Worksheet 8 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... Does Co3+ act as a Lewis acid? Draw the Lewis structure and explain. List and draw two additional Lewis acids. Yes, Co3+ like the transition metal ions acts as Lewis acids. They accept a pair (or several pairs) of electrons to form a new bond (several new bonds). On the left side of the structure be ...
... Does Co3+ act as a Lewis acid? Draw the Lewis structure and explain. List and draw two additional Lewis acids. Yes, Co3+ like the transition metal ions acts as Lewis acids. They accept a pair (or several pairs) of electrons to form a new bond (several new bonds). On the left side of the structure be ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combine in one-to-one ratios. c. Atoms of the same element are always identical. d. Individual atoms can be seen wit ...
... a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combine in one-to-one ratios. c. Atoms of the same element are always identical. d. Individual atoms can be seen wit ...
Grade 10 Science – Unit 2
... By looking at the Lewis Dot Diagram for oxygen, you can see that oxygen has two unpaired electrons, so it has two electrons available for standard bonds. These unpaired electrons might make two single covalent bonds (e.g., water (H2O)) or they might make one double covalent bond, as the case of magn ...
... By looking at the Lewis Dot Diagram for oxygen, you can see that oxygen has two unpaired electrons, so it has two electrons available for standard bonds. These unpaired electrons might make two single covalent bonds (e.g., water (H2O)) or they might make one double covalent bond, as the case of magn ...
Chapter 2
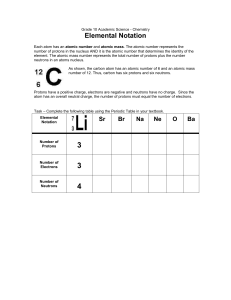
... 1. # protons = atomic number (unique for each element) 2. # protons + # neutrons = atomic mass ...
... 1. # protons = atomic number (unique for each element) 2. # protons + # neutrons = atomic mass ...
The pH Scale…
... • Neutralize- to add an acid to a basic solution or a base to an acidic solution until it is chemically neutral or safe. (pH = 7). • So…how would you neutralize a strong base like a laundry detergent spill on your skin? Pour large amounts of a weak acid on your skin like ...
... • Neutralize- to add an acid to a basic solution or a base to an acidic solution until it is chemically neutral or safe. (pH = 7). • So…how would you neutralize a strong base like a laundry detergent spill on your skin? Pour large amounts of a weak acid on your skin like ...
Unit 9 – Behavior of Gases
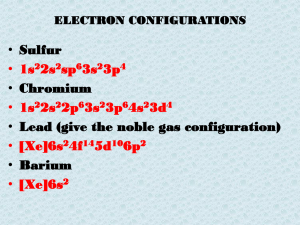
... 1. Which subatomic particle plays the largest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element? Explain. 2. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom. 3. Write the full electron configuration for the following: a. potassium atom b. sulfur atom c. Chlorine ion d. Calcium ion 4. Create a ...
... 1. Which subatomic particle plays the largest role in determining the physical and chemical properties of an element? Explain. 2. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom. 3. Write the full electron configuration for the following: a. potassium atom b. sulfur atom c. Chlorine ion d. Calcium ion 4. Create a ...
Chemistry SOL Review
... – …between 0 and 0.4, the bond is nonpolar, meaning the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms – …between 0.4 and 2, the bond is polar, meaning the more electronegative element is pulling harder on the electrons – …greater than 2, the bond is ionic, meaning the more electronegative eleme ...
... – …between 0 and 0.4, the bond is nonpolar, meaning the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms – …between 0.4 and 2, the bond is polar, meaning the more electronegative element is pulling harder on the electrons – …greater than 2, the bond is ionic, meaning the more electronegative eleme ...
IPC Semester Exam Review – Chemistry Topics
... Questions will include multiple-choice and matching. You will need a calculator and a pencil for the Scantron form. A periodic table and conversion chart will be provided. The Nature of Science Identify each of the following examples as PURE or APPLIED sciences. 1. Development of the computer ch ...
