DNA
... to form dsDNA Temperature at which dsDNA remains together depends on percent of matching and GC content Does not yield the DNA sequence of organisms, just the sequence similarity between organisms Total genomic hybridization can be used to estimate overall genetic similarity between organisms Oligon ...
... to form dsDNA Temperature at which dsDNA remains together depends on percent of matching and GC content Does not yield the DNA sequence of organisms, just the sequence similarity between organisms Total genomic hybridization can be used to estimate overall genetic similarity between organisms Oligon ...
Name - EdWeb
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
... 1. What is DNA? __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? ___________________ ...
Concept checks - WordPress.com
... Explain the relationship between the number of amino acid residues in the enzyme and the number of nucleotide pairs in its gene ...
... Explain the relationship between the number of amino acid residues in the enzyme and the number of nucleotide pairs in its gene ...
DNA and Central Dogma Study Guide
... b) Describe the difference between purines and pyrimidines. c) Circle the bases that are purines. Square the bases that are pyrimidines. 2. What are the base paring rules? 3. Draw and label a nucleotide. 4. What term is used to describe the shape of DNA? Why? 5. What is the backbone of DNA made up o ...
... b) Describe the difference between purines and pyrimidines. c) Circle the bases that are purines. Square the bases that are pyrimidines. 2. What are the base paring rules? 3. Draw and label a nucleotide. 4. What term is used to describe the shape of DNA? Why? 5. What is the backbone of DNA made up o ...
Quiz 3 review sheet
... • Demonstrate how the structure of DNA, including its directionality and its double-stranded base pairing, are critical for its functions. • Explain the “central dogma” and how it relates to how genes determine phenotype • Explain the difference between DNA and RNA and how RNA is synthesized from DN ...
... • Demonstrate how the structure of DNA, including its directionality and its double-stranded base pairing, are critical for its functions. • Explain the “central dogma” and how it relates to how genes determine phenotype • Explain the difference between DNA and RNA and how RNA is synthesized from DN ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... No two individuals (except identical twins) has the same DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes. Fragments (RFLP: restriction fragment length polymorphisms) differ in length and number of fragments produced , will migrate different distances in electrophoretic gel. USES: Forensics: DNA fingerprints ...
... No two individuals (except identical twins) has the same DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes. Fragments (RFLP: restriction fragment length polymorphisms) differ in length and number of fragments produced , will migrate different distances in electrophoretic gel. USES: Forensics: DNA fingerprints ...
chapter 19_updates
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
... DNA at specific nucleotide sequences • Type II restriction enzyme: most useful enzyme • By adding methyl groups to the recognition sequence to protect itself from being digested by its own enzyme in bacteria ...
DNA notes
... • Each strand serves as the template for making a new complementary strand • Nucleotides, in the form of dATP, dCTP, dGTP and dTTP align to the old strand s by base pairing • DNA polymerases connect nucleotides in a 5' to 3' direction only, and only to a pre-existing string of nucleotides (primer) * ...
... • Each strand serves as the template for making a new complementary strand • Nucleotides, in the form of dATP, dCTP, dGTP and dTTP align to the old strand s by base pairing • DNA polymerases connect nucleotides in a 5' to 3' direction only, and only to a pre-existing string of nucleotides (primer) * ...
DNA Fingerprinting – Your Bioremediation “Taq”ometer
... ¾ HydroQual Laboratories Ltd. (HydroQual) does applied biology for environmental management. ¾ We are a wholly-owned subsidiary of Golder Associates Ltd. ¾ Our talented team of professionals all have degrees and expertise in the natural sciences (microbiology, biochemistry, toxicology, ecology, bota ...
... ¾ HydroQual Laboratories Ltd. (HydroQual) does applied biology for environmental management. ¾ We are a wholly-owned subsidiary of Golder Associates Ltd. ¾ Our talented team of professionals all have degrees and expertise in the natural sciences (microbiology, biochemistry, toxicology, ecology, bota ...
Chapter 5
... • Cloning vectors - DNA molecules that can be replicated • Reporter genes • Model organisms ...
... • Cloning vectors - DNA molecules that can be replicated • Reporter genes • Model organisms ...
DNA Replication
... In human beings genes constitute only 3 % of the human genome. The remaining 97 % of the genome – have yet no known functions! These regions are called non-coding regions. Genome = Coding regions (genes) + noncoding regions. ...
