Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
... octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if all of its single electrons are used in a covalent bond, and there are sur ...
Document
... 9. Which statement best explains why there could be a force of attraction between two electrically charged ...
... 9. Which statement best explains why there could be a force of attraction between two electrically charged ...
Electronics background
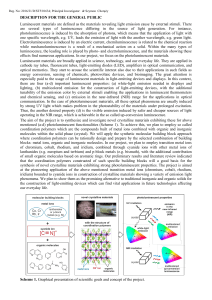
... At the junction of the p-type and n-type some of the electrons will migrate from the ntype into the holes in the p-type. This creates a region at the junction without any charge carriers i.e. an insulating layer. As electrons have left the n-type it becomes positively charged near the junction whil ...
... At the junction of the p-type and n-type some of the electrons will migrate from the ntype into the holes in the p-type. This creates a region at the junction without any charge carriers i.e. an insulating layer. As electrons have left the n-type it becomes positively charged near the junction whil ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... c. sulfur 3. Identify the elements having the following electron configurations: a. 1s22s22p63s23p3 b. [Ar]4s1 c. contains four electrons in its third and outer main energy level d. contains one set of paired and three unpaired electrons in its fourth and outer main energy level 4. Distinguish betwe ...
... c. sulfur 3. Identify the elements having the following electron configurations: a. 1s22s22p63s23p3 b. [Ar]4s1 c. contains four electrons in its third and outer main energy level d. contains one set of paired and three unpaired electrons in its fourth and outer main energy level 4. Distinguish betwe ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
Tips for Learning General Chemistry Rules, Trends and Exceptions
... Not all metals explode in water (thank goodness.) Some require more stringent conditiors and some don't react at all. There are four cases. ...
... Not all metals explode in water (thank goodness.) Some require more stringent conditiors and some don't react at all. There are four cases. ...
Chemical Reactions Chemical Arithmetic
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions • Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction- A chemical reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bon ...
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions • Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction- A chemical reaction in which the oxidation numbers of elements change because of a loss or gain of electrons • Oxidation Number- A number that indicates the charge that an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion would have if all bon ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
Atomic Theory Review
... Ionic compound charges 1. Which is a positive ion: A cation or an anion? 2. What is the charge of zinc in Zn3(PO4)2? 3. What is the charge on the iron atom in FePO4? 4. What is the name of FePO4? 5. What is the name of FeP? 6. Which of the following is incorrect? a) Sulfate is SO32- b) nitrate is a ...
... Ionic compound charges 1. Which is a positive ion: A cation or an anion? 2. What is the charge of zinc in Zn3(PO4)2? 3. What is the charge on the iron atom in FePO4? 4. What is the name of FePO4? 5. What is the name of FeP? 6. Which of the following is incorrect? a) Sulfate is SO32- b) nitrate is a ...
Classifying Reactions: A good summary
... Since all these happens on the negative electrode. So, H2 gas forms from the negative electrode and that's exactly what happens when water reduces at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. S ...
... Since all these happens on the negative electrode. So, H2 gas forms from the negative electrode and that's exactly what happens when water reduces at the cathode. 8. (Trick #2) When CuSO4(aq) is electrolyzed, you know that Cu° metal is going to form because copper's potential is higher than water. S ...
Summer Work
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... - ions can form independent of ionic bonds Remember, atoms can gain or lose electrons. This unbalances the numbers of protons and electrons, resulting in the atom acquiring an electrical charge. If an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged. If it loses electrons it becomes positively cha ...
... - ions can form independent of ionic bonds Remember, atoms can gain or lose electrons. This unbalances the numbers of protons and electrons, resulting in the atom acquiring an electrical charge. If an atom gains electrons it becomes negatively charged. If it loses electrons it becomes positively cha ...
Hydrogen Bonding
... Compound – One of the two interacting atoms is much more electronegative than the other (one or more electrons in the less electronegative atom are transferred to the more electronegative atom) Two electrically charged particles are called ions. Cation – Ion with a positive charge (Ca2+ or H+) Ani ...
