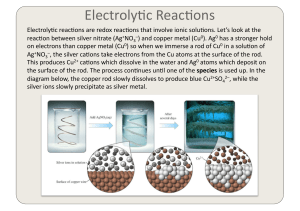
Summer - Honors Chemistry
... when forming ions. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negative and is called an anion. Nonmetals form anions, and the name of that ion is given by adding “-ide” to the root of the element name (e.g. O-2 is oxide). If an atom loses electrons, it becomes positive and is called a cation. Metals for ...
... when forming ions. If an atom gains electrons, it becomes negative and is called an anion. Nonmetals form anions, and the name of that ion is given by adding “-ide” to the root of the element name (e.g. O-2 is oxide). If an atom loses electrons, it becomes positive and is called a cation. Metals for ...
departmentofmaterials scienceandengineering
... exists for removing atoms from their sites using only ionizing radiation, such as UV light, X-rays or γ-rays. This process is called radiolysis and in halides can be surprisingly efficient (up to ~50% of the ionizing energy converted to kinetic energy in displacing a halogen atom from its site). Wit ...
... exists for removing atoms from their sites using only ionizing radiation, such as UV light, X-rays or γ-rays. This process is called radiolysis and in halides can be surprisingly efficient (up to ~50% of the ionizing energy converted to kinetic energy in displacing a halogen atom from its site). Wit ...
CSUS Department of Chemistry Molecular Shapes Chem. 1A Page
... Molecular polarity is a physical property of compounds which relates to other physical properties such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and intermolecular interactions between molecules. For the most part, there is a direct correlation between the polarity of a molecule and number and ty ...
... Molecular polarity is a physical property of compounds which relates to other physical properties such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and intermolecular interactions between molecules. For the most part, there is a direct correlation between the polarity of a molecule and number and ty ...
Electrochemistry 2
... of metals is a redox process, we can use the study of electrochemistry to be[er understand, and thereby prevent, corrosion. Let’s take the case of iron. The first stage of rus)ng is caused by the ...
... of metals is a redox process, we can use the study of electrochemistry to be[er understand, and thereby prevent, corrosion. Let’s take the case of iron. The first stage of rus)ng is caused by the ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
... Metallic bonds consist of the attractions of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions. The free floating valence electrons make metals good conductors and light reflecting off of the free floating valence electrons that travel around the outside of metal give metal ...
Presentation
... of outer electrons, the positive (lose e-) variescharges +1 totend +7 (oxidation or negative Nonmetals to have numbers) can be predicted for negative oxidations single (monatomic) numbers. (gain atoms. e-) varies ...
... of outer electrons, the positive (lose e-) variescharges +1 totend +7 (oxidation or negative Nonmetals to have numbers) can be predicted for negative oxidations single (monatomic) numbers. (gain atoms. e-) varies ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... “like dissolves like.” Atoms/Periodic Table Units 1. Ionic compounds form when atoms gain or lose electrons. Metals lose electrons, nonmetals gain them. 2. The number of electrons gained or lost can be predicted with an understanding of the octet rule and the number of valence electrons an atom cont ...
... “like dissolves like.” Atoms/Periodic Table Units 1. Ionic compounds form when atoms gain or lose electrons. Metals lose electrons, nonmetals gain them. 2. The number of electrons gained or lost can be predicted with an understanding of the octet rule and the number of valence electrons an atom cont ...
Unit 2
... D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. electron clouds. C. d electrons. D. valence electrons. 62. In many compounds, atoms of main-group elements form bonds so that the number of electrons in ...
... D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. electron clouds. C. d electrons. D. valence electrons. 62. In many compounds, atoms of main-group elements form bonds so that the number of electrons in ...
Click Here To File
... Chemical test to distinguish between two isomers:The isomer [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 gives a white precipitate of BaSO4 with BaCl2 solution whereas the isomer [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br does not form this precipitate. (or any other relevant test) (a) KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. Alt ...
... Chemical test to distinguish between two isomers:The isomer [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 gives a white precipitate of BaSO4 with BaCl2 solution whereas the isomer [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br does not form this precipitate. (or any other relevant test) (a) KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. Alt ...
CHEMISTRY – UNITS 3 and 4 REVIEW PACKET Name Date
... fission reaction is much greater than the energy released from a chemical reaction because in a fission reaction (1) mass is converted into energy (2) energy is converted into mass (3) ionic bonds are broken (4) covalent bonds are broken 5. How many days are required for 200. grams of radon-222 to d ...
... fission reaction is much greater than the energy released from a chemical reaction because in a fission reaction (1) mass is converted into energy (2) energy is converted into mass (3) ionic bonds are broken (4) covalent bonds are broken 5. How many days are required for 200. grams of radon-222 to d ...
Topic 2
... 1.)All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. 2.)An element is a type of matter composed of only one kind of atom, each atom of a given element having the same properties. Mass is one such propert ...
... 1.)All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. 2.)An element is a type of matter composed of only one kind of atom, each atom of a given element having the same properties. Mass is one such propert ...
Chapter 2 - Cengage Learning
... – Nucleus: made up of protons and neutrons – Electrons: orbit the nucleus – Protons: positive charge – Electrons: negative charge – Hydrogen atom: simplest atom • One proton and one electron ...
