? a. Rusting iron b. Burning coal c. Tarnishing silver d. Melting ice _ 2. When a base is mixed with an acidic solution, neutralization occurs because the — a. base reaches absolute zero b. acid evaporates c. base chemically reacts with the acid d. mass of the so ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
... 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determine how an atom behaves 2. electrons vary in energy 3. electrons occur at certain energy l ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... the same/different numbers of protons. NaCl+ compoundClIsotopes are atoms of the same element with Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ fro ...
... the same/different numbers of protons. NaCl+ compoundClIsotopes are atoms of the same element with Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ fro ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.