PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... • d) Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) molecules contain polar O–H bonds, similar to water, so it would be expected to be soluble. ...
... • d) Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) molecules contain polar O–H bonds, similar to water, so it would be expected to be soluble. ...
Name_____________________________________ Chemistry
... d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ____ 31. If electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is in the a. ground state. c. excited state. b. inert state. d. radiation-emitting state. ____ ...
... d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ____ 31. If electrons in an atom have the lowest possible energies, the atom is in the a. ground state. c. excited state. b. inert state. d. radiation-emitting state. ____ ...
EXAM # 1
... 4) How can mass spectrometry and atomic emission spectroscopy be used to determine the molecular formula of an unknown? AES can monitor the presence of up to 55 elements in an unknown sample by the observation of the presence/absence of the unique pattern of atomic emission bands for each element. S ...
... 4) How can mass spectrometry and atomic emission spectroscopy be used to determine the molecular formula of an unknown? AES can monitor the presence of up to 55 elements in an unknown sample by the observation of the presence/absence of the unique pattern of atomic emission bands for each element. S ...
Chemistry Mid-Term Review: 2015-2016
... 25. What does the term STP mean? 26. What is the volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP? 27. When given the name of the compound or the formula of the ions, how do you write formulas for ionic compounds? 28. What is Avogadro’s number? 29. What is a mole? 30. What are representative particles of elements ...
... 25. What does the term STP mean? 26. What is the volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP? 27. When given the name of the compound or the formula of the ions, how do you write formulas for ionic compounds? 28. What is Avogadro’s number? 29. What is a mole? 30. What are representative particles of elements ...
4b. Orbital Diagrams
... Orbital Diagrams • Use individual orbitals • Give subshell arrangement • Each orbital takes one electron before any other orbital in the same subshell can receive a second electron ...
... Orbital Diagrams • Use individual orbitals • Give subshell arrangement • Each orbital takes one electron before any other orbital in the same subshell can receive a second electron ...
3-CProvencher
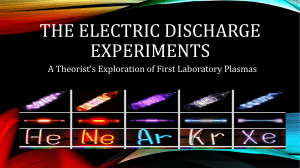
... • “The study of the electrical properties of gases seems to offer the most promising field for investigating the Nature of Electricity and Matter, for thanks to the Kinetic Theory of Gases our idea of non-electric processes in gases is much more vivid than they are for liquids or solids”– ...
... • “The study of the electrical properties of gases seems to offer the most promising field for investigating the Nature of Electricity and Matter, for thanks to the Kinetic Theory of Gases our idea of non-electric processes in gases is much more vivid than they are for liquids or solids”– ...
Family
... Professor Dmitri Mendeleev published the first Periodic Table of the Atomic Elements in 1869 based on properties which appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest. When Mendeleev proposed his periodic table, he noted gaps in the table, and predicted that as-of ...
... Professor Dmitri Mendeleev published the first Periodic Table of the Atomic Elements in 1869 based on properties which appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest. When Mendeleev proposed his periodic table, he noted gaps in the table, and predicted that as-of ...
Chemistry I – Fall 2004
... 12. Describe the nature of the bonds formed in a compound QT if elements Q and T have a large difference in electronegativity. ...
... 12. Describe the nature of the bonds formed in a compound QT if elements Q and T have a large difference in electronegativity. ...
Chapter 30 - The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... into simpler units. An element is designated by either a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its Arabic, English, German, or Latin name. For example, O is the symbol for the element oxygen, H stands for hydrogen, and Na is the symbol for sodium (from the Latin, natrium). Currently, scientists recogni ...
... into simpler units. An element is designated by either a one- or two-letter abbreviation of its Arabic, English, German, or Latin name. For example, O is the symbol for the element oxygen, H stands for hydrogen, and Na is the symbol for sodium (from the Latin, natrium). Currently, scientists recogni ...
Electrochemistry File
... The S.H.E. is not a convenient electrode for regular use as a reference. A reference electrode needs to be easy to use, stable, reproducible, and reliable. The calomel electrode is the electrode of choice: Pt (s) | Hg (l) | Hg2Cl2 (s) | saturated aq. KCl. ...
... The S.H.E. is not a convenient electrode for regular use as a reference. A reference electrode needs to be easy to use, stable, reproducible, and reliable. The calomel electrode is the electrode of choice: Pt (s) | Hg (l) | Hg2Cl2 (s) | saturated aq. KCl. ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.2 – The Nuclear Atom Date: Period:
... follow different rules. Additionally, some compounds (H2O, NH3, CH4, etc.) simply have common names that must be memorized. The two types of compounds we will focus on first are ionic compounds (formed from positive and negative ions) and binary nonmetal compounds (molecular compounds). Later we wil ...