... – Nucleus: made up of protons and neutrons – Electrons: orbit the nucleus – Protons: positive charge – Electrons: negative charge – Hydrogen atom: simplest atom • One proton and one electron ...
Objective 4
... substances to combine in different ways to make other substances are called chemical reactions. 2H2 + O2 ...
... substances to combine in different ways to make other substances are called chemical reactions. 2H2 + O2 ...
IONIZATION METHODS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY
... c) The laser light is applied in pulses of short duration in contrast to exposure to a continuous beam of energetic atoms or ions. d) The analyte is ionized by energy transfer from the matrix rather than being "sputtered or ripped" from a liquid matrix. In a typical MALDI analysis, a 10 µM solution ...
... c) The laser light is applied in pulses of short duration in contrast to exposure to a continuous beam of energetic atoms or ions. d) The analyte is ionized by energy transfer from the matrix rather than being "sputtered or ripped" from a liquid matrix. In a typical MALDI analysis, a 10 µM solution ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
PPT - kimscience.com
... All matter is made of indivisible atoms; they can be neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numb ...
... All matter is made of indivisible atoms; they can be neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions All atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties; they differ from atoms of every other element Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numb ...
chapter 2 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
... Chemistry is fundamental to an understandingof life, becauseliving organisms are made of matter. Matter: Anything that takes up spaceand has mass. Mass : A measure of the amount of matter an obiect contains. You might want to distinguish between mass and weight for your students. Mass is the measure ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the center of an atom is a positively charged, compact, heavy nucleus. The charge on the atomic nucleus is +Ze (Z is the atomic number of the atom). The fundamental unit of positive charge in the nucleus is the proton. ♦ Chemical identity of an ...
... kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the center of an atom is a positively charged, compact, heavy nucleus. The charge on the atomic nucleus is +Ze (Z is the atomic number of the atom). The fundamental unit of positive charge in the nucleus is the proton. ♦ Chemical identity of an ...
File
... A) Charge can be transferred – only by contact, discharging B) Conductors and Insulators (1) Conductors move charge easily (2) Insulators can be charged, but charge cannot move easily 25.2 Charge I) Convention for positive and negative began with Ben Franklin A) Positive B) Negative II) Atoms and El ...
... A) Charge can be transferred – only by contact, discharging B) Conductors and Insulators (1) Conductors move charge easily (2) Insulators can be charged, but charge cannot move easily 25.2 Charge I) Convention for positive and negative began with Ben Franklin A) Positive B) Negative II) Atoms and El ...
Ionic bonding - Nidderdale High School
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Name
... of the following. Your responses must include specific information about all substances referred to in each question. (a) At a pressure of 1 atm, the boiling point of NH3(l) is 240 K, whereas the boiling point of NF3(l) is 144 K. Account for the difference in the boiling points of the substances. ...
... of the following. Your responses must include specific information about all substances referred to in each question. (a) At a pressure of 1 atm, the boiling point of NH3(l) is 240 K, whereas the boiling point of NF3(l) is 144 K. Account for the difference in the boiling points of the substances. ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... Ionic compounds are formed when two or more oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other. This chemical attraction is called a chemical bond. An ionic bond is formed when a negatively charged ion is attracted to a positively ...
... Ionic compounds are formed when two or more oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other. This chemical attraction is called a chemical bond. An ionic bond is formed when a negatively charged ion is attracted to a positively ...
Chem. 1A Week 11 Discussion Notes Dr. Mack/S12 Page 1 of 5 B
... Molecular Polarity: Molecular polarity is a physical property of compounds which relates to other physical properties such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and intermolecular interactions between molecules. For the most part, there is a direct correlation between the polarity of a molec ...
... Molecular Polarity: Molecular polarity is a physical property of compounds which relates to other physical properties such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and intermolecular interactions between molecules. For the most part, there is a direct correlation between the polarity of a molec ...
Northgate High School Chemistry Department
... Northgate High School Chemistry Department AS Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Module 1.3.3 Group 7 explain, in terms of van der Waals’ forces, the trend in the boiling points of Cl2, Br2 and I2; describe the redox reactions, including ionic equations, of the Group 7 elements Cl2, Br2 and I2 with ...
... Northgate High School Chemistry Department AS Unit F321: Atoms, Bonds and Groups Module 1.3.3 Group 7 explain, in terms of van der Waals’ forces, the trend in the boiling points of Cl2, Br2 and I2; describe the redox reactions, including ionic equations, of the Group 7 elements Cl2, Br2 and I2 with ...
LN_atoms_etc
... Modern View of Atomic Structure Experiments by Thomson and Millikan confirmed the existence of electrons as the negatively charged particles within an atom. Electrons have a charge of e = 1.6021773 10–19 C and a mass of 9.109390 10–31 kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the ce ...
... Modern View of Atomic Structure Experiments by Thomson and Millikan confirmed the existence of electrons as the negatively charged particles within an atom. Electrons have a charge of e = 1.6021773 10–19 C and a mass of 9.109390 10–31 kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the ce ...