Chapter 4
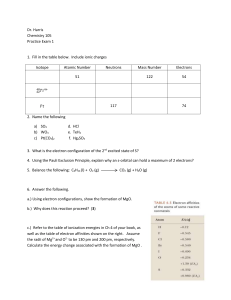
... Solve problems based on balanced chemical equations with quantities given or sought in a variety of units. ...
... Solve problems based on balanced chemical equations with quantities given or sought in a variety of units. ...
Chemistry Quiz #2 Study Guide (Answers)
... sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
... sublimation, evaporation) • Exothermic Reaction – Energy (heat) leaving a reaction (condensation, solidification, deposition) 2. What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory? The theory that all molecules are in constant motion. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OBJECTIVES 1. To study reactions
... Reactions that evolve heat are called exothermic reactions. In an exothermic reaction, the products have less energy than the reactants. When the products have more energy than the reactants, the reaction is endothermic. The additional energy needed for formation of the products is absorbed from the ...
... Reactions that evolve heat are called exothermic reactions. In an exothermic reaction, the products have less energy than the reactants. When the products have more energy than the reactants, the reaction is endothermic. The additional energy needed for formation of the products is absorbed from the ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... The periodic table of the elements. The weights of the elements increase from left to right. Each vertical column groups elements with similar chemical properties. ...
... The periodic table of the elements. The weights of the elements increase from left to right. Each vertical column groups elements with similar chemical properties. ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
Chapter 2 - Cengage Learning
... – One atom is charged and there is an unlike charge in another atom • Electrons can flow between the two ...
... – One atom is charged and there is an unlike charge in another atom • Electrons can flow between the two ...
AQA C2 revision book
... These are liquids which conduct electricity, and are decomposed by it. They are ionic substances which are dissolved in water or have been melted. This includes all acids and metal compounds. Examples: Copper sulphate solution, iron chloride solution, molten sodium chloride, dilute sulphuric acid. N ...
... These are liquids which conduct electricity, and are decomposed by it. They are ionic substances which are dissolved in water or have been melted. This includes all acids and metal compounds. Examples: Copper sulphate solution, iron chloride solution, molten sodium chloride, dilute sulphuric acid. N ...
Intro to Chemical Equations note
... The way atoms are joined is changed Atoms aren’t created or destroyed. Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. 2. In a word equation Copper + chlorine copper (II) chloride ...
... The way atoms are joined is changed Atoms aren’t created or destroyed. Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. 2. In a word equation Copper + chlorine copper (II) chloride ...
Table showing examples of Complex ions with their bond
... An oxidising agent (or oxidant) is an atom or molecule or ion, which readily captures electrons. A reducing agent (or reductant) is an atom or molecule or ion, which readily releases electrons. Chemical reaction taking place in galvanic cells or during electrolysis are simple electron- transfer reac ...
... An oxidising agent (or oxidant) is an atom or molecule or ion, which readily captures electrons. A reducing agent (or reductant) is an atom or molecule or ion, which readily releases electrons. Chemical reaction taking place in galvanic cells or during electrolysis are simple electron- transfer reac ...
1. All the questions are compulsory. 2. Q. N
... (b) Give any one example of these polymers and name its monomers. (c) Comment on the qualities of Shalini. 24. (a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following: (i) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid ...
... (b) Give any one example of these polymers and name its monomers. (c) Comment on the qualities of Shalini. 24. (a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following: (i) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid ...
Chemistry - CBSE Academic
... (b) Give any one example of these polymers and name its monomers. (c) Comment on the qualities of Shalini. 24. (a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following: (i) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid ...
... (b) Give any one example of these polymers and name its monomers. (c) Comment on the qualities of Shalini. 24. (a) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following: (i) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid ...
Topic 9 - Anderson High School
... 9.4.2 State that oxidation occurs at the negative electrode (anode) and reduction occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). • ANOX and RED CAT • The oxidation occurs at the anode. • The reduction occurs at the cathode. • Which of the metals is being reduced? • So which is the cathode? ...
... 9.4.2 State that oxidation occurs at the negative electrode (anode) and reduction occurs at the positive electrode (cathode). • ANOX and RED CAT • The oxidation occurs at the anode. • The reduction occurs at the cathode. • Which of the metals is being reduced? • So which is the cathode? ...
Topic Book periodicity
... Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of reaction while being recoverable in the end stage of the reaction, unchanged. Examples of catalytic transition metals: Fe is used in Haber process; V2O5 in Contact process; Ni in hydrogenation reactions; MnO2 with hydrogen peroxide. ...
... Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of reaction while being recoverable in the end stage of the reaction, unchanged. Examples of catalytic transition metals: Fe is used in Haber process; V2O5 in Contact process; Ni in hydrogenation reactions; MnO2 with hydrogen peroxide. ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
... • The impure metal or metalloid is passed slowly through a heating coil in an inert atmosphere. • A small zone of the impure solid melts, and as the next zone melts, the dissolved impurities from the first zone lowers the freezing point. • The purer solid of the first zone refreezes. • Gradually imp ...
Redox Reactions - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
... Oxidation and reduction reaction = redox rxn Oxidation is loss of electrons and reduction is gain of electrons = transfer of electrons Those 2 reactions are occurring simultaneously ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... 1.) Identify the type of reaction for those listed below: A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a ...
... 1.) Identify the type of reaction for those listed below: A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a ...
Group II Elements - Innovative Education.org
... As for any group in the Periodic Table the Group 2 atoms get larger. So do their ions. The ions have a charge of +2 when the atoms lose the two outermost-level electrons, leaving this level empty. The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions suc ...
... As for any group in the Periodic Table the Group 2 atoms get larger. So do their ions. The ions have a charge of +2 when the atoms lose the two outermost-level electrons, leaving this level empty. The two electrons of the Be2+ ion occupy the first energy level only so the ion is very small. Ions suc ...
group iv elements
... The structure of the elements range from macro-molecular non-metals through metalloids to metallic lattices of close-packed ions. Carbon exists either as a diamond formation or as graphite, in either form, there are strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms which must be broken, resulting in a ...
... The structure of the elements range from macro-molecular non-metals through metalloids to metallic lattices of close-packed ions. Carbon exists either as a diamond formation or as graphite, in either form, there are strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms which must be broken, resulting in a ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.