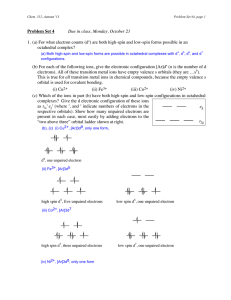
Atomic number
... Temperature will affect solubility- the solubility will be INCREASED as the temperature is increased. Stirring will increase solubility. Molecular or Particle Size will affect the solubility. The larger the molecule or particle the less soluble the substance will ...
... Temperature will affect solubility- the solubility will be INCREASED as the temperature is increased. Stirring will increase solubility. Molecular or Particle Size will affect the solubility. The larger the molecule or particle the less soluble the substance will ...
Document
... ii. Few elements are found in nature in their pure state. Instead they exist in combination with other elements in the form of compounds. ...
... ii. Few elements are found in nature in their pure state. Instead they exist in combination with other elements in the form of compounds. ...
Atomic Theories- Part I - Tenafly Public Schools
... Thompson showed that the production of the cathode ray was not dependent on the type of gas in the tube, or the type of metal used for the electrodes. He concluded that these particles were part of every atom. ...
... Thompson showed that the production of the cathode ray was not dependent on the type of gas in the tube, or the type of metal used for the electrodes. He concluded that these particles were part of every atom. ...
Chapter 4 – Matter - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... sub-microscopic scale; one phase throughout: ...
... sub-microscopic scale; one phase throughout: ...
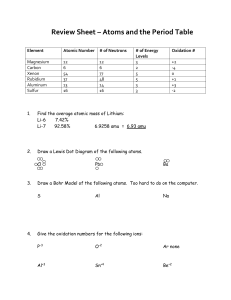
oxidation number
... The outer electrons are involved in bonding. These are called valence electrons. ...
... The outer electrons are involved in bonding. These are called valence electrons. ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding
... the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms Ex: Calcium Oxide A triple covalent bond is a covalent bond produced by the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms Ex: Ethyne C2H2 Resonance refers to bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single s ...
... the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms Ex: Calcium Oxide A triple covalent bond is a covalent bond produced by the sharing of three pairs of electrons between two atoms Ex: Ethyne C2H2 Resonance refers to bonding in molecules or ions that cannot be correctly represented by a single s ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energy when the electrons are in different orbitals with their spins pointing in the same direction (e.g., all spin up, ↑↑). It is higher energy if the electrons pair in one orbital or even if they have opposite s ...
... When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energy when the electrons are in different orbitals with their spins pointing in the same direction (e.g., all spin up, ↑↑). It is higher energy if the electrons pair in one orbital or even if they have opposite s ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... dissociate into ions in water – Ions (electrolytes) conduct electrical currents in solution – Ions play specialized roles in body functions (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium, and iron) – Ionic balance vital for ...
... dissociate into ions in water – Ions (electrolytes) conduct electrical currents in solution – Ions play specialized roles in body functions (e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium, and iron) – Ionic balance vital for ...
Chap 2.1 Notes - Nature of Matter
... The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its atoms. The atomic mass of an element is a sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. Some elements have isotopes – atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons. ...
... The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in its atoms. The atomic mass of an element is a sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. Some elements have isotopes – atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons. ...
Bonding Challenge
... Station 2 (Get in “shape”) 1) (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. (b) Put the three species in order of increasing C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. (c) Predict the molecular shapes for the three spe ...
... Station 2 (Get in “shape”) 1) (a) Draw the Lewis electron-dot structures for CO32-, CO2, and CO, including resonance structures where appropriate. (b) Put the three species in order of increasing C-O bond length? Explain the reason for your answer. (c) Predict the molecular shapes for the three spe ...
The Role of Ions in Body Chemistry Negative Ion Report: The CBS
... the acupuncture meridians in the human body; they originate from cellular metabolism and ionic atmospheric and geomagnetic forces and result in electrically measurable force fields about the human body. Electro-magnetic energy can adversely affect these fields, resulting in subjacent cellular derang ...