... Compound – One of the two interacting atoms is much more electronegative than the other (one or more electrons in the less electronegative atom are transferred to the more electronegative atom) Two electrically charged particles are called ions. Cation – Ion with a positive charge (Ca2+ or H+) Ani ...
DESCRIPTION FOR THE GENERAL PUBLIC Luminescent materials
... Thus, the another desired property (d) is the visible emission induced by safer and cheaper sources of light operating in the NIR range, which is achievable in the so called up-conversion luminescence. The aim of the project is to synthesize and investigate novel crystalline materials exhibiting the ...
... Thus, the another desired property (d) is the visible emission induced by safer and cheaper sources of light operating in the NIR range, which is achievable in the so called up-conversion luminescence. The aim of the project is to synthesize and investigate novel crystalline materials exhibiting the ...
CHEM_S1CourseReview_2011
... Unit 2: Atomic Structure Essential questions: What is an atom? What are the early models of the atom and how has scientific exploration lead to the current model? What is a theory? How do you identify the relative mass, relative charge, and location of the three smaller subatomic particles o ...
... Unit 2: Atomic Structure Essential questions: What is an atom? What are the early models of the atom and how has scientific exploration lead to the current model? What is a theory? How do you identify the relative mass, relative charge, and location of the three smaller subatomic particles o ...
Chem fundamentals 1a
... of protons (and electrons for a neutral form) • The periodic table presents these arranged by increasing numbers of protons and electrons • Columns represent GROUPS of elements sharing outermost (valence) electron numbers and therefore chemical behaviors • Rows in the periodic table dep ...
... of protons (and electrons for a neutral form) • The periodic table presents these arranged by increasing numbers of protons and electrons • Columns represent GROUPS of elements sharing outermost (valence) electron numbers and therefore chemical behaviors • Rows in the periodic table dep ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 16. Explain how you know whether or not SR or DR reaction will occur. Provide an example for SR and DR that will occur. Provide an example for SR and DR that will not occur. (Use blue solubility sheet) A SR reaction will occur if the element that is by itself is more reactive (higher up) on the reac ...
... 16. Explain how you know whether or not SR or DR reaction will occur. Provide an example for SR and DR that will occur. Provide an example for SR and DR that will not occur. (Use blue solubility sheet) A SR reaction will occur if the element that is by itself is more reactive (higher up) on the reac ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
... 5. If you have 4 g NaOH, and 10 g HBr, what is the limiting reagent and how much salt is produced? In lab if you produce1 g salt, what is the percent yield? ...
Unit 6 Naming Binary Compounds
... Binary covalent compounds contain two types of nonmetals bonded together, or a metalloid and a nonmetal. 1. Name the elements in the order listed in the formula. 2. Use prefixes to indicate the number of each kind of atom. 3. Omit the prefix mono- when the formula contains only one atom of the first ...
... Binary covalent compounds contain two types of nonmetals bonded together, or a metalloid and a nonmetal. 1. Name the elements in the order listed in the formula. 2. Use prefixes to indicate the number of each kind of atom. 3. Omit the prefix mono- when the formula contains only one atom of the first ...
Station 1-Lewis Structures For the following formulas, complete the
... 2. Two 3. Electricity can only be conducted when ions are moving. In their crystalline form, the ions in the ionic compound are locked tightly in one place. 4. a. The high melting point points toward an ionic compound, though the fact that it dissolves is irrelevant. b. This is ionic. The brittlenes ...
... 2. Two 3. Electricity can only be conducted when ions are moving. In their crystalline form, the ions in the ionic compound are locked tightly in one place. 4. a. The high melting point points toward an ionic compound, though the fact that it dissolves is irrelevant. b. This is ionic. The brittlenes ...
Name
... How do you determine the number of valence electrons for an element using the periodic table? Give the number of valence electrons for: ...
... How do you determine the number of valence electrons for an element using the periodic table? Give the number of valence electrons for: ...