Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... lose electrons when they form ions form positively charged ions form ions with charges -3, -2, and -1, respectively form ions with a numerical charge equal to their group number ...
... lose electrons when they form ions form positively charged ions form ions with charges -3, -2, and -1, respectively form ions with a numerical charge equal to their group number ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... Polyatomic compounds – metal and group of nonmetals – name metal followed by polyatomic ion ...
... Polyatomic compounds – metal and group of nonmetals – name metal followed by polyatomic ion ...
Electron wavepackets and microscopic Ohm`s law (PPT
... Microscopic Scattering A local, unexpected change in V(x) of electron as it approaches the impurity ...
... Microscopic Scattering A local, unexpected change in V(x) of electron as it approaches the impurity ...
1.0 basic concepts
... Ag1+(aq) and NO31-(aq) are dissociated ions As they are different, they are not spectator ions and cannot be cancelled out 6) Rewrite the balanced ionic equation without the spectator ions ...
... Ag1+(aq) and NO31-(aq) are dissociated ions As they are different, they are not spectator ions and cannot be cancelled out 6) Rewrite the balanced ionic equation without the spectator ions ...
CHAPTER 5 NOTES – ELECTRONS IN ATOMS
... Schrödinger equation – determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus ...
... Schrödinger equation – determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... The number of protons in an atom determines the element – # of protons = atomic number – this also tells you # of electrons ...
... The number of protons in an atom determines the element – # of protons = atomic number – this also tells you # of electrons ...
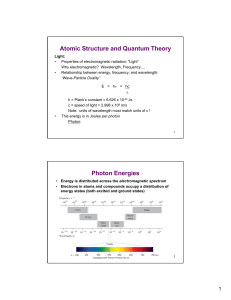
Atomic Structure and Quantum Theory Photon Energies
... • Need to consider radial and angular components • In some instances, ψ2 goes to zero (ψ changes sign) – nodes: planar (angular) or spherical (radial) ...
... • Need to consider radial and angular components • In some instances, ψ2 goes to zero (ψ changes sign) – nodes: planar (angular) or spherical (radial) ...
Chapter 9
... • We can picture the formation of a ions as a situation in which the bond is so polar that electrons have ...
... • We can picture the formation of a ions as a situation in which the bond is so polar that electrons have ...
Chemistry 102B What`s in an atom? Before “Chemistry” Other Early
... of different elements are different. 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of 2 or more elements combine w/ each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, but not atoms are destroyed or created. “ ...
... of different elements are different. 3. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of 2 or more elements combine w/ each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 4. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atoms, but not atoms are destroyed or created. “ ...
CHEMISTRY 1000 - U of L Class Index
... Oxidation states are used as a means to track the movement of electrons in a reaction. An atom’s oxidation state is the charge it would have if all bonds in the molecule were 100% ionic (except bonds between atoms of the same element). To determine oxidation states for atoms in a molecule or ion: ...
... Oxidation states are used as a means to track the movement of electrons in a reaction. An atom’s oxidation state is the charge it would have if all bonds in the molecule were 100% ionic (except bonds between atoms of the same element). To determine oxidation states for atoms in a molecule or ion: ...
Chemistry Reference Table Review
... 84. Based on Table G, a solution of NaNO3 that contains 120 grams of solute dissolved in 100 grams of H2O at 50°C is best described as (1) saturated and dilute (2) saturated and concentrated (3) supersaturated and dilute (4) supersaturated and concentrated 85. A student calculated the percent by mas ...
... 84. Based on Table G, a solution of NaNO3 that contains 120 grams of solute dissolved in 100 grams of H2O at 50°C is best described as (1) saturated and dilute (2) saturated and concentrated (3) supersaturated and dilute (4) supersaturated and concentrated 85. A student calculated the percent by mas ...
Atomic Theory - World of Teaching
... the size of the individual atoms. the net electrical charge of the individual molecules. the average speed of movement of the individual molecules. ...
