Chemistry Major Understandings
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
Solid-state physics
... The forces between the atoms in a crystal can take a variety of forms. For example, in a crystal of sodium chloride (common salt), the crystal is made up of ionic sodium and chlorine, and held together with ionic bonds. In others, the atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds. In metals, electro ...
... The forces between the atoms in a crystal can take a variety of forms. For example, in a crystal of sodium chloride (common salt), the crystal is made up of ionic sodium and chlorine, and held together with ionic bonds. In others, the atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds. In metals, electro ...
A. Atomic and Nuclear Structure
... negative instead of positive. In an uncharged atom, the number of orbital electrons equals the number of protons within the nucleus. When the number of orbital electrons does not equal the number of protons in the nucleus, an overall imbalance of charge exists for the atom. A charged atom is known a ...
... negative instead of positive. In an uncharged atom, the number of orbital electrons equals the number of protons within the nucleus. When the number of orbital electrons does not equal the number of protons in the nucleus, an overall imbalance of charge exists for the atom. A charged atom is known a ...
Physical Science Week 1
... • Create a diagram showing the correct number and placement (relative) of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Color and neatness count. • Create a legend (key) • Add the square from periodic table for your element. ...
... • Create a diagram showing the correct number and placement (relative) of neutrons, protons, and electrons. Color and neatness count. • Create a legend (key) • Add the square from periodic table for your element. ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... measure of an atom's degree to which it attracts electrons is called its electronegativity. If a covalent bond is formed between two atoms that have drastically different electronegativities, the shared elect ...
... measure of an atom's degree to which it attracts electrons is called its electronegativity. If a covalent bond is formed between two atoms that have drastically different electronegativities, the shared elect ...
Chemical Bonds ch6 p.161
... Most are solids Higher melting point Higher boiling point Many dissolve in water, +ion and -ion break apart in water so will conduct electricity in water. Some do not dissolve because the pull between the charges are greater than the attraction of H2O molecule ...
... Most are solids Higher melting point Higher boiling point Many dissolve in water, +ion and -ion break apart in water so will conduct electricity in water. Some do not dissolve because the pull between the charges are greater than the attraction of H2O molecule ...
Lecture 21 – Cations, Anions and Hydrolysis in
... Plus the small coordination number means the oxygen lone pairs are held very tightly by the cation weakening O-H bonds more than would otherwise be expected. ...
... Plus the small coordination number means the oxygen lone pairs are held very tightly by the cation weakening O-H bonds more than would otherwise be expected. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _D__ 32) Which of the following elements is in the same period as krypton? a. helium b. magnesium c. nitrogen d. bromine _B__ 33) Of the elements Fr, Sb, Al, and Rn, which is a metalloid? a. Fr b. Sb c. Al d. Rn _A__ 34) Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. Atoms of the same element mus ...
... _D__ 32) Which of the following elements is in the same period as krypton? a. helium b. magnesium c. nitrogen d. bromine _B__ 33) Of the elements Fr, Sb, Al, and Rn, which is a metalloid? a. Fr b. Sb c. Al d. Rn _A__ 34) Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. Atoms of the same element mus ...
So where did all the matter on Earth come from - Bennatti
... atomic number of helium is two. Each helium atom has two protons. No other element is made of atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letter ...
... atomic number of helium is two. Each helium atom has two protons. No other element is made of atoms with two protons in the nucleus. Each element is represented with a chemical symbol. Most chemical symbols are one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If it has two or three letter ...
Ang. bindningstyper och elektronegativitet
... A coordinate covalent bond is one where both bonding electrons are from one of the atoms involved in the bond. These bonds give rise to Lewis acids and bases. The electrons are shared roughly equally between the atoms in contrast to ionic bonding. Such bonding occurs in molecules such as the ammoniu ...
... A coordinate covalent bond is one where both bonding electrons are from one of the atoms involved in the bond. These bonds give rise to Lewis acids and bases. The electrons are shared roughly equally between the atoms in contrast to ionic bonding. Such bonding occurs in molecules such as the ammoniu ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... light. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom's electrons making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy differe ...
... light. The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom's electrons making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The energy of the emitted photon is equal to the energy differe ...
Nomenclature
... • Some compounds contain H2O in their structure. These compounds are called hydrates. • This is different from (aq) because the H2O is part of the molecule (not just surrounding it). • The H2O can usually be removed if heated. • A dot separates water: e.g. CuSO4•5H2O is ...
... • Some compounds contain H2O in their structure. These compounds are called hydrates. • This is different from (aq) because the H2O is part of the molecule (not just surrounding it). • The H2O can usually be removed if heated. • A dot separates water: e.g. CuSO4•5H2O is ...
STRUCTURE OF AN ATOM
... gases are poor conductors of electricity at normal pressures but Discharge tube experiment-Production of by decreasing pressure they can behave as electrolytes ...
... gases are poor conductors of electricity at normal pressures but Discharge tube experiment-Production of by decreasing pressure they can behave as electrolytes ...
Midterm Review Answers
... sodium fluoride, and sodium hydroxide you need to separate the barium, mercury(II), and magnesium ions. How would you go about separating these ions? Discuss your experimental procedure and defend your answer. Using the solubility rules, chloride compounds are generally soluble, but mercury is an ex ...