... Questions will include multiple-choice and matching. You will need a calculator and a pencil for the Scantron form. A periodic table and conversion chart will be provided. The Nature of Science Identify each of the following examples as PURE or APPLIED sciences. 1. Development of the computer ch ...
Semester 1 Study Guide – Chemistry
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
... meaning that only certain discrete energy levels are allowed. ...
Writing formulas and naming ionic bonds
... The amount of matter in a substance? Matter The amount of space an object takes up is Volume A ratio that compares the mass of an object to its volume? • Density • If you cut a piece of gold in half, it’s volume and mass change. Does it’s density? • No- density is an intrinsic property ...
... The amount of matter in a substance? Matter The amount of space an object takes up is Volume A ratio that compares the mass of an object to its volume? • Density • If you cut a piece of gold in half, it’s volume and mass change. Does it’s density? • No- density is an intrinsic property ...
pH scale learning goals
... Learning goals for pH scale Students will be able to use pH Scale to • Write descriptions that demonstrate the use of pH and/or relative hydronium and hydroxide ions as shown in the simulation to: A. Determine if a liquid is acidic or basic B. Place liquids in relative order of acidity or basicity ...
... Learning goals for pH scale Students will be able to use pH Scale to • Write descriptions that demonstrate the use of pH and/or relative hydronium and hydroxide ions as shown in the simulation to: A. Determine if a liquid is acidic or basic B. Place liquids in relative order of acidity or basicity ...
Slajd 1 - Uniwersytet Warszawski
... The following values were obtained: ∆H = -36.27 kcal/mol and ∆G = -32.42 kcal/mol. These values prove that the reaction between verapamil and the calcium ion is spontaneous and hence thermodynamically possible. The calculated values of ∆G give information whether the reaction is spontaneous and ther ...
... The following values were obtained: ∆H = -36.27 kcal/mol and ∆G = -32.42 kcal/mol. These values prove that the reaction between verapamil and the calcium ion is spontaneous and hence thermodynamically possible. The calculated values of ∆G give information whether the reaction is spontaneous and ther ...
Chapter 2 - A
... allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and ...
... allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and ...
Reporting Category 3: Bonding and Chemical Reactions
... Background information: Atoms in covalent compound are held together by covalent bond—bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. A covalent bond forms between two atoms with high electronegativity, usually nonmetals. Because their attractions for a given electron are about equally stron ...
... Background information: Atoms in covalent compound are held together by covalent bond—bonds formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. A covalent bond forms between two atoms with high electronegativity, usually nonmetals. Because their attractions for a given electron are about equally stron ...
Solid State Physics
... bond is called the pi () bond. In pi bonds, the resulting overlap is not maximum and these bonds are relatively weak. Covalent Bonds have well-defined directions in space. Attempting to alter those directions is resisted – making them both hard and brittle. ...
... bond is called the pi () bond. In pi bonds, the resulting overlap is not maximum and these bonds are relatively weak. Covalent Bonds have well-defined directions in space. Attempting to alter those directions is resisted – making them both hard and brittle. ...
Nearly Free Electron Approximation
... cannot be a net change into any particular direction or particular set of them. So then the material cannot conduct electricity, (no net momentum in a particular direction) In a metal however, even at 0K, there is not a problem because in the case of the alkali metals and noble metals there are alwa ...
... cannot be a net change into any particular direction or particular set of them. So then the material cannot conduct electricity, (no net momentum in a particular direction) In a metal however, even at 0K, there is not a problem because in the case of the alkali metals and noble metals there are alwa ...
bond is
... Lewis Structure for Compounds • Covalent Compounds ▫ The central atom is usually the one with the lowest electronegativity (but never ______) ▫ Determine total valence electrons ▫ Move electrons so that each terminal atom has an octet (but not H who gets 2) ▫ Any extra electrons go on the _________ ...
... Lewis Structure for Compounds • Covalent Compounds ▫ The central atom is usually the one with the lowest electronegativity (but never ______) ▫ Determine total valence electrons ▫ Move electrons so that each terminal atom has an octet (but not H who gets 2) ▫ Any extra electrons go on the _________ ...
