Student Expectation
... Key Concept 1: During a chemical reaction, the atoms of substances rearrange themselves into a new configuration forming new substances. The reactants (or the energy and atoms or molecules of the original substance) combine to produce products (or the energy, atoms, and molecules of the new substanc ...
... Key Concept 1: During a chemical reaction, the atoms of substances rearrange themselves into a new configuration forming new substances. The reactants (or the energy and atoms or molecules of the original substance) combine to produce products (or the energy, atoms, and molecules of the new substanc ...
Document
... Gas chromatography linked to mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) is an example of an instrumental method: ■ gas chromatography allows the separation of a mixture of compounds ■ the time taken for a substance to travel through the column can be used to help identify the substance ■ the output from the gas chro ...
... Gas chromatography linked to mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) is an example of an instrumental method: ■ gas chromatography allows the separation of a mixture of compounds ■ the time taken for a substance to travel through the column can be used to help identify the substance ■ the output from the gas chro ...
Chemistry of Cars unit_7_chemistry_of_cars
... Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 242 ...
... Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste, World of Chemistry 2002, page 242 ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - An introduction
... magnetic interaction between an electron’s spin and its orbital angular momentum. Example Ti. Upon photoemission an electron from the p orbital is removed - remaining electron can adopt one of two configurations: a spin-up (s=+1/2) or spin-down (s=-1/2) state. If no spin-orbit interaction these two ...
... magnetic interaction between an electron’s spin and its orbital angular momentum. Example Ti. Upon photoemission an electron from the p orbital is removed - remaining electron can adopt one of two configurations: a spin-up (s=+1/2) or spin-down (s=-1/2) state. If no spin-orbit interaction these two ...
Critical Thinking Questions 4
... From above, a solution of NaCl contains Na+(aq) and Cl-(aq) and a solution of MgNO3 contains Mg2+(aq) and NO3-(aq). If you mix a solution of each of these, nothing happens – we have the same present at the end: Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) à Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Ions ...
... From above, a solution of NaCl contains Na+(aq) and Cl-(aq) and a solution of MgNO3 contains Mg2+(aq) and NO3-(aq). If you mix a solution of each of these, nothing happens – we have the same present at the end: Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) à Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Ions ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... Postulates of Dalton s Atomic Theory 1.) All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. 2.) An element is a type of matter composed of only one kind of atom, each atom of a given kind having the same ...
... Postulates of Dalton s Atomic Theory 1.) All matter is composed of indivisible atoms. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. 2.) An element is a type of matter composed of only one kind of atom, each atom of a given kind having the same ...
1 The modern model of the atom is based on the work of (1) one
... State, in terms of the number of subatomic particles, one similarity and one difference between the atoms of these isotopes of sulfur. ...
... State, in terms of the number of subatomic particles, one similarity and one difference between the atoms of these isotopes of sulfur. ...
Phase Transitions of Dirac Electrons Observed in Bismuth
... suddenly become relevant. In addition, the crystal environment also introduces conditions that are inaccessible in high-energy physics or astrophysics. The application ...
... suddenly become relevant. In addition, the crystal environment also introduces conditions that are inaccessible in high-energy physics or astrophysics. The application ...
Second Semester Notes 09-10
... Draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule 2. Identify the central atom 3. Count total # of electron pairs around the central atom 4. Count # of bonding pairs of electrons around the central atom 5. Count # of lone pairs of electrons around the central atom ...
... Draw the Lewis dot structure for the molecule 2. Identify the central atom 3. Count total # of electron pairs around the central atom 4. Count # of bonding pairs of electrons around the central atom 5. Count # of lone pairs of electrons around the central atom ...
CHEMISTRY Periodic Table of the Elements
... Chemistry Terminology Place the following terms next to the appropriate definition. anion ...
... Chemistry Terminology Place the following terms next to the appropriate definition. anion ...
1. Which terms describe components of atomic structure? • Proton
... • permeability - measure of how easily fluids can pass through a rock • tensile stress - forces acting on a rock to pull it apart. ...
... • permeability - measure of how easily fluids can pass through a rock • tensile stress - forces acting on a rock to pull it apart. ...