... sodium fluoride, and sodium hydroxide you need to separate the barium, mercury(II), and magnesium ions. How would you go about separating these ions? Discuss your experimental procedure and defend your answer. Using the solubility rules, chloride compounds are generally soluble, but mercury is an ex ...
Investigating the formulae of Complex Ions
... the number of EDTA molecules that combine with one nickel (II) ion and hence determine the formula of the complex formed between the Ni2+ and the EDTA. In this experiment EDTA is used in the form of its disodium salt. You should prepare the following solutions ...
... the number of EDTA molecules that combine with one nickel (II) ion and hence determine the formula of the complex formed between the Ni2+ and the EDTA. In this experiment EDTA is used in the form of its disodium salt. You should prepare the following solutions ...
Honors Chemistry First Marking Period Review Sheet
... four quantum numbers. I understand that electrons are assigned to the subshells of an atom in order of increasing subshell energy. In the H atom, the subshell energies increase with increasing n , but in a many-electron atom, the energies depend on both n and l. I can use the Aufbau principle to hel ...
... four quantum numbers. I understand that electrons are assigned to the subshells of an atom in order of increasing subshell energy. In the H atom, the subshell energies increase with increasing n , but in a many-electron atom, the energies depend on both n and l. I can use the Aufbau principle to hel ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2013 - Chapter 7 Homework 7 (Chapter 7: Periodic
... A) alkali metals have lower densities B) alkali metals have greater electron affinities C) alkali metals have lower ionization energies D) alkali metals have lower melting points E) alkali metals are not more reactive than alkaline earth metals ...
... A) alkali metals have lower densities B) alkali metals have greater electron affinities C) alkali metals have lower ionization energies D) alkali metals have lower melting points E) alkali metals are not more reactive than alkaline earth metals ...
1 - KCSE Online
... √ 1mk Copper (III) oxide (CuO) where ammonia is √ 1mk oxidize to nitrogen/(Y) (ii) 2NH3(g) + 3CuO (s) → N2(g) + 3Cu(s) + 3H2O(l) √ 1mk (e) Carbon (IV) oxide/CO2 √ 1mk (f) Any noble gases (He, Ne, Ar) √ 1mk (g) (i) Haber process √ 1mk (ii) More of gas X formed √ 1mk lower temperature favours forward ...
... √ 1mk Copper (III) oxide (CuO) where ammonia is √ 1mk oxidize to nitrogen/(Y) (ii) 2NH3(g) + 3CuO (s) → N2(g) + 3Cu(s) + 3H2O(l) √ 1mk (e) Carbon (IV) oxide/CO2 √ 1mk (f) Any noble gases (He, Ne, Ar) √ 1mk (g) (i) Haber process √ 1mk (ii) More of gas X formed √ 1mk lower temperature favours forward ...
name
... CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERISTICS OF ELEMENTS Use a periodic table of the elements to help you answer the following questions. 1. a) ...
... CHAPTER 5 CHARACTERISTICS OF ELEMENTS Use a periodic table of the elements to help you answer the following questions. 1. a) ...
Chapter 2 – Chemical Composition of the Body
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
... • Bonds formed between the hydrogen end (+ charged) of a polar molecule and the – end of any other polar molecule or highly electronegative atom (e.g. P, N, O) are called hydrogen bonds. • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molec ...
AP Chemistry
... Hydrogen bonding London dispersion forces Van der Waal forces Surface tension Capillary action Viscosity Crystalline solids Lattice unit cell Ionic solids Atomic solids (metallic, network, Group 18) Molecular solids Malleable Ductile Band model Alloys: substitutional, interstitial Diamonds vs graphi ...
... Hydrogen bonding London dispersion forces Van der Waal forces Surface tension Capillary action Viscosity Crystalline solids Lattice unit cell Ionic solids Atomic solids (metallic, network, Group 18) Molecular solids Malleable Ductile Band model Alloys: substitutional, interstitial Diamonds vs graphi ...
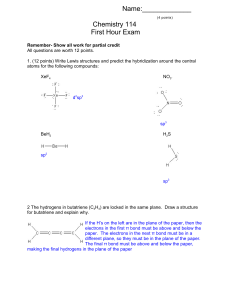
Name:______ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
... 3. One of the compounds you have met in the lab is NO gas, the nasty smelling brown gas that can come out of an internal combustion engine and that forms the brown haze of air pollution around big cities. NO uses the same series of molecular orbitals as C2 or N2. Show the occupied and unoccupied mo ...
Unit 2 Review Questions Fill in the blank In a(n) change, a new
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
... The mass number is the sum of electrons and protons in the atom. l. A Bohr diagram shows electrons in orbits about the nucleus. m. A row of the periodic table is called a period. n. The size of atoms increase down a column of the periodic table. o. Alkali metals include fluorine, chlorine, and iodin ...
- Bright Star Schools
... 2. Describe what an atom looks like in your own words (use the vocabulary) ...
... 2. Describe what an atom looks like in your own words (use the vocabulary) ...