... the size of the individual atoms. the net electrical charge of the individual molecules. the average speed of movement of the individual molecules. ...
Chemical Nomenclature, Formulas, and Equations
... (c) Each calcium ion (Ca2+) bears two positive charges, and each phosphate ion ( ) bears three negative charges. To make the sum of the charges equal zero, we must adjust the numbers of cations and anions: ...
... (c) Each calcium ion (Ca2+) bears two positive charges, and each phosphate ion ( ) bears three negative charges. To make the sum of the charges equal zero, we must adjust the numbers of cations and anions: ...
document
... 3. Pick an element to balance. Avoid element in multiple compounds. Do free elements last. Since Mg already balanced, pick O. 4. Find the LCM of both sides 5. and multiply each side by factor so it equals LCM. LCM of 2 and 1 is 2. ...
... 3. Pick an element to balance. Avoid element in multiple compounds. Do free elements last. Since Mg already balanced, pick O. 4. Find the LCM of both sides 5. and multiply each side by factor so it equals LCM. LCM of 2 and 1 is 2. ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separate ...
... 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separate ...
Semester 2 review questions
... 1. ____________________ was a Russian chemist who arranged the known elements in vertical columns in order of increasing mass and noticed a pattern in physical and chemical properties. 2. ____________________ was a British physicist who determined the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) ...
... 1. ____________________ was a Russian chemist who arranged the known elements in vertical columns in order of increasing mass and noticed a pattern in physical and chemical properties. 2. ____________________ was a British physicist who determined the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... How did we find out the structure of the atom if it is so small? ...
... How did we find out the structure of the atom if it is so small? ...
Name - Net Start Class
... 29. If one variable increases while the other variable decreases, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. An inversely proportional relationship ...
... 29. If one variable increases while the other variable decreases, what type of relationship is it? Sketch a graph of this relationship. An inversely proportional relationship ...
Exam Review - Manistique Area Schools
... What does each line in a atomic emission spectrum represent? Why are there spaces between the lines of color? Why do we see one color? ...
... What does each line in a atomic emission spectrum represent? Why are there spaces between the lines of color? Why do we see one color? ...
File
... 6. Use the principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding to explain each of the following. In each part, you answer must include references to both substances. a.) The atomic radius of Li is larger than that of Be. b.) The second ionization energy of K is greater than the second ionization ...
... 6. Use the principles of atomic structure and/or chemical bonding to explain each of the following. In each part, you answer must include references to both substances. a.) The atomic radius of Li is larger than that of Be. b.) The second ionization energy of K is greater than the second ionization ...
Semester I CP Chemistry Review
... increases as you go down the group, plus Na has 3 energy levels and Li only has 2. b. Sr or Mg – Sr. Sr has 5 energy levels and Mg only has 3. c. C or Ge – Ge has 4 energy levels, C has 2 d. Se or O – Se has 4 energy levels, O has 2 ...
... increases as you go down the group, plus Na has 3 energy levels and Li only has 2. b. Sr or Mg – Sr. Sr has 5 energy levels and Mg only has 3. c. C or Ge – Ge has 4 energy levels, C has 2 d. Se or O – Se has 4 energy levels, O has 2 ...
Chapter 4: Introduction to Earth Chemistry Section 1 Notes
... Chemical bonds form because of ____________________________________________________________. Atoms form chemical bonds by either _____________or_________________ electrons from one atom to another. Scientists can study _____________________of atoms to predict which kinds of atoms will form chemical ...
... Chemical bonds form because of ____________________________________________________________. Atoms form chemical bonds by either _____________or_________________ electrons from one atom to another. Scientists can study _____________________of atoms to predict which kinds of atoms will form chemical ...
Prelim Revision Paper 4
... The table shows the numbers of protons, electrons and neutrons in four particles, W, X, Y and Z. ...
... The table shows the numbers of protons, electrons and neutrons in four particles, W, X, Y and Z. ...