Units 3 and 4 Revision
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
1st Term Review
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
Are You suprised ?
... a. two elements in the same group (A) b. two elements in the same period (B) c. a transition metal (C) d. A lanthanide (D) e. An alkali Earth Metal (E) f. A non-metal (F) g. A metalloid (G) ...
... a. two elements in the same group (A) b. two elements in the same period (B) c. a transition metal (C) d. A lanthanide (D) e. An alkali Earth Metal (E) f. A non-metal (F) g. A metalloid (G) ...
atomic theory - unit a
... • Atomic size: 0.1 - 0.5 nm • 1981 - STM (scanning tunneling microscope) used to "see" atoms Dalton's Atomic Theory - 1808 1) Each element is composed of small particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical to each other. 3) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4) Atoms of one ele ...
... • Atomic size: 0.1 - 0.5 nm • 1981 - STM (scanning tunneling microscope) used to "see" atoms Dalton's Atomic Theory - 1808 1) Each element is composed of small particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of an element are identical to each other. 3) Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. 4) Atoms of one ele ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... • Every element wants 8 valence electrons to become stable. They will gain or lose valence electrons to form an octet • For example…Group 1A elements have 1 valence electron. They can either gain 7 electrons to have an octet or lose 1. • What is easier? Lose 1 ...
... • Every element wants 8 valence electrons to become stable. They will gain or lose valence electrons to form an octet • For example…Group 1A elements have 1 valence electron. They can either gain 7 electrons to have an octet or lose 1. • What is easier? Lose 1 ...
coppin state college
... Name _____________________________________ID#_____________ Last First Chemistry 103-101 Examination II Chapter 2 – The Composition and Structure of the Atom. March, 2004. Time 60 minutes. Dr. Alfred N. Amah This examination consists of 38 multiple choice questions with five possible responses. Read ...
... Name _____________________________________ID#_____________ Last First Chemistry 103-101 Examination II Chapter 2 – The Composition and Structure of the Atom. March, 2004. Time 60 minutes. Dr. Alfred N. Amah This examination consists of 38 multiple choice questions with five possible responses. Read ...
cell molecules
... • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturally-occurring elements. • Each element has a unique symbol, usually from the first one or ...
... • Organisms are composed of matter. • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. • There are 92 naturally-occurring elements. • Each element has a unique symbol, usually from the first one or ...
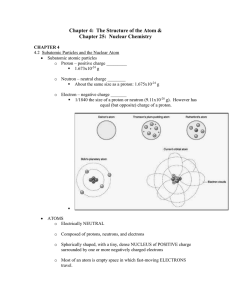
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-28 g). However has equal (but opposite) charge of a proton. ...
... 1.673x10-24 g o Neutron – neutral charge ________ About the same size as a proton: 1.675x10-24 g o Electron – negative charge _______ 1/1840 the size of a proton or neutron (9.11x10-28 g). However has equal (but opposite) charge of a proton. ...
Chapt3
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
... Ionic Compounds -- Ionic Bonding -- electron transfer result from transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another to yield oppositely-charged particles called ions cation = positive ion ...
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... repeat the process above with each other. Walk around and check their work, making sure that they correctly understand and answering any questions that come up. Having them answer each other’s questions is a great confidence builder, as they see that they have the skills to help each other. Finally, ...
... repeat the process above with each other. Walk around and check their work, making sure that they correctly understand and answering any questions that come up. Having them answer each other’s questions is a great confidence builder, as they see that they have the skills to help each other. Finally, ...
File
... are in a fixed and definite ratio, (e.g. NaCl is always 60.66% of Na and 39.34% of Cl by mass regardless of the size or the source of the compound). Law of multiple proportions-When two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element are combined with the same mass of the o ...
... are in a fixed and definite ratio, (e.g. NaCl is always 60.66% of Na and 39.34% of Cl by mass regardless of the size or the source of the compound). Law of multiple proportions-When two elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element are combined with the same mass of the o ...
Properties of Ionic and Covalent Substances
... obtain a stable valence shell atoms can either gain or lose electrons or share electrons. Ionic Compounds If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms a positive ion (cation). Negative and positive ions attract each other and form “ionic bonds”. Ioni ...
... obtain a stable valence shell atoms can either gain or lose electrons or share electrons. Ionic Compounds If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms a positive ion (cation). Negative and positive ions attract each other and form “ionic bonds”. Ioni ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule (covalent compound) and an ionic compound. Include the interaction between valence electrons and the types of bonds for each. 11. There ar ...
... 9. Describe how the current periodic table is arranged by comparing groups, periods and properties of the elements. 10. Explain the difference between a molecule (covalent compound) and an ionic compound. Include the interaction between valence electrons and the types of bonds for each. 11. There ar ...
Gas-forming Reactions
... the peroxide ion (O22–) in which its oxidation state is - 1, 4. Hydrogen almost always has an oxidation state of +1. Exceptions include metal hydrides (such as NaH) in which its oxidation state is -1. 5. Fluorine (as an ion) always has an oxidation state of – 1. No exceptions. 6. The other halogens ...
... the peroxide ion (O22–) in which its oxidation state is - 1, 4. Hydrogen almost always has an oxidation state of +1. Exceptions include metal hydrides (such as NaH) in which its oxidation state is -1. 5. Fluorine (as an ion) always has an oxidation state of – 1. No exceptions. 6. The other halogens ...
Review Material
... from left to right across a period. Fluorine is the most electronegative element. ...
... from left to right across a period. Fluorine is the most electronegative element. ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... – non-metal (poor conductor) – metalloid (between metal and non-metal) ...
... – non-metal (poor conductor) – metalloid (between metal and non-metal) ...
All That Matters - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Enthalpy (H) is a measure of the internal energy of a system. It can be thought of as the sum total of all the energy in the chemical bonds of a material, the energy of its state, the kinetic energy of its internal particles and any other way that a substance can contain energy. ...
... Enthalpy (H) is a measure of the internal energy of a system. It can be thought of as the sum total of all the energy in the chemical bonds of a material, the energy of its state, the kinetic energy of its internal particles and any other way that a substance can contain energy. ...
V. Chemical reactions
... b. Which elements have two valence electrons? Column 2 c. Which elements have three valence electrons? Column 13 d. Which elements have four valence electrons? Column 14 e. Which elements have five valence electrons? Column 15 f. Which elements have six valence electrons? Column 16 g. Which elements ...
... b. Which elements have two valence electrons? Column 2 c. Which elements have three valence electrons? Column 13 d. Which elements have four valence electrons? Column 14 e. Which elements have five valence electrons? Column 15 f. Which elements have six valence electrons? Column 16 g. Which elements ...
summer learning G10
... Which group is it in? What period is it in? When bonding, would it prefer to lose or gain electrons? If so, how many? ...
... Which group is it in? What period is it in? When bonding, would it prefer to lose or gain electrons? If so, how many? ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Chapter 2
... - a substance, that within a certain range, maintains a constant pH by combining with H+ when mixed with an acid, or releasing H+ when mixed with a base - Buffers do not necessarily maintain a pH of 7. H2O + CO2 H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ ...
... - a substance, that within a certain range, maintains a constant pH by combining with H+ when mixed with an acid, or releasing H+ when mixed with a base - Buffers do not necessarily maintain a pH of 7. H2O + CO2 H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... Formed from only non-metallic elements Does not form ions in solution Does not conduct electricity when dissolved in water Solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature. ...
... Formed from only non-metallic elements Does not form ions in solution Does not conduct electricity when dissolved in water Solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature. ...