The New Alchemy
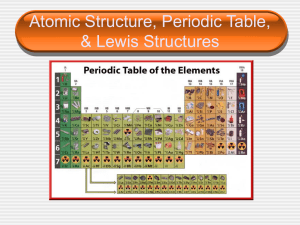
... fusion. Splitting of the nucleus of an atom into smaller parts The Search Went On Half life – time required for half the atoms of a radioactive material to decay Periodic Table Transition elements – an element that is found in the center of the periodic table that is a metal Lanthanides – Elements h ...
... fusion. Splitting of the nucleus of an atom into smaller parts The Search Went On Half life – time required for half the atoms of a radioactive material to decay Periodic Table Transition elements – an element that is found in the center of the periodic table that is a metal Lanthanides – Elements h ...
2 NaCl + MgO → Na2O + MgCl2 CuSO4 Mg(NO3)2
... numbers assigned to the _____________ in a chemical ____________ that give the _______________ charge of the ________________. ...
... numbers assigned to the _____________ in a chemical ____________ that give the _______________ charge of the ________________. ...
Bioenergetics Key
... a thioester has no resonance between the sulfur and the oxygen while an ester does. Therefore an ester has lower energy. when either is hydrolyzed, the result is a resonance stabilized carboxylate ion. 8. What molecules are electron carriers? NAD, FADH 9. For the electron carriers, which is used to ...
... a thioester has no resonance between the sulfur and the oxygen while an ester does. Therefore an ester has lower energy. when either is hydrolyzed, the result is a resonance stabilized carboxylate ion. 8. What molecules are electron carriers? NAD, FADH 9. For the electron carriers, which is used to ...
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
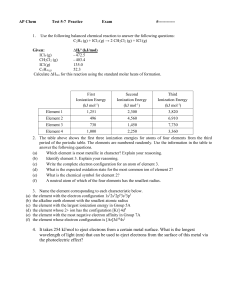
... 1. The value of ∆H0 for the reaction below is -126 kJ. The amount of heat that is released by the reaction of 25.0 g of Na2O2 with water is __________ kJ. 2 Na2O2 (s) + 2 H2O(l) 4 NaOH(s) + O2(g) A) 20.2 B) 40.4 C) 67.5 D) 80.8 E) -126 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodiu ...
... 1. The value of ∆H0 for the reaction below is -126 kJ. The amount of heat that is released by the reaction of 25.0 g of Na2O2 with water is __________ kJ. 2 Na2O2 (s) + 2 H2O(l) 4 NaOH(s) + O2(g) A) 20.2 B) 40.4 C) 67.5 D) 80.8 E) -126 2. The ΔH for the exothermic solution process when solid sodiu ...
Summer Resources - mvhs
... In covalent network solid each atom is covalently bonded to its nearest neighboring atoms. The covalent bonding extends throughout a network that includes a very large number of atoms. Ex: diamond (Cx), quartz(SiO2)x, silicon carbide(SiC)x. Such solids are essentially giant molecules. The subscript ...
... In covalent network solid each atom is covalently bonded to its nearest neighboring atoms. The covalent bonding extends throughout a network that includes a very large number of atoms. Ex: diamond (Cx), quartz(SiO2)x, silicon carbide(SiC)x. Such solids are essentially giant molecules. The subscript ...
Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory
... • Very good at showing what can and cannot form! • Predicts directionality. • Works very well with organic compounds. • Exceptions are interesting and will be discussed later! ...
... • Very good at showing what can and cannot form! • Predicts directionality. • Works very well with organic compounds. • Exceptions are interesting and will be discussed later! ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
... 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric curren ...
... 33. The contribution to the periodic table made by Dobereiner was his early attempt to classify small groups of elements according to their properties. 34. If an atom has high ionization energy, its electron affinity is also high. 35. (a) An electrolyte is a compound that conducts an electric curren ...
Electrons_Holes
... A bond can break when a Si atom absorbs enough energy from phonons (packets of heat) to equal the bandgap energy. Or, if it absorbs a photon that has as much or more energy than the bandgap energy, the atom can use the energy to break one of the bonds with another Si atom. ...
... A bond can break when a Si atom absorbs enough energy from phonons (packets of heat) to equal the bandgap energy. Or, if it absorbs a photon that has as much or more energy than the bandgap energy, the atom can use the energy to break one of the bonds with another Si atom. ...
SEPARATION OF MATTER - Los Angeles City College
... • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nuc ...
... • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nuc ...
Analysis of a Matter
... • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nuc ...
... • Molecules: the smallest grouping which a substance can be divided into without forming a new substance, a group of 2 or more atoms held together by strong forces called "bonds". • Atoms: the smallest particle of matter which has distinctive chemical characteristics, generic term, composed of a nuc ...
key concepts of matter
... levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and have the highest energy. Key Concept 4: Valence electrons determine the chemical pro ...
... levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and have the highest energy. Key Concept 4: Valence electrons determine the chemical pro ...
Key Concept 1: An atom is the smallest unit of an element that
... cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
... cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
The Atomic Theory of Matter
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
... • The rest of the subatomic particles were found when scientists made theories on where the electrons were in an atom. In 1910, a scientist named Rutherford examined the effects of passing alpha rays through a gold foil a few thousand atoms thick. He found that most passed right through the gold foi ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... • Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down any further. It is in its simplest form! Each element is represented by an atom. • Molecules are particles made up of two or more atoms bonded together that make up substances. ...
... • Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down any further. It is in its simplest form! Each element is represented by an atom. • Molecules are particles made up of two or more atoms bonded together that make up substances. ...
Chemical Bonding I
... nuclei of the bonded atoms. • As with bond energies, these are averages since there are slight variaGons according to the molecular structure. • The next few slides give some typical values. • N ...
... nuclei of the bonded atoms. • As with bond energies, these are averages since there are slight variaGons according to the molecular structure. • The next few slides give some typical values. • N ...
This is an overview of what can happen during the
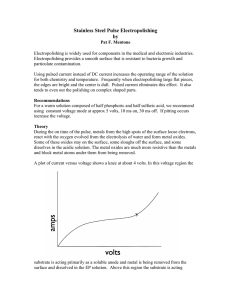
... primarily as an insoluble anode and the water is being electrolyzed to oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. In order for polishing to occur, the current and voltage must be above the knee of the curve, this location is marked with an X in the above graph If the substrate functioned as a 100% soluble anode ...
... primarily as an insoluble anode and the water is being electrolyzed to oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. In order for polishing to occur, the current and voltage must be above the knee of the curve, this location is marked with an X in the above graph If the substrate functioned as a 100% soluble anode ...
Electron wavepackets and microscopic Ohm`s law
... Microscopic Scattering A local, unexpected change in V(x) of electron as it approaches the impurity ...
... Microscopic Scattering A local, unexpected change in V(x) of electron as it approaches the impurity ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... unfold when Rutherford played around with atoms made of gold. When a few of his alpha particles came bounding back, he hypothesized a nucleus had knocked them off the track. ...
... unfold when Rutherford played around with atoms made of gold. When a few of his alpha particles came bounding back, he hypothesized a nucleus had knocked them off the track. ...
Section 3.6
... (c) A magnet should separate these coins easily, because nickel is ferromagnetic (strongly magnetic) and silver is not. 17. ESR spectroscopy places samples of paramagnetic material in a high uniform magnetic field to split the energy levels of the ground state. The results can be used to help determ ...
... (c) A magnet should separate these coins easily, because nickel is ferromagnetic (strongly magnetic) and silver is not. 17. ESR spectroscopy places samples of paramagnetic material in a high uniform magnetic field to split the energy levels of the ground state. The results can be used to help determ ...
Name: : :___ Building Atoms An atom is made of 3 particles. Name
... isotopes. For example, hydrogen has 2 isotopes. One has a mass number of “1” and is called hydrogen-1. The other has a mass number of “2” and is called hydrogen-2. How many isotopes can one element have? Can an atom have just any number of neutrons? No; there are "preferred" combinations of neutrons ...
... isotopes. For example, hydrogen has 2 isotopes. One has a mass number of “1” and is called hydrogen-1. The other has a mass number of “2” and is called hydrogen-2. How many isotopes can one element have? Can an atom have just any number of neutrons? No; there are "preferred" combinations of neutrons ...
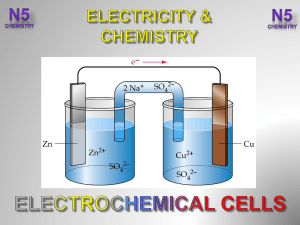
3.-Electrochemical-Cells-V2-
... The number of (aq) decrease as they change into (s). The solution needs +ve ions to remain electrically neutral. ...
... The number of (aq) decrease as they change into (s). The solution needs +ve ions to remain electrically neutral. ...
What other element has similar properties to Chlorine Cl (#17)
... Chemistry review questions 2a-2b 1. What other element has similar properties to Chlorine Cl (#17) 2. How many valence electrons does oxygen have? 3. What is group 18 called? alkali, alkaline-earth, transition, noble gases, or halogen 4. What type of bond will beryllium & sulfur form? Covalent, ioni ...
... Chemistry review questions 2a-2b 1. What other element has similar properties to Chlorine Cl (#17) 2. How many valence electrons does oxygen have? 3. What is group 18 called? alkali, alkaline-earth, transition, noble gases, or halogen 4. What type of bond will beryllium & sulfur form? Covalent, ioni ...