Document
... • The – side of the H2O dipole is attracted to the Na+ ions while the + side of the H2O dipole heads for the Cl- ions. • The H2O molecules surround and carry off each ion, until the crystal is completely dissolved. ...
... • The – side of the H2O dipole is attracted to the Na+ ions while the + side of the H2O dipole heads for the Cl- ions. • The H2O molecules surround and carry off each ion, until the crystal is completely dissolved. ...
O O O O BF3 BF3 C N C N C O C O C N BF C N BF C N F3B
... 5. Phenol is a moderately acidic molecule, and was used in water solution by Pasteur as the first antiseptic. Assuming the acidity is the feature responsible for the antibiotic activity, would it have been more or less effective to use solution of phenol in DMSO instead of water? Explain by showing ...
... 5. Phenol is a moderately acidic molecule, and was used in water solution by Pasteur as the first antiseptic. Assuming the acidity is the feature responsible for the antibiotic activity, would it have been more or less effective to use solution of phenol in DMSO instead of water? Explain by showing ...
Answers to Review Questions
... No. A compound is defined as a combination of atoms of 2 or more different elements, but the term molecule is not exactly appropriate when referring to ionic compounds such as sodium chloride, as no discrete molecules exist between the 2 atoms. 4. How do ionic and covalent bonds differ? Ionic bonds ...
... No. A compound is defined as a combination of atoms of 2 or more different elements, but the term molecule is not exactly appropriate when referring to ionic compounds such as sodium chloride, as no discrete molecules exist between the 2 atoms. 4. How do ionic and covalent bonds differ? Ionic bonds ...
enzyme
... between the substrate and the enzyme. If those bonds were needed to attach the substrate and activate it, then at a lower pH, the enzyme will not work. ...
... between the substrate and the enzyme. If those bonds were needed to attach the substrate and activate it, then at a lower pH, the enzyme will not work. ...
Chemistry I - Net Start Class
... 44. How many dots would appear in the Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom whose electron configuration ended in 6s2 5d2 4f14 ? 45. What is the abbreviated electron configuration for the Zn2+ ion? 46. What is the electron configuration for silver? 47. What is the electron configuration of copper? ...
... 44. How many dots would appear in the Lewis electron dot diagram for an atom whose electron configuration ended in 6s2 5d2 4f14 ? 45. What is the abbreviated electron configuration for the Zn2+ ion? 46. What is the electron configuration for silver? 47. What is the electron configuration of copper? ...
Sep 2
... will have the same proportions of elements Two different samples of CO2: Sample 1: 25.6 g O; 9.6 g C Sample 2: 21.6 g O; 8.10 g C ...
... will have the same proportions of elements Two different samples of CO2: Sample 1: 25.6 g O; 9.6 g C Sample 2: 21.6 g O; 8.10 g C ...
Atoms and the Particles They Contain Chemistry Packet: Honors
... Neutrons are also found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral with no charge and have a mass of 1 amu, just like the proton. Electrons are found constantly moving around the nucleus in a random fashion. For teaching purposes we say that electrons travel in electron clouds or energy levels ...
... Neutrons are also found in the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are neutral with no charge and have a mass of 1 amu, just like the proton. Electrons are found constantly moving around the nucleus in a random fashion. For teaching purposes we say that electrons travel in electron clouds or energy levels ...
2nd Semester Chemistry Terms - Glancy 4TH PERIOD PHYSICAL
... 76. Valence shell- the outermost occupied shell of an atom 77. Electron-dot structure- a shorthand notation of the shell model of the atom 78. Nonbonding pairs- two paired valence electrons that tend not to participate in a chemical bond 79. Ion- an electrically charged particle created when an atom ...
... 76. Valence shell- the outermost occupied shell of an atom 77. Electron-dot structure- a shorthand notation of the shell model of the atom 78. Nonbonding pairs- two paired valence electrons that tend not to participate in a chemical bond 79. Ion- an electrically charged particle created when an atom ...