... the acupuncture meridians in the human body; they originate from cellular metabolism and ionic atmospheric and geomagnetic forces and result in electrically measurable force fields about the human body. Electro-magnetic energy can adversely affect these fields, resulting in subjacent cellular derang ...
Deconstructed HS-PS1-2
... Distinguish between how element properties progress among families (vertical/patterns) compared to across families (horizontal/trend) on the periodic table. ...
... Distinguish between how element properties progress among families (vertical/patterns) compared to across families (horizontal/trend) on the periodic table. ...
section_2_review_set
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
... 1. What is the claim to fame for the proton? 2. What is the claim to fame for the electron? 3. What is the claim to fame for the neutron? 4. What is the mass of each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; electron. 5. What is the charge for each of the following particles?: proton; neutron; e ...
Slide 1
... • Oxidation by molecular oxygen - Almost all elements combine with molecular oxygen to form binary oxides; the loss of electrons is called oxidation because elements lose electrons when they combine with oxygen. The more easily a metal is oxidized, the more readily it reacts with molecular ...
... • Oxidation by molecular oxygen - Almost all elements combine with molecular oxygen to form binary oxides; the loss of electrons is called oxidation because elements lose electrons when they combine with oxygen. The more easily a metal is oxidized, the more readily it reacts with molecular ...
Midterm Review Date
... shared with nitrogen. B) Nitrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with hydrogen. C) Hydrogen transfers a pair of electrons to nitrogen. D) Nitrogen transfers a pair of electrons to ...
... shared with nitrogen. B) Nitrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with hydrogen. C) Hydrogen transfers a pair of electrons to nitrogen. D) Nitrogen transfers a pair of electrons to ...
Chemistry 3202 Name: Acid-base Theory Problems Assignment 1
... Strong acids, such as perchloric acid, have been shown to react quantitatively with strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide. ...
... Strong acids, such as perchloric acid, have been shown to react quantitatively with strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide. ...
Review Sheet Filled Out
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
... List the number of facts you know about electrons. Electrons closest to the nucleus have the least amount of energy Electrons farthest away from the nucleus have the most energy – valence e Have a negative charge Have insignificant mass and volume Reside in the 99.996% of the atom outside t ...
File
... • When atoms form ions they aim to attain electron shells that are either completely full or completely empty. • If we know the electron configuration of an atom we can usually work out how many electrons it must lose or gain to achieve a noble gas configuration. • This will tell us the charge on it ...
... • When atoms form ions they aim to attain electron shells that are either completely full or completely empty. • If we know the electron configuration of an atom we can usually work out how many electrons it must lose or gain to achieve a noble gas configuration. • This will tell us the charge on it ...
8.1 Classifying inorganic compounds
... Acidity is a measure of the relative amounts of H+ and OH- ions in solution (Table 4 p.205) – the higher the number of H+ ions in solution the ...
... Acidity is a measure of the relative amounts of H+ and OH- ions in solution (Table 4 p.205) – the higher the number of H+ ions in solution the ...
I CAN write Chemical formulas
... oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
... oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... If lose 1 e- = +1 charge If gain 1 e- = -1 charge If lose 2 e- = +2 charge If gain 2 e- = -2 charge ...
... If lose 1 e- = +1 charge If gain 1 e- = -1 charge If lose 2 e- = +2 charge If gain 2 e- = -2 charge ...
SCH3U Course Review
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... Ionization energies tend to increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
NOMENCLATURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS CHEMISTRY 1411
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
... The prefixes mono, di, tri, tetra etc are used only for binary covalent compounds. ...
Topic 3&4 Atoms and the per.table
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
... Q4. Explain why the metal elements in group 1 are (a) called the alkali metals. (b) stored under oil. Q5. What happens to the melting point of the elements in group 7 (the halogens) as you go the group? Answers:- Q3. Lithium. Q4. (a) The elements in group 1 react with water to form an ...
Atom QuizO
... A.) A element with a positive charge B.) A subatomic particle in the nucleus with no charge C.) A element with no charge and in the nucleus D.) An ingredient used in Pepsi. ...
... A.) A element with a positive charge B.) A subatomic particle in the nucleus with no charge C.) A element with no charge and in the nucleus D.) An ingredient used in Pepsi. ...