... follow different rules. Additionally, some compounds (H2O, NH3, CH4, etc.) simply have common names that must be memorized. The two types of compounds we will focus on first are ionic compounds (formed from positive and negative ions) and binary nonmetal compounds (molecular compounds). Later we wil ...
Bonding
... Ionic ✦ Electrons are transferred ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
... Ionic ✦ Electrons are transferred ✦ Metals react with nonmetals ✦ Ions paired have lower energy (greater stability) than separated ions Covalent ✦ Electrons are shared by nuclei ✦ Pure covalent (nonpolar covalent) - electrons are shared evenly ✦ Polar covalent - electrons shared unequally ...
IPC Final Exam Review
... 1. A liquid at 24 °C was determined to have a density of 1.3 g/ml. What mass would 50.0 ml of this liquid have? ...
... 1. A liquid at 24 °C was determined to have a density of 1.3 g/ml. What mass would 50.0 ml of this liquid have? ...
Directed Reading
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-metal. The metal portion will always appear first in the name and formula. b) The total number of electrons lost by the metal atom(s) must equal the total number of electrons gained by the nonmetal atom(s). (The charge left after an atom ...
... a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-metal. The metal portion will always appear first in the name and formula. b) The total number of electrons lost by the metal atom(s) must equal the total number of electrons gained by the nonmetal atom(s). (The charge left after an atom ...
www.theallpapers.com
... A more accurate estimate of L comes from electro-deposition of copper during electrolysis of CuSO4(aq), making assumptions about valency and Mr of Cu, and the charge on the electron) ...
... A more accurate estimate of L comes from electro-deposition of copper during electrolysis of CuSO4(aq), making assumptions about valency and Mr of Cu, and the charge on the electron) ...
formation of chemical bonds. -
... A. The factors that determine the type of A. The electrons in the inner shells of an bond that will be formed between two atom are strongly bounded with the force atoms are of attraction of nucleus. They are all ready (i) Number of valence electrons stable electrons. The electrons in the (ii) The st ...
... A. The factors that determine the type of A. The electrons in the inner shells of an bond that will be formed between two atom are strongly bounded with the force atoms are of attraction of nucleus. They are all ready (i) Number of valence electrons stable electrons. The electrons in the (ii) The st ...
Zumdahl`s Chap. 4 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Use moles divided by Final Volume to get concentration of leftovers. ...
... Use moles divided by Final Volume to get concentration of leftovers. ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... a. is an electrically charged mixture of ions and electrons. b. is a mixture of neutrons and protons with no charge. c. exists at very low temperatures. d. is another name for the solid phase of matter. ...
... a. is an electrically charged mixture of ions and electrons. b. is a mixture of neutrons and protons with no charge. c. exists at very low temperatures. d. is another name for the solid phase of matter. ...
www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with
... a. with gases, the volumes consumed and produced are in ratios of small whole numbers. b. atoms combine in fixed ratios of whole numbers. c. atoms of different elements have different properties. d. elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. ...
... a. with gases, the volumes consumed and produced are in ratios of small whole numbers. b. atoms combine in fixed ratios of whole numbers. c. atoms of different elements have different properties. d. elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms. ...
S1-2-02: What is the basic subatomic structure of an atom?
... c) You add a bit of salt to the water. d) You poach the eggs by placing them into the water. e) You cut the eggs up to eat them. 10. Which one of the following is a physical change? a) Acid damages the surface of a car. b) The car burns up gasoline on a trip. c) The car explodes in a collision. d) T ...
... c) You add a bit of salt to the water. d) You poach the eggs by placing them into the water. e) You cut the eggs up to eat them. 10. Which one of the following is a physical change? a) Acid damages the surface of a car. b) The car burns up gasoline on a trip. c) The car explodes in a collision. d) T ...
Energy and Matter in Chemical Change Science 10
... 1) All substances are made of matter 2) All particles in a pure substance are the same. Different pure substances are made of different particles. 3) Particles are always in motion. The speed of the particles increases when temperature increases. 4) Particles have space between them 5) Particles may ...
... 1) All substances are made of matter 2) All particles in a pure substance are the same. Different pure substances are made of different particles. 3) Particles are always in motion. The speed of the particles increases when temperature increases. 4) Particles have space between them 5) Particles may ...