File
... 7. A different structural form of the same element, resulting in different properties. _______ 8. An element that has both metallic and nonmetallic properties. _______ 9. The weighted average mass of all naturally-occurring isotopes in a sample of an element. _______ 10. These negatively-charged sub ...
... 7. A different structural form of the same element, resulting in different properties. _______ 8. An element that has both metallic and nonmetallic properties. _______ 9. The weighted average mass of all naturally-occurring isotopes in a sample of an element. _______ 10. These negatively-charged sub ...
E:\My Documents\sch3u\SCH3Ureview.wpd
... c) Explain why all the atoms in this family form stable ions with this charge. 13) The Alkali Metals are a very reactive family of metals. a) Explain what happens to these atoms when they react with an atom of Chlorine. b) Why do all atoms in this family behave in this manner with Chlorine? c) Potas ...
... c) Explain why all the atoms in this family form stable ions with this charge. 13) The Alkali Metals are a very reactive family of metals. a) Explain what happens to these atoms when they react with an atom of Chlorine. b) Why do all atoms in this family behave in this manner with Chlorine? c) Potas ...
C2 Additional Chemistry Thursday 14 May
... Recall the masses and charges of protons, neutrons and electrons Remember that protons + neutrons = mass number Define the word isotope. Recall that the relative atomic mass of an element (Ar) compares the mass of atoms of the element with the 12C isotope. It is an average value for the isotopes of ...
... Recall the masses and charges of protons, neutrons and electrons Remember that protons + neutrons = mass number Define the word isotope. Recall that the relative atomic mass of an element (Ar) compares the mass of atoms of the element with the 12C isotope. It is an average value for the isotopes of ...
Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez - Institut de Mathématiques de Toulouse
... emission due to ionic bombardment), – if r > rc, E < Ed, the electrons are evacuated, they rapidly attach to neutrals, – the negative charges (negative ions) are accelerated because of the strong electric field, ...
... emission due to ionic bombardment), – if r > rc, E < Ed, the electrons are evacuated, they rapidly attach to neutrals, – the negative charges (negative ions) are accelerated because of the strong electric field, ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
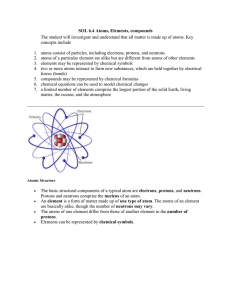
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Unit 1 Notes (general chem review)
... may NOT indicate shape may or may not show the unbonded pairs of electrons ...
... may NOT indicate shape may or may not show the unbonded pairs of electrons ...
Molar Heat of Reaction
... Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
... Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
Homework 1 - Devin Gatherwright IET 307 Portfolio
... Covalent bonds are directional in nature, meaning that the bond exists between specific atoms and can only exist in the direction between one atom and the neighboring atom that takes part in the sharing of the electron. Some characteristics of covalent bonding are as follows: covalent bonding is th ...
... Covalent bonds are directional in nature, meaning that the bond exists between specific atoms and can only exist in the direction between one atom and the neighboring atom that takes part in the sharing of the electron. Some characteristics of covalent bonding are as follows: covalent bonding is th ...
History of Atomic Theories (No Videos)
... b. Electron cloud- region where you have a 90% chance of finding an electron ...
... b. Electron cloud- region where you have a 90% chance of finding an electron ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... A more accurate estimate of L comes from electro-deposition of copper during electrolysis of CuSO4(aq), making assumptions about valency and Mr of Cu, and the charge on the electron) ...
... A more accurate estimate of L comes from electro-deposition of copper during electrolysis of CuSO4(aq), making assumptions about valency and Mr of Cu, and the charge on the electron) ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic pattern when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number is called a. the periodic law b. the law of octaves c. Mendeleev’s law d. Meyer’s periodicity 74. The elements in group 1 (1A) of the peri ...
... 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic pattern when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number is called a. the periodic law b. the law of octaves c. Mendeleev’s law d. Meyer’s periodicity 74. The elements in group 1 (1A) of the peri ...
A.P. Chemistry
... Definition of Oxidation- loss of electrons Definition of Reduction- gain of electrons ...
... Definition of Oxidation- loss of electrons Definition of Reduction- gain of electrons ...