... In human beings genes constitute only 3 % of the human genome. The remaining 97 % of the genome – have yet no known functions! These regions are called non-coding regions. Genome = Coding regions (genes) + noncoding regions. ...
Slide 1
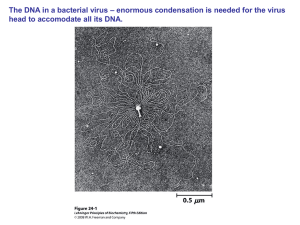
... In Escherichia coli the DNA is about 1 med mer long, while the cell is close to 1 μm. Here the DNA information also has to be read! ...
... In Escherichia coli the DNA is about 1 med mer long, while the cell is close to 1 μm. Here the DNA information also has to be read! ...
E co
... T4DNA ligase.Note that the ligation reaction can add multiple linkers on each end of the blunt-ended DNA. EcoRI digestion removes all but the terminal one,leaving the desired 5’-overhangs.(b)cloning vectors often have polylinkers consisting of a multiple array of restriction sites at their coning si ...
... T4DNA ligase.Note that the ligation reaction can add multiple linkers on each end of the blunt-ended DNA. EcoRI digestion removes all but the terminal one,leaving the desired 5’-overhangs.(b)cloning vectors often have polylinkers consisting of a multiple array of restriction sites at their coning si ...
No Slide Title
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
... Out of Africa • Neanderthal mT DNA: – Very different from modern humans – Hard to reconcile difference with possible presence of some Neanderthal ancestry in modern ...
Isolation of DNA from 96 Well Plates
... Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel. 8. Rinse 3 times with 100μl 70% ethanol. With each rinse, quickly invert plate over sink then bl ...
... Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel. 8. Rinse 3 times with 100μl 70% ethanol. With each rinse, quickly invert plate over sink then bl ...
DNA isol
... 1. Know the experiment’s level of forgiveness. Another way of saying that it pays to know the chemistry of your procedure. Inevitably, each experiment has a degree of forgiveness, which is a really useful thing to know. This allows you to gauge your level of care, which in turn will reflect on your ...
... 1. Know the experiment’s level of forgiveness. Another way of saying that it pays to know the chemistry of your procedure. Inevitably, each experiment has a degree of forgiveness, which is a really useful thing to know. This allows you to gauge your level of care, which in turn will reflect on your ...
DNA
... DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
... DNA consists of two molecules that are arranged into a ladder-like structure called a Double Helix. A molecule of DNA is made up of millions of ...
8.1-8.2 TAKE DOWN NOTES AND SKETCH MOLECULES
... Watson & Crick discovered the double helix shape with help from Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins *We will go over the movie answers…..just hold onto them. DNA is composed of NUCLEOTIDES that are repeating units….running anti-parallel to each other. The Nitrogenous bases are in two groups: PYRIM ...
... Watson & Crick discovered the double helix shape with help from Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins *We will go over the movie answers…..just hold onto them. DNA is composed of NUCLEOTIDES that are repeating units….running anti-parallel to each other. The Nitrogenous bases are in two groups: PYRIM ...
Southern transfer
... This technique, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), is also frequently used with probes whose normal chromosomal locations are already known. This is particularly useful for studying cells in which chromosomal rearrangements have occurred. ...
... This technique, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), is also frequently used with probes whose normal chromosomal locations are already known. This is particularly useful for studying cells in which chromosomal rearrangements have occurred. ...
7echap20guidedreading
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
... 4. What are the 3 essential functions of DNA (In the text, they compared this to a book)? 5. DNA is a _________________________ made up of many small repeating units called ________________________. ...
Biotechnology
... Matching an unknown sample with a known to see if they match up is DNA profiling Identical band patterns means that is the individual in question – similar patterns usually mean the individuals are relatives ...
... Matching an unknown sample with a known to see if they match up is DNA profiling Identical band patterns means that is the individual in question – similar patterns usually mean the individuals are relatives ...
Genetics
... Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids DNA/RNA. These units are made-up of 3 parts: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate ...
... Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids DNA/RNA. These units are made-up of 3 parts: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar (5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate ...
understanding dna molecule of heredity - Cal State LA
... The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to two strands The four bases found in DNA are Adenine-A, Cytosine – C, Guanine-G, Thymine-T ...
... The DNA double helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the bases attached to two strands The four bases found in DNA are Adenine-A, Cytosine – C, Guanine-G, Thymine-T ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).